Grounding hardware refers to the equipment and components used to establish an effective grounding system. This grounding system provides protection and proper operation for the electrical infrastructure. The system also ensures safety, fault protection and minimizes the risk of damage to equipment and personnel. Additionally, the specific components, design and configuration depends on design requirements, voltage levels and local regulations.
Components of grounding systems

The components making up the grounding hardware work together to establish an effective grounding system. They also ensure safety, reliability and stability of power transmission and distribution networks. The following are the main components of the grounding hardware.
- Grounding rods -These are metallic rods made from copper that drive into the ground to provide a low resistance path for fault currents.
- Grounding conductors – The conductive cables connect various components of the grounding system such as metallic structures and electrical equipment. They create a continuous path to the ground.
- Grounding clamps – These are devices that secure grounding conductors to the structure they connect to. Thy also provide a reliable and low-resistance electrical connection between the conductor and the object to ground.
- Grounding switches – These are switches used to establish or break the connection between the transmission line and the ground. They mostly install at substations for easier maintenance and safety purposes.
- Surge arrestors – Surge arrestors are often used in conjunction with grounding systems to protect the power transmission line against voltage surges and lightning strikes. They divert the excessive voltages to the ground and prevent damage to the electrical infrastructure.
Types of grounding hardware

There are several common types of grounding hardware used in electrical systems which also depend on specific application, voltage level, local regulations and system requirements. The following are the common types of grounding hardware used on the power transmission lines.
- Grounding rods – These are also known as ground rods or earth electrodes made of copper, galvanized steel or a combination of the material. They establish a low-resistance electrical connection with the earth.
- Grounding clamps -Grounding camps secure grounding conductors to various objects or structures to provide a reliable and low resistance connection between the conductor and the object to ground.
- The Grounding conductors – These are cables that connect different components of the grounding system such as grounding rods, metallic structures and equipment.
- Grounding busbars – Grounding busbars are metal bars or strips used to consolidate and distribute grounding connections within electrical panels, switchgears or substations. They also create a centralized grounding point to the grounding conductors.
- Grounding plates – These are large metal plates or grids buried in the ground to increase the surface area for grounding. This provides a greater contact area with the earth which enhances the effectiveness of the grounding system.
- Grounding mesh – Grounding mesh consists of interconnected conductive wires or grids buried in the ground. Furthermore, the grounding mesh mostly work in areas with high soil resistivity to improve the grounding system’s performance.
- Grounding switches – Thes switches establish or disconnect the electrical connection between the power system and the ground. They are commonly installed in key locations for maintenance, safety and fault protection purposes.
- Grounding resistors – The resistive devices insert into the grounding system to limit fault currents and provide a controlled path for fault current dissipation. Grounding resistors help protect equipment and personnel during fault conditions.
- Surge arrestors -Surge arrestors are commonly used in conjunction with grounding hardware to protect against voltage surges and divert excessive electrical energy to the ground. This safe guards the power system from transient overvoltage.
Applications of grounding hardware
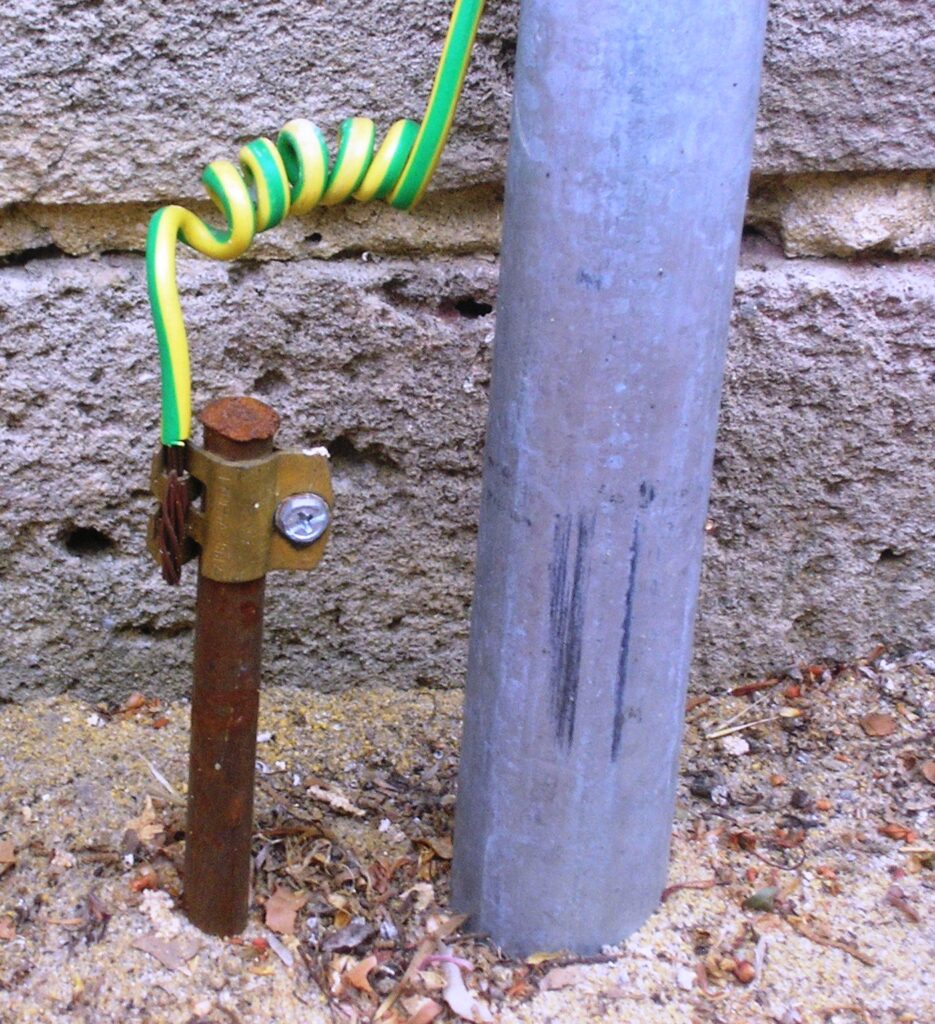

