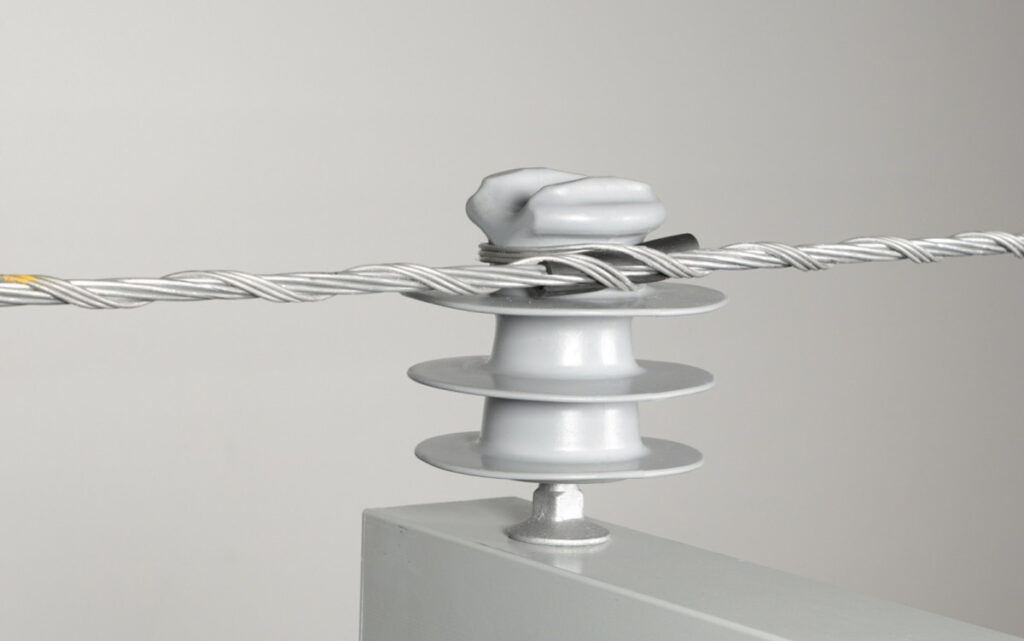

A side tie is a structural device used to provide extra support and stability to the conductor or wire on the transmission line. It installs horizontally between the main supporting structure and the conductor themselves. It also prevents galloping caused by wind or other environmental factors. A side tie is from materials such as steel cables or rods. They help to withstand mechanical stresses and environmental conditions that transmission lines experience. Corrosion-resistant side ties can withstand the coastal environments of Southeast Asia. Common types include spacer dampers, Stockbridge dampers, dead-ends and vibration dampers. They find help in maintaining conductor spacing, reducing conductor vibration, enhancing structural integrity and supporting line insulators.
Key features of side tie
Side ties have various features that make them essential components. This is by ensuring the safe and reliable operation of the transmission system. The features help them maintain the integrity of the transmission system. They also ensure the consistent supply of electricity. The following are the common features of the side ties.
- Stability enhancement – side ties enhance stability of transmission line conductors. This helps prevent galloping, oscillations and unwanted movements from winds or ice.
- Vibration damping – they help to dampen vibrations to help extend the life of the conductors, reduce wear and tear and reduce the need for maintenance.
- Material – they are from durable materials such as steel, cables, aluminum or composite materials. These materials withstand exposure to UV radiation, moisture and temperature extremes.
- Insulating properties – they also have insulating materials to help ensure electrical isolation between conductors and supporting structures.
- Streamlined design – the design helps reduce wind resistance and aerodynamic effects.
- Ease of installation – the design allows for easy installation on the utility poles and during maintenance.
- Weather resistance – the side ties are resistant to weather-related degradation. These include corrosion, rust or degradation of insulating materials.
- Flexibility – their flexibility allows them to accommodate the movement and expansion of conductors.
Selection and installation of side tie
There are various factors to consider when selecting the best side tie for your application. this helps to ensure the transmission lines meet the specific requirements of the application. These include line designs, environmental conditions, conductor size, mechanical load requirements, vibration and galloping, insulating properties, material and costs. The installation process should ensure the stability and reliability of the system. The following is a basic installation guide for side tie.

- Preparation – ensure you have all the necessary tools and materials. These include wrenches, insulating materials, tensioning equipment and safety gear. Ensure every worker observes the safety protocols for the installation.
- Conductor preparation – inspect the conductor to ensure they are in good condition.
- Positioning – identify the locations where the side tie will install along the transmission line and mark those positions.
- Anchor points – identify the anchor points on the supporting structures where the side tie will attach. Ensure the anchor points are strong and can withstand the mechanical loads.
- Attachment points – determine where the side ties will attach which may depend on the type and design of the side tie.
- Installation of side tie – install the side tie one by one following the manufacturers guidelines. Secure them to the conductor, insulating components or directly to the supporting structure.
- Tensioning – use suitable tensioning equipment to achieve the desired tension in the side ties.
- Alignment and spacing – ensure the side tie align correctly and they maintain the specified spacing between conductors.
- Insulation – if applicable, ensure the insulating components install properly. Also, ensure it provides the necessary electrical isolation.
- Inspection – conduct a visual inspection of the side ties checking for signs of damage, loose connections or misalignment.
- Documentation – maintain detailed records of the installation process. This is including location, tension levels and other issues.
Maintenance and inspection of the side ties
Maintenance and inspection ensure the reliability and safety of overhead transmission lines. the tropical climates of Southeast Asia pose unique challenges to the maintenance and inspection of side ties. Therefore, it requires proactive planning and diligent execution due to these conditions. The following is a basic guide on the maintenance and inspection of the side ties in Southeast Asian applications.

