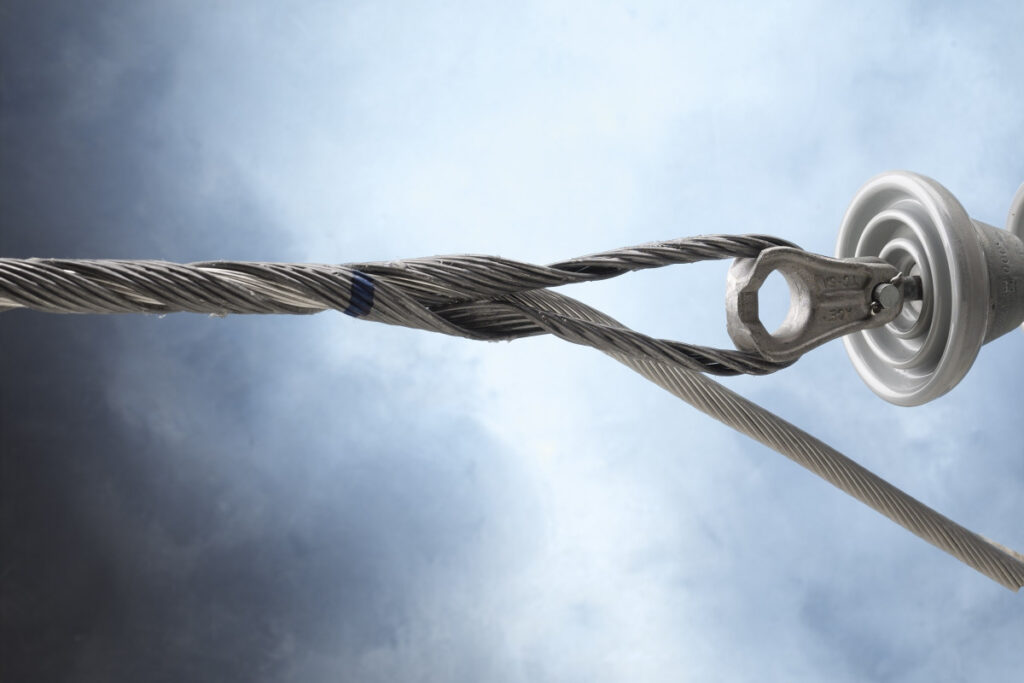

A distribution grip dead end is a hardware used to secure a conductor at the end of a distribution line. It helps ensure the stability and proper functioning of the electrical distribution system. The type and design of the grip depends on voltage level, conductor type and environmental conditions. It is from materials such as aluminum, steel or composite materials. Their design allows them to withstand tropical climates in Southeast Asia. This helps to ensure the continuous electricity supply in any weather. Common types of distribution grip dead ends include preformed dead ends, swage dead ends and bolted dead ends among others. They find use in termination points, suspension clamps, high-tension application, repair and maintenance.
Key features of distribution grip dead end
The features of the dead-end help to securely anchor and terminate the conductors on the transmission lines. The features depend on voltage levels, conductor types and environmental conditions. The following are the common features of the distribution grip dead ends.
- Material – the dead ends are from high-strength materials such as aluminum or steel. These materials help them to resist the diverssse weather conditions in Southeast Asia.
- Corrosion resistance – they have corrosion-resistance coatings. They help them ensure the longevity and reliability.
- Compatibility – they are compatible with specific conductor types, sizes and configurations.
- Mechanical strength – the mechanical strength helps them to withstand stresses. It also helps them maintain the tension in the conductor.
- Ease of installation – they involve simple tooling for a candid installation process.
- Load ratings – they rate for specific loads and tensions to ensure they handle the mechanical forces.
- Environmental resistance – the design should withstand factors such as UV radiation, extreme temperatures and moisture.
- Maintenance accessibility – distribution grip dead ends allow for ease of maintenance or replacement. This helps to reduce downtime and repair costs.
Selection and installation of distribution grip dead end
There are various factors to consider during the selection process of the distribution grip dead end. These include conductor type and size, voltage level, environmental conditions, mechanical load requirements, grip type, durability and corrosion resistance. The installation process should ensure the safety and reliability of the distribution system. Additionally, it is advisable to consult with experts for guidance in the installation. The following is a basic installation process of the distribution grip dead end.
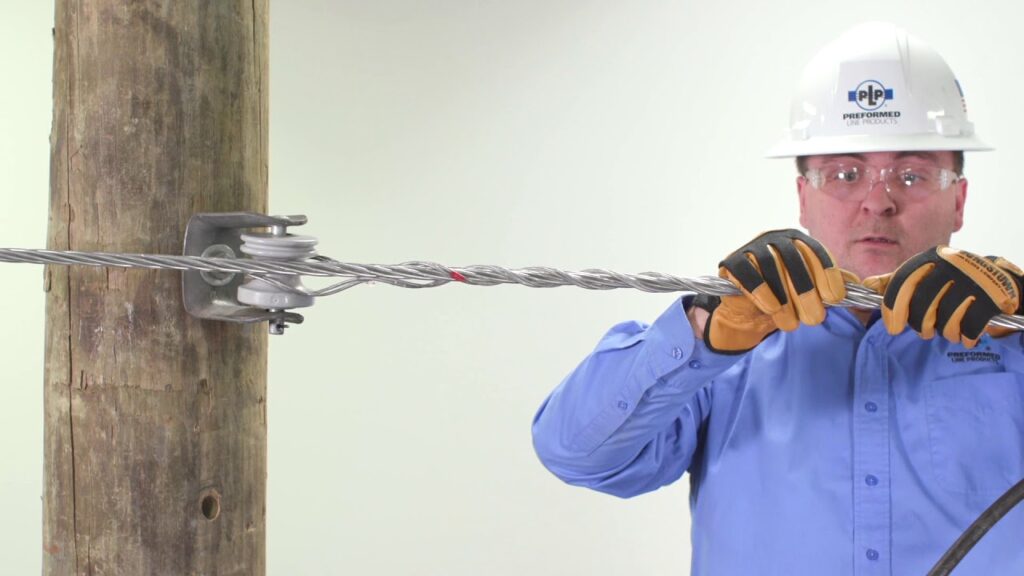

