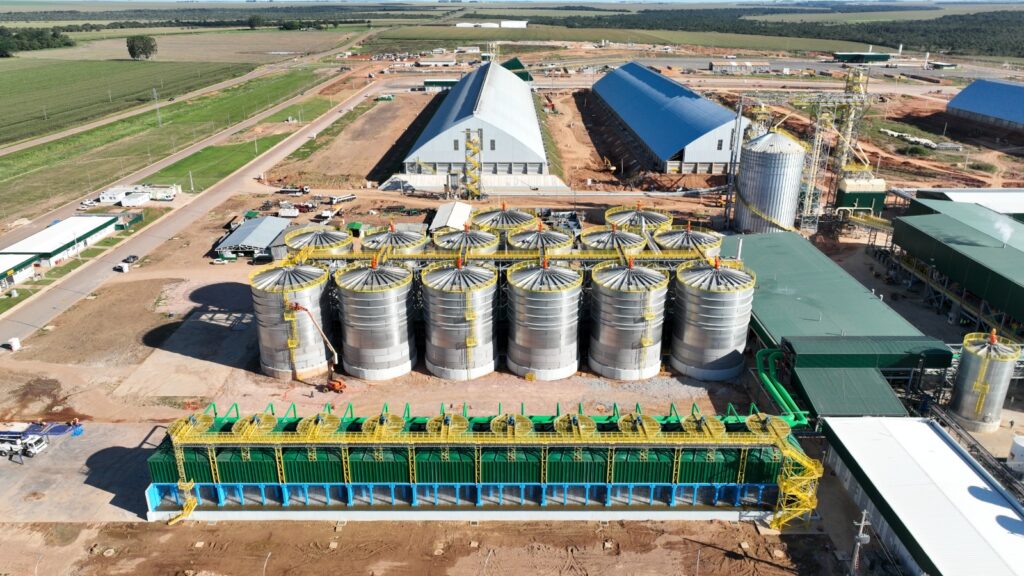

In more recent times, biofuels have emerged as an important component of South America’s energy strategy. This is a result of the region’s abundant agricultural resources and the global shift toward renewable energy. For example, Brazil’s large sugarcane crop serves as a main feedstock for ethanol. Similarly, Argentina’s soybean production places biodiesel as an appropriate component of the energy mix. The use of biofuels is critical for reducing carbon emissions and decreasing reliance on fossil fuels. Ethanol made from sugarcane emits less carbon than corn-based ethanol. Brazilian ethanol can reduce greenhouse gas emissions by up to 90% compared to gasoline. This makes it one of the most sustainable biofuels accessible. Furthermore, the use of pole line hardware is critical to maintaining the efficiency and dependability of biofuel production in South America.
High-quality pole line hardware ensures a consistent power supply to biofuel production facilities. This decreases downtime and improves production operations. Furthermore, biofuels provide a chance for governments to reduce their dependency on imported fossil fuels while improving energy security. South America’s substantial agricultural sector provides a good base for biofuel feedstock development. This is accomplished by using current crops like sugarcane, soybeans, and palm oil. As governments continue to set tough emissions objectives, South America has the potential to become a major source of sustainable biofuels. How can biofuels and pole line hardware improve biofuel output and efficiency? in
The importance of pole line hardware in biofuel production
Pole line hardware originates from components that support and maintain the infrastructure for power distribution. In the context of biofuel production, this hardware is critical for maintaining the energy infrastructure required to run biofuel production plants. Poles, crossarms, insulators, clamps, and fasteners are all typical components. They help to improve efficiency and optimize supply chains throughout South America. The following sections describe the roles of pole line hardware in biofuel producing plants.

- Promoting rural electrification in agricultural areas – it is vital to establish power lines that provide reliable energy access to agricultural regions. Pole line hardware is instrumental in extending the electrical grid to rural areas. High-quality pole line hardware reduces the risk of power interruptions. This helps in enhancing the efficiency of biofuel production.
- Facilitating energy distribution for biofuel production facilities – the process of biofuel production demands much energy. Pole line hardware plays a critical role in ensuring efficient energy distribution. This is especially to power mills, refineries, and processing plants. Additionally, this hardware aids in the integration of renewable energy sources, such as solar and wind into the grid.
- Improving sustainability and energy efficiency – pole line hardware sends energy efficiently. Utilizing high-grade pole line hardware minimizes energy loss, contributing to a more sustainable and cost-effective biofuel production process.
- Streamlining transportation and distribution of biofuels – dependable power lines are crucial for the effective transportation and distribution of biofuels. This hardware ensures that the necessary electricity is supplied to operate pipelines efficiently.
The use of biofuels to reduce greenhouse gas emissions in South America
By replacing fossil fuels, the region helps to reduce carbon emissions. This is particularly in line with the goals of the Paris Agreement. Brazil’s dominance in ethanol production, along with Argentina’s supremacy in biodiesel, positions South America as a renewable energy leader. Pole line hardware also plays an important role in sustaining the energy infrastructure required for continuing biofuel production. Biofuels play an important role in both decreasing environmental impact and boosting energy sustainability. The following describes how biofuels help to reduce greenhouse gas emissions in South America.
- Decreased carbon intensity – biofuels such as ethanol and biodiesel exhibit lower carbon emissions compared to conventional fossil fuels. This is due to the renewable characteristics of their feedstock and the inherent carbon cycle.
- Carbon sequestration during cultivation – the growth of biofuel feedstock contributes to carbon sequestration. This mitigates some emissions associated with biofuel production and consumption.
- Reduced reliance on fossil fuels – the adoption of biofuels leads to a reduction in the combustion of gasoline and diesel. These are primary sources of carbon emissions. The biofuel initiatives in South America effectively displace large quantities of fossil fuels.
- Enhanced energy efficiency and integration of renewable power – the production of biofuels in South America has achieved significant energy efficiency. This thereby decreases the demand for fossil-fuel-based electricity and resulting in lower emissions.
- Advancement of global climate objectives – biofuels are instrumental in fulfilling the region’s climate commitments. This is by lessening dependence on fossil fuels and encouraging the adoption of low-carbon alternatives.
