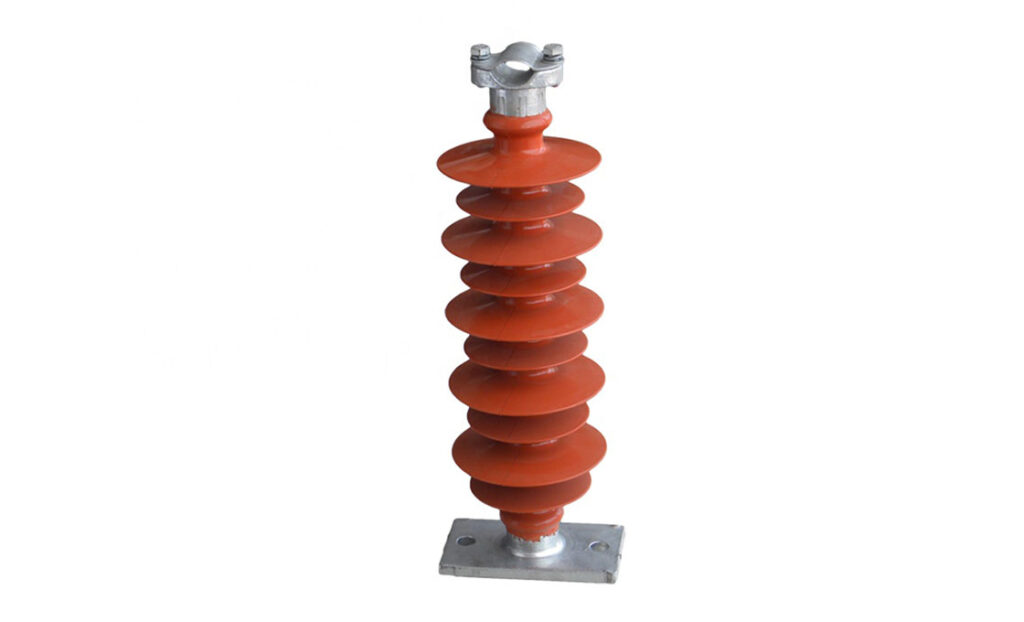

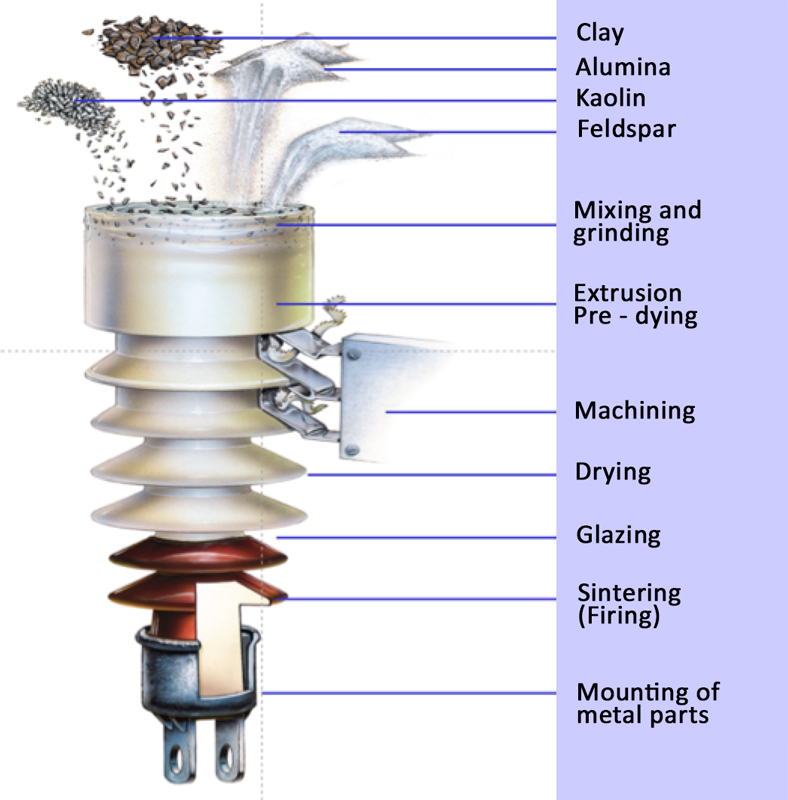
Post insulator is a cylindrical or rectangular-shaped insulating component. It is from materials like porcelain, glass or composite. The post insulator supports and insulates electrical conductors in the various power applications. The devices mounts on transformers, circuit breakers or switchgears. Post insulators work in applications with high voltage levels like power transmission and distribution systems. They also provide mechanical support, electrical insulation and environmental protection. This is to ensure the safe and reliable operation of the electrical equipment. The design varies depending on specific applications and voltage requirements. It also depends on voltage rating, mechanical strength, environmental resistance and electrical performance.
Components of a post insulator
Post insulator consist of different components that allow the efficiency during insulation. The design and components of the post insulator also vary depending on various factors. These include voltage rating, application requirement and specific manufacturer designs. They work together to provide electrical insulation, mechanical support and safe operation. Below are the common components of a post insulator.
- Insulating core – this is the central part of the post insulator made of a non-conductive material like porcelain, glass or polymer. It provides the primary electrical insulation and supports the conductive fittings or terminals.
