
Steel fasteners are components used to secure and support various elements of the transmission line. They are able to withstand the mechanical stresses, environmental conditions and electrical requirements. They are also used to join two or more objects together permanently or temporarily. Steel fasteners are available in a variety of shapes and sizes for use in a wide range of applications. They are from versatile and durable materials that offer durable and corrosion resistance.
Components of steel fasteners
Steel fasteners consists of various components working together to provide secure connections. The components vary depending on the type of fastener and its intended purpose. They also vary depending on construction, manufacturing and overhead transmission lines. The best components for Southeast Asian countries are from durable materials that resist the humid weather. The following are the main components of the steel fasteners.
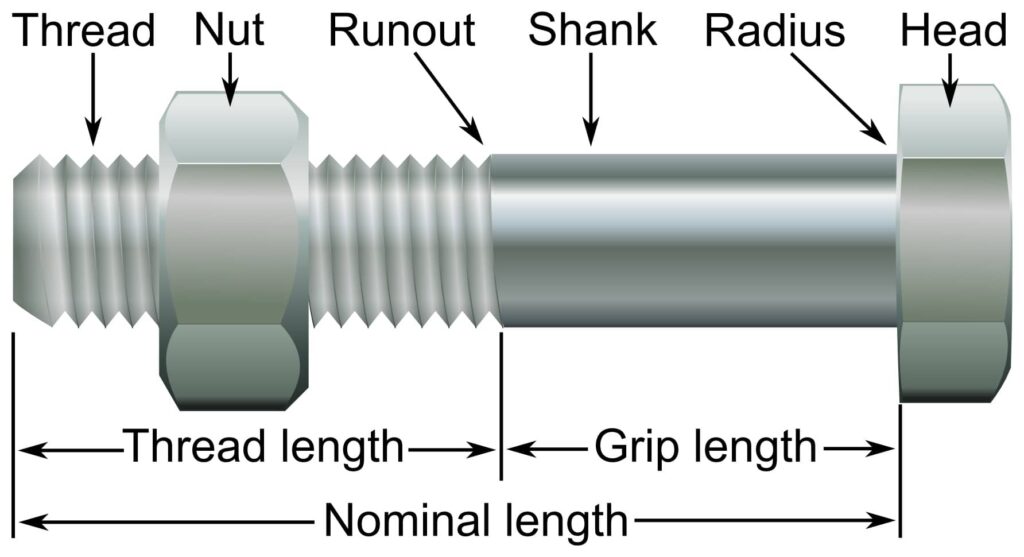
- Head – this is the main component of the fastener that drives into the components to fasten. They are available in different lengths, diameters and shapes that allow them to tighten and secure the connection.
- Shaft – this is the long, cylindrical part of the fastener extending from the head. It has threads on one end to connect with the nuts or other fasteners.
- Threaded end – these are the helical ridges running through the end of the bolt to allow it to engage with the nut’s threads.
- Shank – this is the unthreaded part of the bolt that sits within the material fastened.
- Coating/finish – this is the protective coating such as zinc or galvanization. It helps to prevent corrosion and increase their longevity.
Types of steel fasteners
There are various types and designs of the steel fasteners designed for specific applications and purposes. The choice of fastener depends on factors such as type of materials to join, load requirements, environmental conditions and desired level of security. The following are the common types of steel fasteners.
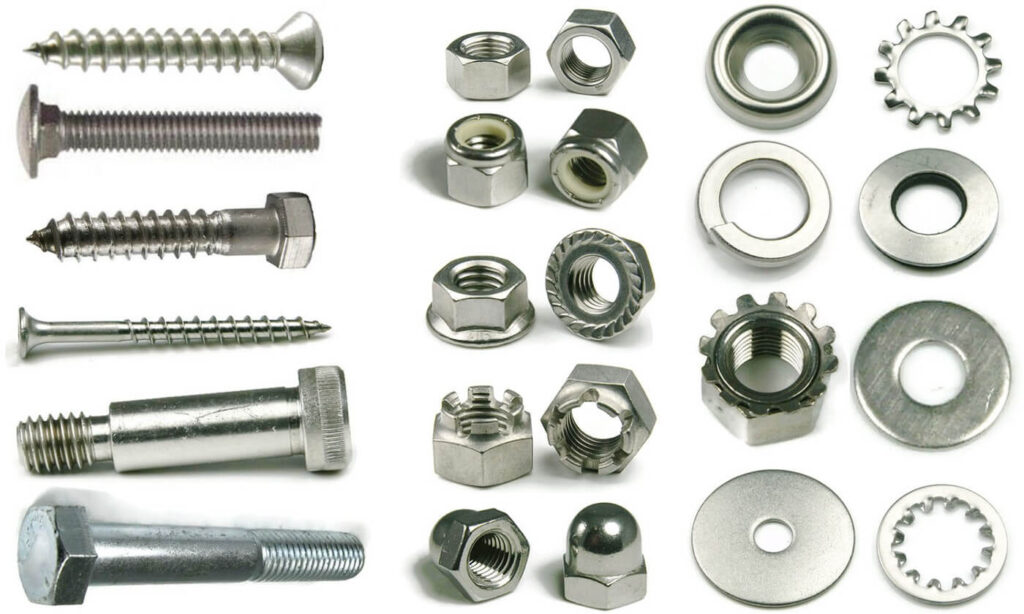

