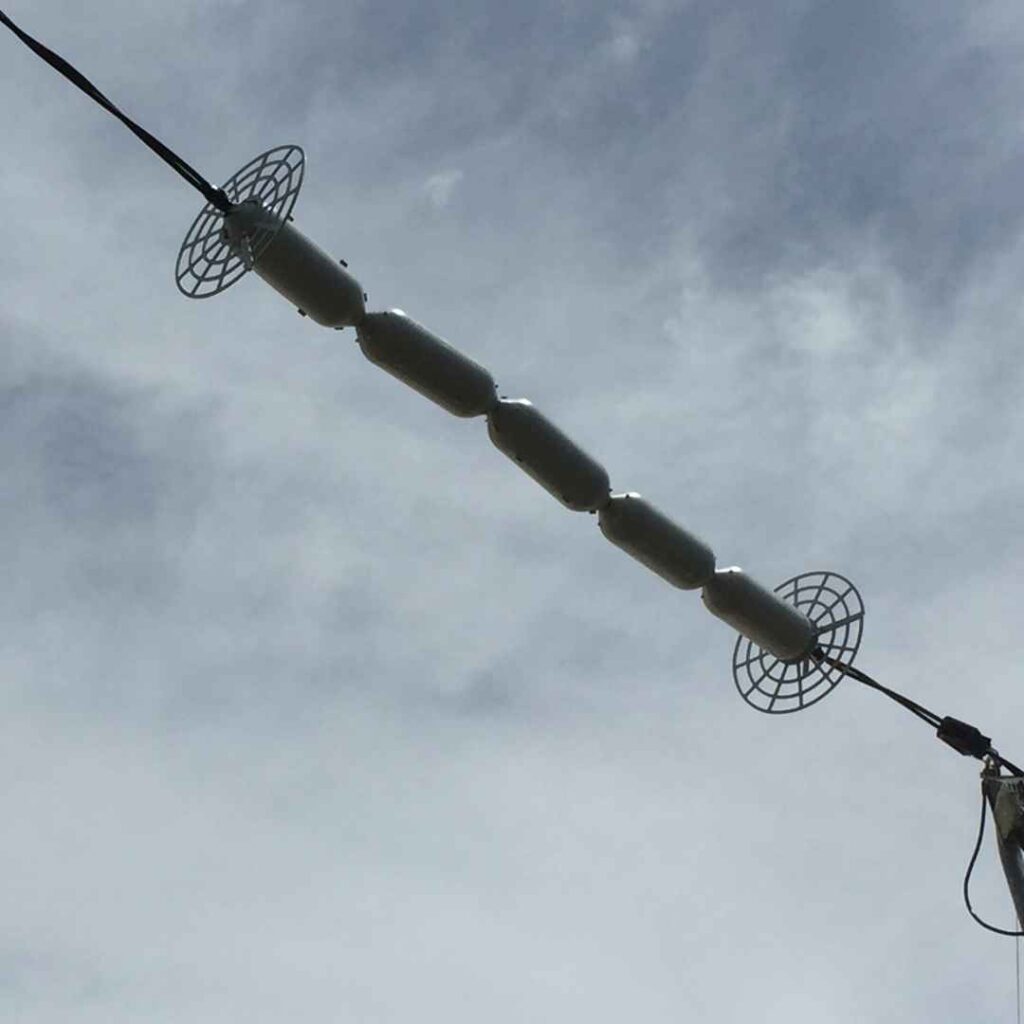

A line guard is a device that protects the conductor and other components of the transmission system. Its primary role is to ensure the integrity and dependability of the infrastructure. Line guards protect wires from mechanical damage. This could be due to vibrations, friction, or physical contact with other items. They also reduce wear and tear at the areas where conductors are hanging. Line guards serve to stop birds and animals from nesting on conductors. This also helps to keep birds and animals away from high voltage wires, ensuring the safety of wildlife. Line guards also help to protect the environment by ensuring that conductors remain in place.
Line Guard Properties:
The characteristics of a line guard ensure its effectiveness in protecting transmission lines. The qualities are specifically designed to address the issues that conductors and other components confront. They assist the line guard in addressing mechanical, thermal, electrical, and environmental concerns. The following are the characteristics of a line guard.