- Conductive fittings – post insulators have conductive fittings at each end made of metal. They serve as connection points between the insulator and the associated electrical equipment. The fittings provide electrical connectivity for the energized conductor. It also allows the insulator to mount on the supporting structures.
- Mounting components – the insulators require hardware and mounting components to secure them to the supporting structure or electrical equipment. They include metal flanges, clamps, bolts among others. These components allow proper alignment, stability and mechanical strength of the insulator assembly.
- Leakage path – the leakage path provides extra surface distance and improved pollution performance. This is by creating a longer electrical path along the insulator’s outer surface.
- Grading rings – grading rings work in areas with high voltage post insulators. They help to help distribute the electrical field evenly along the insulator surface. This helps reduce the risk of electrical stress concentrations and corona discharge.
Types of post insulators used on transmission lines
There are two main types of post insulators used on the overhead transmission lines. Select by material they are from which consists of porcelain, glass or polymer. The two types of the post insulators help to provide electrical insulation and mechanical support. The two main types of the post insulator are as detailed below.
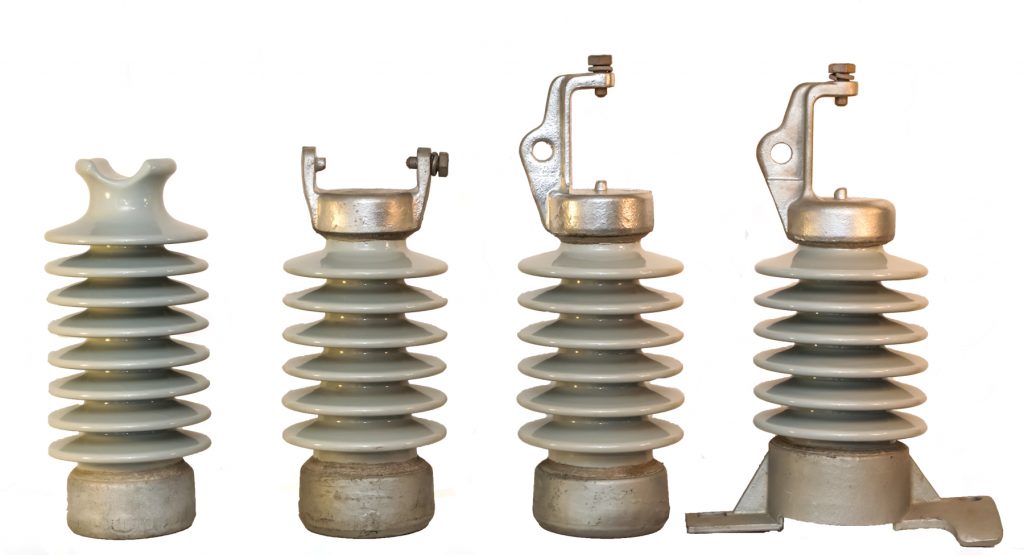