- Conduct regular visual inspections of all side ties along the transmission lines. this varies depending on factors such as climate, conductor type and load conditions.
- Consider the environmental factors such as high humidity, heavy rainfall and tropical storms.
- Apply suitable coatings or treatments to side ties and related hardware. This is to protect them from corrosion caused by the humid and salty air in coastal areas.
- Regularly assess the transmission line for vibration and galloping risks. Ensure the side ties are effectively dampening vibrations and oscillations.
- Keep side ties and insulators clean and free of debris such as leaves, bird droppings and vegetation. This helps them maintain their performance and insulation properties.
- Check the tightness and tension of side ties to enhance their effectiveness and performance.
- Inspect the insulating components on the side ties for signs of damage or wear. Ensure they provide adequate electrical insulation.
- Assess the structural integrity of the side ties and their attachments to supporting structures. Check for signs of rust, corrosion or mechanical damage that could weaken their load-bearing capacity.
- Maintain detailed records of all inspections including photographs, condition assessments and any corrective actions taken.
Comparative analysis for side ties in Southeast Asia
A comparative analysis for side ties involves considering and comparing various aspects in the market. Some of the factors include specific challenges, needs and environmental conditions of the region. Additionally, it is advisable to consult with experts to help make the best choice for side ties in southeast Asia. The following are some of the factors to include in the comparative analysis for side ties.

- Type of side tie – the different types of the side ties have different benefits and limitations to the application. Consider each of the benefits and limitations for a specific type for your project.
- Environmental challenges – the side tie should offer corrosion resistance for the tropical climates in Southeast Asia.
- Materials – common materials include stainless steel or composite materials that offer corrosion resistance.
- Compliance with standards – ensure the side tie complies with the relevant industry standards in the region.
- Market trends – various market trends influence the use of side ties in the applications. these include infrastructure development, local manufacturing, safety and reliability.
- Installation and maintenance – the humid and tropical climate necessitate regular maintenance. This is to ensure proper functioning of side ties.
Certifications and standards in Southeast Asia
Compliance with standards and certifications help ensure safety and reliability. The standards in Southeast Asia vary depending on the country and region. Some of the countries adapt the international and regional standards. The following are the common standards and certifications for side ties in Southeast Asia.

- IEC standards – this provides guidelines for the design and assessment of galloping and vibration in conductors.
- ASTM standards – this outlines the procedures for conducting salt spray testing to assess corrosion resistance.
- IEE standards – this addresses calculation methods for electric and magnetic forces between conductors.
- ISO certifications – this ensures the manufacturer’s quality management system meets international standards.
- Environmental standards – consider regional environmental standards. This is to ensure that side tie materials and installation practices do not harm the environment.
Regional market for side tie in Southeast Asia
The growth of the regional market for side tie is from the ongoing expansion and development of power transmission infrastructure. The rapid urbanization and industrialization also lead to the increased demand for electricity. Additionally, it is advisable to consult industry reports, market research and local industry. The following are the key factors that shape the regional market for side ties in southeast Asia.

- Increased energy demand – increased energy demand if from population growth, urbanization and economic development. This leads to the expansion of power networks that require the use of side ties.
- Infrastructure development – upgrading and expanding electrical grids includes construction of new transmission lines which requires reliable side ties.
- Renewable energy integration – wind and solar farms require new transmission lines and side ties to connect to the grid.
- Safety and reliability – ensuring the safety and reliability of transmission lines involve the use of side ties. They help prevent galloping, maintain conductor spacing and reducing the risk of electrical faults.
- Local manufacturing – many Southeast Asian countries have established local manufacturing of side ties. This can lead to increased competition and options for buyers in the region.
- Export opportunities – exportation of side ties to neighboring countries to capitalize on regional infrastructure development projects.
Frequently asked questions
What is the purpose of side ties in overhead transmission lines?
Side ties help to provide stability, prevent conductor oscillations, maintain conductor spacing and enhance the overall reliability of the transmission system.
What are the environmental challenges for side ties in Southeast Asia?
The tropical climate, high humidity and coastal locations in the region pose challenges related to corrosion resistance and durability of side ties.
What are the consequences of not maintaining side ties properly?
Absence of maintenance can lead to conductor instability, increased vibration, potential galloping and risks of electrical faults. These can impact the reliability and safety of the transmission system.
