
A hex bolt and nut are types of fasteners used to secure two or more components or fittings together. The nuts and bolts ensure stability and safety of the transmission line structures. A hex bolt is a threaded fastener with a hexagonal head. This feature allows easy tightening and loosening using a wrench or socket. They are from high-strength materials such as steel to provide load bearing capacity. A hex nut is an equal of the hex bolt that is internally threaded to screw into the threaded portion of the hex bolt. The nut helps to secure the bolt and keep the joint tight. It is from durable materials that withstand the mechanical stresses in the lines. The hex bolt and nut help in connecting towers and poles. It also helps attaching hardware and fittings, maintenance and repairs and line splicing.
Components of the hex bolt and nut
This type of fastening mechanisms is widely used in various applications. The use of the threaded bolt and nuts allows for easier connection of the two devices. Hex bolt and nut are two separate components and have different parts as discussed below.
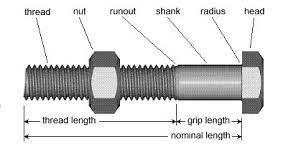
The hex bolt
- Head – the hex bolt head is flat and six-sided at one end of the bolt to provide a means for gripping and turning the bolt.
- Threaded shaft – the threaded shaft is the cylindrical part of the bolt with helical grooves called threads. This is the part that inserts into the nut to form a secure connection.
- Threaded tip – this is the end opposite to the bolt head which allows the bot to drive into a threaded nut.
The hex nut
- Body – the body of the nut is a six-sided, internally threaded component to fit onto the external threads of a bolt.
- Top surface – this is the flat end facing away from the bolt head where turning force applies during tightening or loosening.
- Threaded interior – the interior of the nut contains matching threads corresponding to those on the bolt.
Types of hex bolt and nut
Hex bolts and nuts have various designs and configurations designed for specific applications. The following are the common types of hex bolt and nuts in the industry.

- Hex cap screws – these are standards hex bolts with fully threaded bolt. They work when the entire length of the bolt needs to engage with a threaded hole or nut.
- Tap bolt – these are bolts with a portion of the shaft without threads mostly at the end. The unthreaded part allows the bolt to insert into a pre-tapped hole. The threaded part provides grip when used with a nut.
- Hex machine bolt – these bolts have a flat head designed for use with a matching nut.
- Hex lag bolts – lag bolts have a hexagonal head and a sharp-pointed tip designed for use with wood. These bolts do not require a nut since they screw directly into the wood for secure hold.
- Hex flange bolt – these bolts have a built-in flange under the head to distribute the load over a larger surface area. This eliminates the need for a separate washer when used in certain applications.
- Hex socket bolts – these are commonly known as Allen bolts with a hexagonal socket on the head in place of the traditional hex head.
- Carriage bolts – these have a rounded head with a square section under it for use with wood or metal components. The square section prevents the bolt from turning during tightening.
- Hex weld nuts – these nuts have a hexagonal shape designed for welding to another object. They provide a threaded connection without the need for a through hole.
- Hex jam nuts – jam nuts are thinner than hex nuts for use as second nuts to lock the first nut in place.
- Nylon Insert lock nuts – these nuts have a nylon ring inside to create resistance and help prevent the nut from loosening.
Application areas of hex bolts and nuts
Hex bolts and nut find use in various applications due to their versatility, strength and ease of use. These factors have made them indispensable across a wide range of industries. Additionally, you should consult with industry professionals for guidance on the best hex bolt and nut that suits the specific needs of the application. The following are the common application areas of the hex bolt and nut.