- Bolts – these are the threaded fasteners with a head that is larger than the threaded portion. They are from materials like carbon steel or stainless steel. Common types of bolts include hex bolts, carriage bolts, anchor bolts and eye bolts.
- Nuts – these are the threaded fasteners used to secure bolts and screws. They are from materials like steel, brass or plastic. Common types of nuts include hex nuts, lock nuts, wing nuts and cap nuts.
- Screws – screws are the threaded fasteners that drive into the materials directly. They are from materials like carbon steel, stainless steel or brass. Common types include wood screws, sheet metal screws and machine screws.
- Washers – these are flat discs placed under the nut or bolt heads to distribute the load and protect the material surface. They include flat washers, lock washers and fender washers.
- Rivets – these are fasteners that insert through aligned holes in materials and then deform to hold the materials together.
- Anchors – these secure fasteners in materials like concrete or masonry. They include expansion anchors, wedge anchors and sleeve anchors.
- Studs – these are the threaded rods with no head used to secure objects by threading into a tapped hole.
- Nails – these are short, pointed fasteners used for joining wood or similar materials.
Applications of fasteners
Steel fasteners find use in applications across various industries and sectors. The selected fasteners should ensure the structural integrity, safety and longevity of the assembled components. Additionally, you should seek advice from experts for guidance on the best fastener to use for your application. The following are the common application areas of steel fasteners.

- Construction – steel fasteners help to assemble structural components, secure beams and columns. They also help to connect trusses, fasten roof panels and attach siding.
- Aerospace industry – steel fasteners ensure safety and integrity of aircraft and spacecraft structures. This is due to their versatility and high strength. They help in the assembly of airframes, engines and critical components.
- Transportation – steel fasteners help in bridges, highways, railways and other infrastructure projects.
- Automotive industry – the fasteners help assemble vehicles such as in engine components, chassis, body panels, interior elements and various mechanical systems.
- Electrical industry – the fasteners help to secure components in electronic devices, control panels and electrical enclosures.
- Energy sector – steel fasteners aid in power lants, wind turbines and solar panel installations.
- Oil and gas industry – steel fasteners aid in pipelines, refineries and other facilities for connecting pipes, valves and equipment.
- Automated systems – they also work in robotics and automation systems for assembling components, securing joints and ensuring precise movement.
Installation guide for steel fasteners
Installation of steel fasteners should ensure security, safety and reliability of the connections. Some manufacturers offer installation guidelines for the specific type of fastener. Also, it is advisable to consult with industry professionals for guidance whenever in doubt of the installation. The installation process consists of several steps to follow which are as detailed below.
- Select the suitable type and size of steel fastener for your specific application and consider factors involved. These include load requirements, material type, environmental conditions and the type of connection needed.
- Ensure the materials to fasten are properly aligned and prepared. Drill the necessary holes, align components and clean the surfaces to remove debris or rust.
- Place the fasteners in the correct position of the materials and place the washers over the threaded end of the fastener if applicable.
- Tighten the fasteners using the necessary tools and the suitable torque. This is to ensure proper load distribution and prevent over-tightening or under tightening.
- Verify that the fastened components are properly aligned and that the fastener is securely tightened.
- Inspect the fastener and the surrounding area to ensure the fastener and connection can handle the intended load and conditions.
Selecting the best fastener
The selected steel fasteners should provide the desired strength, durability and reliability for the integrity of your project. The selection also depends on the load requirements, type of material used and the intended use of the fastener. The selection process also involves various factors to consider. These factors are as discussed below.

- Consider the cost of the fasteners and balance the quality and performance with the budget.
- Choose fasteners that are easy to install using available tools and equipment.
- Identify the specific purpose of the fasteners in your project and determine the load and stress the fasteners will need to withstand.
- Consider the materials used to produce the fasteners which should be able to handle corrosion, magnetic properties and the environmental conditions.
- Choose the appropriate type of fastener needed for your specific application.
- Ensure the size and dimensions of the fastener are compatible with the materials to connect.
- Determine the required load-bearing capacity of the fasteners based on the loads they will experience in your application.
- Select fasteners with features like locking mechanisms, lock washers or thread-locking compounds to prevent loosening.
- Consider fasteners with finishes that match the surrounding materials for aesthetic purposes.
Frequently asked questions
What are steel fasteners used in overhead transmission lines?
Steel fasteners are components used to secure and support various elements of the transmission lines. They withstand mechanical stresses, environmental conditions and electrical requirements specific to overhead power lines.
What are the benefits of steel fasteners?
Steel fasteners offer several benefits across various industries and applications due to their durability, strength and versatility. These benefits include corrosion resistance, ease of installation, wide availability, secure connections, safety and reduced maintenance.
What are the limitations of steel fasteners?
Steel fasteners also have various limitations to consider when selecting them for specific applications. they include material compatibility, cost consideration, thread galling, vibration loosening, installation complexity, electrical conductivity, corrosion and temperature sensitivity.