- Suspension post insulators – the suspension post insulators help to support the conductors and provide insulation between the conductors and supporting structures. They consist of a solid insulating core made of materials like porcelain or polymer. It attaches to the conductor through a suspension assembly. This includes metal end fittings and an insulator cap. It allows the insulator to hang from the supporting structure. This also help in providing electrical connectivity to the conductor.They install in a series of insulators with each insulator providing voltage rating. Suspension post insulator can handle high mechanical loads caused by conductor weight, wind, ice and line tension.
- Strain post insulators – these are also known as line post insulators used in areas of overhead transmission lines. This is where the conductors change direction or require extra support. They can withstand mechanical stresses caused by conductor tension and line configuration changes. They are shorter in length than the suspension post insulators and consist of a solid insulating core made of porcelain or composite. This core has a metal end fitting for connection to the conductor and supporting structure. The strain post insulators install in vertical or angled configurations. This is to provide extra support and maintain proper conductor alignment. They also absorb and distribute the mechanical forces along the length of the insulator. This is to reduce stress on the conductor and the supporting structure.
Application of post insulators
Post insulators work in various electrical applications where the primary focus is to providing electrical insulation and mechanical support. They meet specific voltage ratings, mechanical load requirements and environmental conditions. They also ensure a safe and reliable operation of electrical equipment and systems. Below are the various applications of the post insulators in detail.

- Switchgear – post insulators work in switchgears to insulate and support switching devices. These include circuit breakers, isolators and load break switches in switchgears.
- Power transmission and distribution – they support and insulate the conductors on transmission lines. They also provide electrical insulation between the conductive parts of the equipment and the grounded structures.
- Capacitor banks – they help in capacitor banks to support and insulate the capacitor units.
- Instrument transformers – they also work in current transformers and voltage transformers. Tis helps to provide electrical insulation and mechanical support for the primary and secondary windings.
- Railway traction systems – post insulators help to support and insulate overhead catenary wires. They ensure efficient transmission of electrical power to the trains. This is while maintaining proper electrical insulation.
- Substations – post insulators support various equipment like transformers, circuit breakers, disconnect switches and bus bars.
- Surge arrestors – these help to protect electrical equipment and systems from voltage surges. These surges are from lightning strikes or switching operations.
Installation of the post insulators on the overhead transmission lines
The installation of the post insulators depends on the type of insulator, manufacturer guidelines and project specifications. Also, follow the manufacturers instructions foe safe connections. Ensure to work under the applicable industry standards and safety regulations. Below are the various steps to follow during installation.

- Prepare all the tools and equipment needed during the installation.
- Position and align the insulators along the transmission lines.
- Mount the post insulators to the supporting structure suing the provided mounting hardware.
- Connect the conductors to the post insulators suing the appropriate fittings and connectors.
- Assemble the insulator strings by connecting multiple insulators together. This helps to achieve the required voltage rating.
- Ensure that grading rings install and position properly along the length of the post insulator.
- Conduct thorough visual inspection of the installed post insulators. Check for any signs of damage or improper installation.
- Establish a regular maintenance and monitoring schedule. This is to ensure the ongoing integrity and performance of the post insulator.
Choosing the best post insulator in the market
There are plenty of different manufacturers and suppliers in the market for the post insulators. Choosing the best for your application can sometimes be tedious. This is because they should meet the specific requirements for your application. Also, it is advisable to consult with experts in the field to determine the most suitable insulator for your application. Below are the key factors to consider before selecting the post insulators.

- Determine the voltage level of your application and choose a post insulator with a voltage rating suitable for that specific voltage.
- Consider the material of the insulator that have potential to resist environmental conditions.
- Assess the mechanical requirements of your application. This includes conductor tension, wind loads, ice loads and seismic considerations.
- Consider a post insulator with good pollution performance.
- Evaluate the insulation performance of the post insulator. This includes the flashover voltage and insulation resistance.
- Consider the reputation and track record of the manufacturer. They should have a record pf producing high-quality and reliable post insulators.
- Consider the cost effectiveness of the post insulator and if they meet your application requirements.
- Assess the availability and quality of technical support and after sales provided by the manufacturer.
Frequently asked questions
What is a post insulator?
A post insulator is an insulating device used to support and insulate electrical conductors.
How do post insulators provide electrical insulation?
Post insulators have a non-conductive core made from porcelain, glass or polymer. It helps prevent the flow of electrical current between the conductor and the supporting materials.
What are the benefits of post insulators?
Post insulators offer several benefits that make them a popular choice in the overhead transmission lines. These include electrical insulation, mechanical support, voltage distribution, environmental resistance, high voltage capabilities, flexibility and versatility and lightweight and compact.
What are the limitations of using post insulators?
Thet also have various limitations to take into account when selecting for your applications. They include mechanical limitations, fragility, pollution performance, surface condition, initial cost, compatibility and limited flexibility.