- Safety precautions – follow all the safety protocols such as wearing personal protective equipment. Ensure the distribution line is de-energized, locked out and tagged out to prevent accidents.
- Gather tools and equipment – collect all the necessary tools and equipment. This is including wrenches, socket sets, torque wrenches and hoists.
- Inspect the grip – inspect the grip for any signs of damage or defects and ensure it matches the conductor size and type.
- Conductor preparation – clean and inspect the conductor to ensure it is free from dirt, debris or defects.
- Positioning – position the distribution grip dead end at the intended location on the conductor.
- Attachment – attach the grip to the conductor following manufacturer’s guidelines. This involves clamping, bolting, swaging or other attachment methods.
- Tightening – use the suitable tools and torque values to tighten any bolts, nuts or other fasteners.
- Inspection – conduct a visual inspection of the grip and the conductor to ensure that the installation is secure and there are no loose parts.
- Alignment and tensioning – ensure the conductor is properly aligned and at the desired tension.
- Secure the dead end – ensure the grip dead end fastens to the supporting structure.
- Documentation – keep detailed records of the installation including grid type, conductor size, torque values and installation date.
- Energize the line – after installation, follow the established procedures to safely energize the distribution line.
Maintenance and inspection of distribution grip dead end
The dead ends require regular maintenance and inspection. This is to ensure safety and reliability of the distribution lines. This also helps to prevent unexpected failures, ensure safety and maintain reliability of the lines. The following is a basic maintenance and inspection guide for the distribution dead ends.

- Establish a routine of visual inspections of all distribution grip dead ends in your distribution line.
- Check the grip dead ends for any signs of corrosion or rust which can affect its performance.
- Ensure the fasteners, bolts and clamps on the grip dead ends are properly tightened to the recommended torque levels.
- Look for signs of wear and tear on the grip and conductor including abrasion, cracks or deformation.
- Check the electrical continuity of the grip dead end and ensure there are no interruptions in the electrical path.
- Verify that the conductor remains properly aligned and tensioned.
- Keep detailed records of your inspection findings including dates, location and condition of each grip dead end.
- Clean the grip dead ends to remove dirt, dust and contaminants that could affect performance.
- Replace any dead ends that show signs of wear, damage or corrosion.
Comparative analysis of distribution grip dead ends
Conducting a comparative analysis includes assessing different grip types, their suitability and evaluating key factors. These factors may include cost, durability and ease of installation. Additionally, it is advisable to consult with engineers and suppliers for valuable insights in decision making. The following are the key factors to consider in southeast Asian countries.
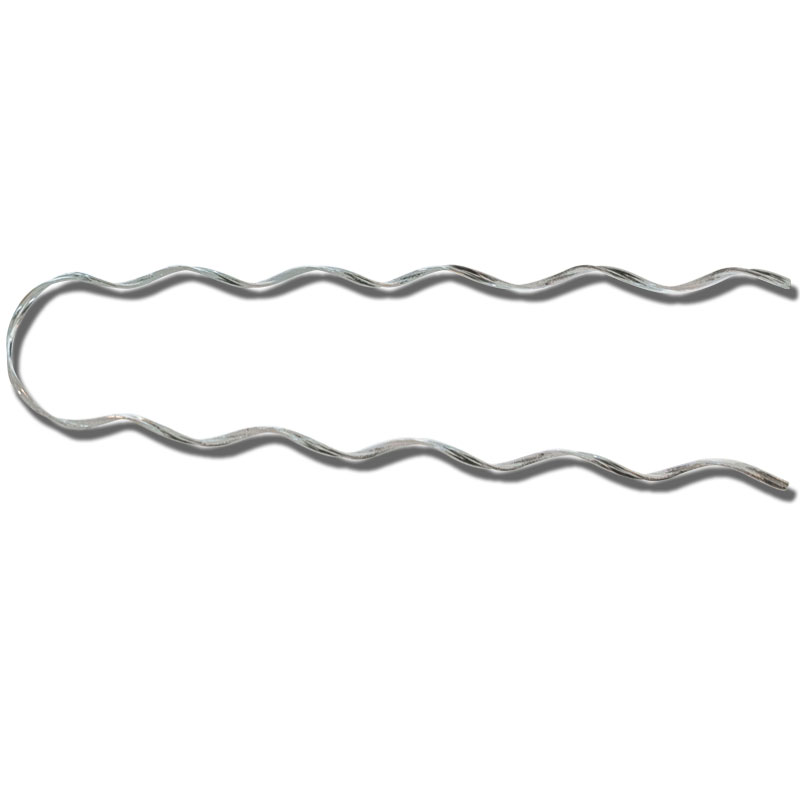