- Construction and infrastructure – hex bolts and nuts work in construction for various purposes. These include assembling structural components, securing beams and fastening metal or wood elements.
- Automotive industry – hex bolts and nuts work in the assembly of vehicles, securing engine components, chassis parts and various accessories.
- Furniture manufacturing – they are also used in furniture such as beds, tables, chairs and cabinets.
- Machinery and equipment – the bolt and nut help to hold machinery components together, mount motors, secure gears and assemble equipment.
- Electrical and electronics – hex bolts and nuts fasten components, secure circuit boards and assemble electrical enclosures.
- Marine applications – they are also used in boat and ship construction. These include hull components and mounting equipment.
- Renewable energy projects – the devices help in construction of renewable energy projects like solar panel mounting structures and wind turbine assemblies.
- Telecommunications – hex bolts and nuts secure antennas, feeders and other components in telecommunication towers and equipment.
- Transmission lines and power distribution – hex bolts and nuts secure overhead transmission line components and power distribution structures.
Hex bolt and nut installation guide
The installation of the hex bolt and nut should ensure the safety and security of the connections. During installation, the tightness of the bolt and nut will depend on the specific application and the tools used. Additionally, it is advisable to follow manufacturer’s instructions for the suitable torque specifications. Also, enhance proper installation of hex bolts and nuts to ensure stability and safety of the assembled structure or equipment. Follow this step-by-step hex bolt and nut installation guide to assemble your connections. The following is the installation process used for the hex bolt and nut.

- Ensure you have the correct size and type of hex bolt and nut for your specific application.
- Place the hex bolt through the hole or onto the desired surface for fastening. Place a washer on the bolt before inserting it through the hole if applicable.
- Position the hex nut onto the bolt on the opposite side of the hole. Rotate the nut clockwise to tighten it onto the bolt.
- Use your fingers to tighten the nut onto the bolt as much as you can to ensure the bolt and nut engage properly before using a tool.
- Take a wrench or socket that fits the nut size and place it on the flat sides of the nut. Hold the bolt securely with one hand to prevent it from turning while tightening.
- Apply force in a clockwise direction to tighten the nut farther until the desired level of tightness.
- Check to ensure that the bolt is securely in place and the nut is tight enough.
Choosing the best hex bolt and nut for your application
There are several factors to consider when selecting the hex bolt and nut for your application. The selected hex bolt and nut should ensure that the fasteners meet the specific requirements of your application. Additionally, proper selection and installation of fasteners are critical for the safety and performance of the assembled structure. Also, it is advisable to consult with the industry experts for guidance on the best hex bolt and nut for your application. the following are the factors to consider during the selection process.

- Consider the installation method and tools you will be using beforehand.
- Assess the load bearing capacity required for the fasteners depending on the weight and stresses the joint will experience during operation.
- Choose the suitable head type based on your access and tightening requirements.
- Consider the length of the bolt to ensure it provides enough thread engagement when fastening the components together. It should hold the thickness of the materials joined.
- Ensure you select the right size of hex bolt and nut that fits the application.
- Choose hex and bolts made from materials such as stainless steel, carbon steel, alloy steel, brass and more. This will depend on factors like the environment, load bearing capacity and temperature conditions.
- Consider the grade of the hex bolt and nut that indicates the tensile strength and hardness of the fastener.
- Ensure the selected hex bolt and nut adheres to the necessary safety standards and regulations.
Frequently asked questions
What is a hex bolt and nut as used in overhead transmission lines?
A hex bolt and nut are devices used to offer stability and security to two or more components. They are however different components in the case that the hex bolt is a threaded fastener with a hexagonal head. A hex nut is a six-sided, internally threaded fastener that screws into the threaded portion of the hex bolt.
What are the common types of hex bolt and nut?
There are various designs and configurations of the hex bolt and nuts used in the overhead transmission lines. These include socket head cap screws, flange nuts, tap bolts, machine bolts, lag bolts, weld nuts and jam nuts.
What are the benefits of using hex bolt and nuts?
The benefits of the hex bolts and nuts make them a popular choice for various applications in the industry. This is because they are reliable, easy to use and versatile. Other benefits include industry acceptance, variety of head styles, standardization, cost effective, corrosion resistance, resistance to vibration and load bearing capacity.
What are the limitations of the hex bolt and nut?
Hex bolts and nuts also have various limitations which include limited accessibility, risk of over tightening, vibration loosening, susceptibility to corrosion, environmental impact, temperature limitations and tightening sequence. Choosing the right materials and specialized coatings, following proper installation procedures and conducting regular maintenance may help to overcome these limitations.