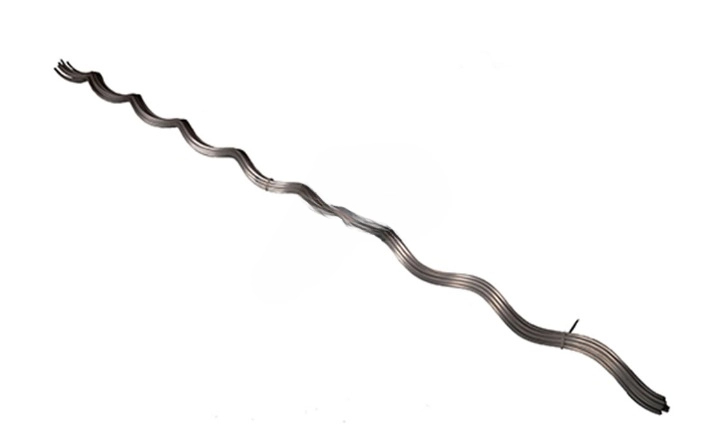

- Mechanical strength – line guards are from materials that offer high durability and resistance to mechanical stresses. This ensures they can withstand the physical stresses from wind, vibration and mechanical contact. They also help to distribute mechanical loads and stresses along the conductor.
- Material composition – the line guard materials are resistant to corrosion and environmental degradation. They are also lightweight to avoid adding significant extra weight to the transmission lines.
- Thermal properties – line guards have designs to accommodate the thermal expansion and contraction. This is due to temperature changes to ensure they remain effective in climatic conditions.
- Electrical insulation – the line guards are from non-conductive materials to prevent electrical arcing. They also ensure they do not interfere with the electrical properties of the conductors.
- Flexibility and conformability – line guards should be flexible enough to conform to the shape of the conductors. The design should ease installation and removal to allow maintenance without extensive effort.
- Environmental resistance – line guards face direct sunlight for extended periods. They should be resistant to UV radiation to prevent degradation. They should be capable of withstanding extreme weather conditions including rain and snow.
- Design and structure – helical line guards wrap around the conductor to help in distributing stress. A smooth surface helps reduce friction and wear on the conductors.
- Impact resistance – line guards should be able to absorb impacts from falling objects, bird strikes and other forces.
Materials needed for constructing a line guard
Line guards can be from a variety of materials. The chosen materials depend on their capacity to provide mechanical protection and environmental resistance. It is also advisable to consider mechanical stress, environmental resistance, cost, and electrical qualities. The following are the most common materials used to make line guards.

- Aluminium – this material has excellent strength-to-weight ratio. It also provides strong mechanical protection without adding extra weight to the conductors. It forms a protective oxide layer that resists corrosion. Aluminum also has good thermal conductivity which helps in dissipating heat generated by the electrical current.
- Galvanized steel – this offer high mechanical strength. This makes it ideal for environments where the line guard faces physical stresses. The galvanization process coats the steel with a layer of zinc providing corrosion resistance.
- Stainless steel – this is common for its durability and resistance to mechanical wear and environmental factors. It has superior resistance to rust and corrosion. It also needs minimal maintenance which makes it a long lasting option.
- Fiberglass – this is an insulator which makes it ideal for applications where electrical insulation is necessary. It also offers good balance of strength, durability and lightweight properties. Fiber glass line guards are resistant to UV radiation, moisture and temperature variations.
- Polymer composites – these materials are non-conductive which is beneficial for preventing electrical faults. They are also highly resistant to corrosion and UV degradation.
- Polyethylene and other plastics – this is an affordable and lightweight material. It provides an electrical insulation and can withstand exposure to various weather conditions.
Technical specifications for line guards
Technical specifications ensure that they can meet the requirements for transmission lines. They also define the performance, material, and design specifications. This is to ensure that they are effective and reliable. Adhering to these requirements also aids in the production of line guards that are both effective and safe. This contributes to the reliability of the electricity transmission infrastructure. The following are some common technical specifications for line guards.
| Specification | Requirements |
| Material | Aluminum Alloy 6061, Galvanized Steel, Fiberglass |
| Tensile strength | ≥ 250 MPa (36,000 psi) |
| Impact Resistance | ≥ 5 kJ/m² (Izod impact test) |
| Operating Temperature Range | -40°C to +85°C (-40°F to +185°F) |
| UV Resistance | Complies with ASTM G154 |
| Dielectric Strength (for non-metallic) | ≥ 12 kV/mm |
| Corrosion Resistance | Complies with ASTM B117 |
| Thermal Expansion Coefficient | ≤ 25 ppm/°C |
| Weight | ≤ 1 kg/m (0.67 lb/ft) |
| Surface Finish | Ra ≤ 1.6 µm |
| Compatibility | Suitable for ACSR, AAAC, and other conductors |
| Standards Compliance | IEEE, IEC, ANSI |
- Material specifications – line guards are from materials like aluminium alloy, galvanized steel, stainless steel or fiberglass. These materials must withstand exposure to corrosive environments and UV exposure.