- Grip types – common types of grip dead ends include helical dead ends, preformed dead ends, socket style dead ends and swage dead ends. Assess the benefits of each type checking for mechanical strength, electrical continuity, durability, ease of installation and corrosion resistance.
- Environmental conditions – Southeast Asia has conditions such as high humidity, rain and monsoon seasons.
- Cost considerations – consider the initial cost of the dead end which varies by type and balance it with the quality.
- Ease of installation – when checking the ease of installation, consider labor costs and tools used.
- Customization – check for the suitability for customization to meet the projects specific requirements.
- Regulations and standards – ensure the selected dead end complies with the local and international standards for electrical systems.
- Supplier availability – consider the availability of grip types and manufacturers. Thi is to ensure timely procurement and maintenance.
- Local expertise – this is necessary for the installation and maintenance of specific grip types in the region.
Certifications and standards in Southeast Asia
There are various standards and regulations that the distribution grip dead end should comply to in the region. Most of the standards in the region align with international and regional electrical and safety standards. Manufacturers and suppliers in the region should comply to these standards to ensure safety and quality of the products. The following are the common certifications and standards in Southeast Asia.

- IEC standards – this provides guidelines for various aspects of electrical equipment
- ASTM international standards – these standard covers aluminum alloy gripping and dead-end strain plates for electrical purposes.
- ANSI standards – these standards relate to electrical and safety equipment.
- IEEE standards – these define the requirements for overhead distribution grip hardware.
- Local electrical code and regulations – each country have their own local standards and regulations for electrical distribution equipment.
- ISO certification – these shows a manufacturer’s commitment to quality and safety.
- IECEE CB scheme – this is an international system for the testing and certification of electrical and electronic equipment.
Regional market for distribution grip dead end in Southeast Asia
There are various factors that affect the regional market of distribution grip dead ends in Southeast Asia. The market depends on the specific needs, infrastructure development and regulatory environments. Manufacturers and suppliers should understand the market conditions for the dead end in the region they operate in. Adapting products to local needs and regulations and building relationships with utilities helps in the success of the regional markets. The following are the key factors affecting the regional market.

- Population density – high populated regions require extensive electrical distribution systems to meet the energy needs.
- Economic growth – the economically thriving regions tend to invest in their electrical infrastructure. This creates opportunities for distribution grip dead end suppliers.
- Infrastructure development – rapid urbanization leads to the growth of the market for distribution grip dead ends.
- Replacement and upgrade – regions with aging electrical distribution infrastructure require upgrades.
- Utility and energy policies – government policies and regulations related to energy sector influences the demand for distribution grip dead ends.
- Energy mix – reliance on renewable energy sources impacts the demand for distribution grip dead ends.
- Political stability – political stability and regulatory consistency provides a favorable environment for infrastructure investments.
- Environmental conditions – challenging conditions such as coastal areas or regions prone to extreme weather events require corrosion-resistant grip dead ends.
Frequently asked questions
What is a distribution grip dead end and their purpose?
This is a hardware used to secure and terminate conductors in overhead electrical distribution systems. They help to maintain the integrity and stability of the distribution line.
What are the common types of distribution grip dead ends used in southeast Asian countries?
The selection of a particular type depends on the specific applications and requirements in Southeast Asia. Common types used include helical, preformed, socket-style, swage and bolted dead ends.
What are the key considerations when installing distribution grip dead ends in Southeast Asia?
Consider proper installation techniques, torque values and alignment of the components. Also, ensure you adhere to safety procedures and use appropriate tools and equipment for installation.