Grounding hardware work in various applications to ensure safety, protect equipment and maintain proper operation. In addition, the grounding requirements and equipment vary depending on the nature of the application and the applicable electrical codes and regulations. The following are the common application areas of the grounding hardware.
- Grounding hardware works in power transmission and distribution systems to help establish effective grounding for overhead lines, underground cables, substations, transformers and other electrical equipment. The grounding hardware provides fault protection, lightning strikes dissipation and maintains system stability.
- The grounding system works in telecommunication systems to establish proper grounding to protect sensitive equipment from electrical surges, electromagnetic interference and static discharge. This may include in areas like telephone networks, data centers and wireless communication infrastructure.
- Grounding hardware is crucial in industrial facilities such as manufacturing plants, refineries and chemical plants. It ensures worker safety by providing a low-resistance path to dissipate fault currents and reduce the risk of electric shock
- The grounding hardware also works in commercial buildings to protect electrical systems, appliances and occupants. This helps to divert fault currents, minimize electrical hazards and reduce the risk of damage from electrical surges. They are also important for grounding lightning protection systems on buildings.
- They also work in residential buildings to protect electrical systems and appliances to provide a safe path for fault currents and helps prevent electrical shocks.
- Grounding hardware plays a crucial role in data centers to protect sensitive electronic equipment from power disturbances, static discharge and electromagnetic interference, this ensures the reliable operation of servers, networking equipment and storage systems.
- The grounding systems work in renewable energy systems such as solar power plants and wind farms. It helps establish proper grounding for equipment, inverters and electrical connections which ensures safe and reliable operations.
Installation process of grounding components

The installation process of the grounding hardware should be by professionals familiar with electrical safety practices and local regulations. The process also varies depending on the specific application and requirements.
- Assess the specific grounding requirements based on the application, local electrical codes and safety regulations. You should consider factors such as equipment, system voltage, soil conditions and fault current levels.
- Develop a grounding system design that meets the requirements which includes determining the number and placement of grounding rods, sizing grounding conductors and selecting appropriate grounding component.
- Clear the site where the grounding system will install ensuring there are no obstructions that could hinder the installation process.
- Drive or install grounding rods into the ground at specific locations and secure firmly
- Connect the grounding conductors between the grounding rods and the equipment or structures to ground.
- Connect any metallic structures that need to ground by use of bonding conductors. This helps ensure electrical continuity and safety.
- Install ground busbars to consolidate and distribute grounding connections. Connect the grounding conductors to the busbars using appropriate connectors.
- Perform testing to verify the effectiveness of the rounding system which may include measurements of ground resistance, continuity checks and fault current testing.
- Document the grounding system installation including drawings, specifications and test results. Also inspect the grounding hardware regularly to ensure the continued effectiveness.
Selecting the best grounding hardware

The selection process involves considering various factors to ensure compliance with regulations and the specific requirements of your application. it is also advisable to consult with professionals and experts in the industry to provide an informed decision on the best grounding hardware for your project. The following are the common factors to consider during the selection process.
- Understand the specific grounding requirements of your application such as voltage levels, fault currents capacity and soil resistivity.
- Ensure that the selected grounding hardware complies with the various guidelines and regulations in your local area
- Consider the type of equipment and system to ground and select the appropriate grounding hardware for the application.
- Develop and grounding system design that meets the requirements of your project which includes determining the number and type of grounding rods an select the appropriate grounding components. These may include components such as clamps, busbars and switches.
- Choose grounding hardware made from materials that provide good electrical conductivity, corrosion resistance and durability.
- Select grounding hardware from reputable manufacturers with a proven track record in producing high quality products that ensure reliability and performance.
- Consider the ease of maintenance and repairs of the grounding hardware. The components should be easily accessible for inspection, maintenance and potential future expansions.
- Evaluate the cost-effectiveness of the grounding hardware while considering the quality of the components.
Frequently asked questions
What is grounding hardware as used on overhead transmission lines?
A grounding hardware is an equipment used to establish effective grounding system for protection and proper operation of the electrical infrastructure. They ensure safety, fault protection and minimize the risk of damage to equipment and personnel.
What are the common application areas of the grounding hardware?
Power transmission and distribution systems
Telecommunications
Industrial facilities
Commercial buildings
Residential buildings
Data centers
Renewable energy systems
What are the benefits of grounding hardware?
Electrical safety
Equipment protection
Surge and lightning
System stability
Compliance with electrical codes
Lightning strike dissipation
Noise reduction
Personnel safety
What are the limitations of grounding hardware?
Influence by soil conditions
Requires regular maintenance
Design and installation
Grounding resistance
Transient overvoltages
Prone to human error
Requires upgrades and modifications