- Mechanical properties – the line guard should have high tensile strength, flexibility and enough weight. They should also be able to withstand impacts without significant damage.
- Electrical properties – they should also be electrically conductive or non-conductive. They should also be able to resist electrical arcing.
- Thermal properties – the line guards should operate within a specified temperature range. The materials should have a low thermal expansion coefficient to reduce deformation with temperature changes.
- Environmental resistance – the line guards should follow standards like ASTM for weathering testing. This is to ensure durability in various climates.
- Design and construction – the specifications should detail helical pitch, diameter and length. This is to ensure proper fit and protection. They should also ensure a smooth surface finish to reduce friction and wear on conductors.
- Standard and compliance – they should show compliance with relevant industry standards. This is including IEEE, IEC and ANSI standards. The line guards should also undergo testing to ensure they meet the specified requirements.
Coatings and treatments for line guards
Coatings and treatments improve the performance and longevity of line guards. They aid to protect the line guards from environmental hazards such as corrosion, UV radiation, and physical wear. Coatings and treatments are critical in ensuring the integrity and dependability of overhead transmission lines. Coatings and treatments serve their purpose in a variety of processes. This includes surface preparation, such as cleaning and blasting. It comprises techniques like as dipping, spraying, brushing, and electrophoretic deposition. The following are the most typical coatings and treatments used on line guards.

- Galvanization – this involves immersing steel line guards in molten zinc. A thinner zinc coating applies through an electroplating process. It provides corrosion resistance with a smoother finish.
- Anodizing – this enhances the natural oxide layer on aluminium line guards. It helps in providing increased corrosion resistance. This can also serve to add color to the line guards for visibility.
- Polymer coatings – this may include one of polyethylene coating, polyurethane coating and epoxy coating. Polyethylene coating forms a protective layer that is resistant to UV radiation, moisture and chemicals. Polyurethane coating offers abrasion resistance and flexibility. It protects against mechanical wear and environmental degradation. Epoxy coating helps to provide a durable, protective barrier against corrosion and physical damage.
- Fluoropolymer coatings – this provides a low-friction, non-stick surface that is resistant to chemicals and UV radiation.
- Ceramic coatings – this offers high heat resistance, abrasion protection and superior corrosion resistance.
- Anti-corrosion treatments – this includes phosphating which applies to steel line guards. It also includes chromate conversion coating which enhances corrosion resistance and provides a good base for coatings.
Line guard-equipped conductors
Line guards work with various conductors in overhead transmission lines. They keep them safe from mechanical damage, abrasion, and environmental hazards. The type and design of line guards employed might depend on the conductor selected. Additionally, understanding the conductor qualities ensures the deployment of appropriate line protection. Mechanical strength, thermal expansion, conductivity, diameter, and construction are all factors to consider while selecting line guards. The following are the most frequent conductor types used with line guards.
- Aluminum conductor steel (ACSR) – ACSR conductors consist of a core of steel strands surrounded by aluminum strands. Line guard used with ACSR conductors need to hold the steel core’s integrity and the aluminum strands softness.
- All Aluminum Conductor (AAC) – line guards for AAC conductors focus on protecting the softer aluminum strands from abrasion and mechanical wear.
- All aluminum alloy conductor (AAAC) – line guards for AAAC conductors need to provide protection against environmental factors. They also protect against mechanical stress while accommodating the conductor’s higher strength.
- Copper conductors – these need line guards that prevent oxidation and provide mechanical protection.
Frequently asked questions
Common conductors used with line guards include ACSR, AAC, AAAC, ACSS, copper, and composite conductors. Each type of conductor has unique properties that influence the design and selection of line guards.
Key properties of a line guard include mechanical strength, corrosion resistance, thermal stability and electrical insulation. It also includes flexibility, environmental resistance and impact resistance.
