
Carbon capture and removal (CCR) technologies offer a route to decarbonize the energy sector in line with climate objectives. Carbon capture can assist South American nations in meeting their nationally determined contributions as outlined in the Paris Agreement. Ongoing investments in research and development are essential to enhance the cost-effectiveness and efficiency of CCR technologies. South America features a terrain that promotes the development of carbon capture and removal technologies. This is attributed to the plentiful natural resources, varied ecosystems, and growing emphasis on sustainability. Nations such as Brazil and Chile are investigating carbon capture initiatives in offshore oil extraction and green hydrogen plans. Transmission insulators are essential in grid infrastructure to accommodate the increasing use of microinverters.
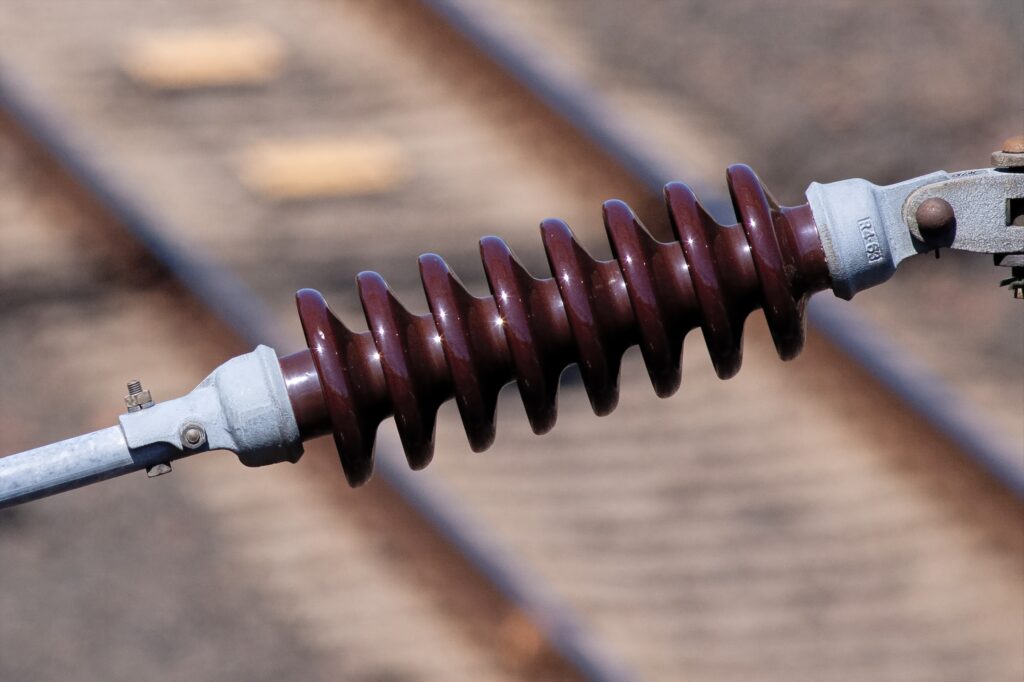
Transmission insulators are crucial components of power lines transmitting electricity from the grid to residential and commercial buildings. They also support the weight of conductors and prevent electrical current from flowing to the support structure. Transmission insulators support the power lines that collect electricity generated by microinverters. This helps maintain grid stability and ensure the seamless integration of power generated from microinverters. Transmission insulators enable the widespread adoption of microinverter-based solar systems in South America.
Carbon capture and removal technologies in South America’s energy sector
There are several technologies and methods employed for carbon capture and removal in South America’s energy sector. The technologies are tailored to the region’s energy mix, natural resources, and industrial activities. TTF is a world-class global provider of high quality overhead line hardware, transmission hardware, distribution hardware, conductors, insulators, cutout switches, anchoring and grounding products. Discussed below are the technologies used for carbon capture and removal in South America.
- Carbon capture and storage (CCS) primarily pertains to industrial and energy production plants throughout the area. The procedure entails capturing CO2 emissions at their origin and storing them in subterranean geological formations. CCS operates in the oil and gas industry and storage facilities in areas such as Argentina, Brazil, and Colombia.
- Direct air capture entails extracting carbon directly from the atmosphere through chemical processes. There is also the possibility for synergy with renewable energy sources like solar and wind to energize DAC systems.
- Bioenergy with carbon capture and storage (BECCS)—this integrates biomass energy generation with CCS to attain negative emissions. Brazil’s sugarcane ethanol manufacturing can incorporate BECCS by sequestering carbon emitted during fermentation.
- Solutions based on nature—such as ecosystems like the Amazon Rainforest, mangroves, and wetlands—can serve as large carbon sinks. Nations such as Colombia and Ecuador preserve and rehabilitate mangroves to sequester carbon in both soil and biomass.
- Enhanced weathering—this entails distributing ground silicate stones across terrain to accelerate natural carbon cycles.
- Carbon utilization technologies—this includes turning captured carbon into useful products. They serve in green hydrogen production, fertilizers, and chemicals.
The importance of transmission insulators in carbon capture and removal technologies
Transmission insulators ensure the effectiveness and reliability of carbon capture and removal technologies. They serve where electrical infrastructure supports large-scale industrial facilities in South America. Transmission insulators the efficiency and sustainability of CCR technologies. They ensure the safe and effective delivery of electricity, support renewable energy integration, and enable the expansion of climate-focused initiatives in the region. TTF is a world-class global provider of high quality overhead line hardware, transmission hardware, distribution hardware, conductors, insulators, cutout switches, anchoring and grounding products. Discussed below are the functions of transmission insulators in carbon capture and removal technologies.

- Ensuring electrical safety—CCR facilities need high-voltage systems to power energy-intensive processes. It includes processes like CO2 compression, transportation, and storage. transmission insulators prevent electrical faults by isolating the conductors from the support structures.
- Enhancing system reliability—high-quality insulators ensure consistent power delivery despite climate conditions.
- Preventing energy losses—insulation reduces power leakages and transmission losses, which improves the energy efficiency of the systems.
- Reducing maintenance costs—transmission insulators reduce the frequency of maintenance. This is crucial for the economic feasibility of CCR projects in South America.
- Facilitating renewable energy integration—transmission insulators play a crucial role in integrating renewable energy sources. Sources like solar and wind into the grid ensure clean energy power.
- Grid stability for CO2 transport networks – CCR technologies include carbon pipelines powered by ecompressors. Transmission insulators in the systems maintain grid stability and ensure the compressors are efficient.
- Supporting large-scale deployments—transmission insulators enable the safe and efficient transport of electricity across long distances. They help connect energy sources to carbon capture and removal technologies.
- Withstanding environmental conditions—high-quality insulators are able to resist corrosion, contamination, and mechanical stresses. This ensures durability in harsh environmental conditions.
