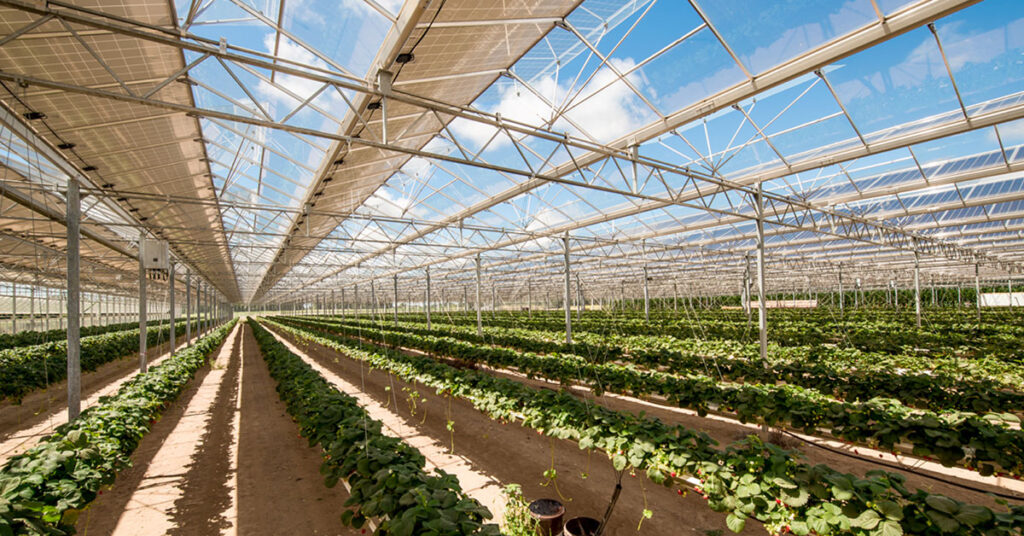

Agrivoltaics in South America involves integrating solar energy production with agricultural activities on the same piece of land. This includes placing solar panels on top of farming fields or incorporating them into agricultural buildings. Nations such as Brazil and Chile are embracing agrivoltaics due to their abundant natural resources. The farmland and sunlight create the ideal setting for agrivoltaics. Agrivoltaics tackles the issues of climate change, food safety, and sustainable energy. The use of agrivoltaics decreases reliance on fossil fuels and supports the agricultural economy. Countries in South America can adopt agrivoltaics by implementing solar photovoltaic systems on their agricultural fields. The cover provided by solar panels assists in minimizing water loss through evaporation. A pin insulator acts as an essential element in the electrical system that underpins the agrivoltaics. It guarantees the secure and dependable functioning of these systems.
A pin insulator holds up power lines that carry electricity produced by solar panels or other renewable energy sources. It stops electrical current from reaching the support structure, ensuring safety and avoiding short circuits. A pin insulator can endure severe environmental conditions like temperature and humidity. It guarantees the dependability and security of power lines, aiding in the effective transfer of electricity produced from agrivoltaics. In this way, a pin insulator contributes to the effective combination of agriculture and renewable energy. This article examines the significance of pin insulators in the implementation of agrivoltaics across South America.
Significance of a pin insulator in advancing agrivoltaics in South America
A pin insulator is a kind of electrical insulator utilized to guarantee the secure and effective growth of agrivoltaics. It aids in protecting and insulating electrical wires in external settings. A pin insulator ensures dependable energy transmission, endures environmental pressures, and allows for cheap grid options. With the advancement of agrivoltaics, we need pin insulators to ease the co-development of energy and agriculture. The significance of a pin insulator in agrivoltaics in South America is as outlined below.

- Improving safety – when agricultural practices and solar energy production take place on the same land, the closeness of farming machinery and personnel necessitates electrical safety measures. A pin insulator holds and isolates overhead power lines and stops electrical failures. It stops current from leaking to the ground, thereby lowering the chance of electrical accidents.
- Severe environmental factors – South America contains areas with extreme sunlight, high humidity, and diverse elevations. A pin insulator can endure elevated temperatures, ultraviolet light, humidity, and intense rain. It additionally offers mechanical support to solar setups and safeguards against harm from moving conductors.
- Effective power transmission – a pin insulator accommodates medium- to high-voltage distribution lines. This guarantees that electricity produced by solar panels efficiently reaches local grids. A pin insulator aids in reducing energy losses over extended distances.
- Enhancing grid stability and renewable integration—pin insulators assist in bolstering the infrastructure essential for agrivoltaics. For example, nations such as Chile and Brazil are striving to enhance their renewable energy capacity. The insulators assist in controlling the extra load and fluctuations that renewable energy sources bring to the grid.
Data analysis related to agrivoltaics in South America
Data analysis is essential for enhancing agrivoltaic systems in South America. Through the gathering and examination of data, farmers are able to make knowledgeable choices to enhance the advantages of the systems. Data analysis facilitates enhanced decision-making, maximizing resource use, and boosting results for both agriculture and solar energy production. TTF is a world-class global provider of high quality overhead line hardware, transmission hardware, distribution hardware, conductors, insulators, cutout switches, anchoring and grounding products. Here are the uses of data analytics in agrivoltaics within South America.
- Optimizing crop production and solar energy generation—agrivoltaic systems harmonize the twin goals of farming and energy output. Data analytics enables the determination of the best arrangement for solar panels. This isi ncluding optimal spacing, tilt, and orientation. This aids in balancing the sunlight needs for crops and optimizing energy production.
- Performance oversight and upkeep – data analysis aids in tracking the performance of the solar energy system. It also tracks the performance of farming elements of the agrivoltaic configuration. This is achieved by utilizing sensors and IoT gadgets. They assist in monitoring energy generation, panel performance, environmental conditions, and soil quality in real time.
- Yield forecasting and economic enhancement – agrivoltaic systems can simulate and expect crop outputs. This is by utilizing environmental data, type of crop, and seasonal variables. The operators are able to harmonize energy and agricultural production to optimize financial gains.
