
A shackle insulator is a component used in electrical systems to provide support and electrical insulation. It is also known as a spool insulator or a suspension insulator. It consists of a metal shackle and an insulating component made of porcelain, glass or polymer. The shackle helps to attach the insulator to the support structure like crossarm. The insulating part of the shackle insulator prevents electrical currents from flowing down to the ground. This helps to prevent power loss or damage to the equipment. Their designs help to withstand environmental factors like wind, rain, ice and temperature variations. Shackle insulators also provide mechanical support to the conductors that help to maintain the integrity of the line. Common types include glass shackle insulator, porcelain shackle insulator and composite shackle insulator.
Components of the shackle insulator
A shackle insulator comprises of component that work together to provide support and insulation. Each of this component have a special purpose in supporting electrical systems. The component helps the insulator to withstand mechanical stresses and electrical current. This also helps to prevent power loss, outages and damage to equipment. The following are the common components of the shackle insulator.
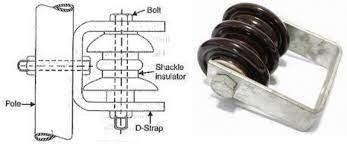
- Shackle – this is the metal component of the insulator that attaches to the support structure. It is from galvanized steel to resist corrosion and provide mechanical strength.
- Insulating housing – this is the main body of the shackle insulator made of porcelain or polymer materials. It provides the insulation between the conductor and the support structure. It also have designs to have high electrical resistance and withstand the voltage stress applied during transmission line operation.
- Core rod – this is a central structural component of the shackle insulator usually made of metal or composite material. It is securely attached to both ends of the insulating housing and supports the load of the conductor.
- End fittings – these are connectors that secure the insulating housing and core rod to the conductor. They provide strong and reliable connection since they have threaded connections to ease installations and maintenance.
- Sealing material – sealing material helps to ensure the stability and integrity of the insulator. It fills any gaps between the insulating housing, core rod and end fittings to prevent moisture from entering the insulator.
- Fittings – shackle insulator uses various fastening fittings like bolts, nuts and washers. They help to secure and assemble the different parts of the shackle insulator.
- Flanges – these are flat surfaces located at the ends of the insulating body for extra support and stability. They help distribute the mechanical loads across the structure. They serve as attachment points for the end fittings and ease the assembly of the insulator.
Common features of the shackle insulator
The insulator has several features that make them crucial components in electrical installations. The features help the shackle insulator to ensure the safe and reliable transmission of electricity. It is wise to understand the features each shackle insulator comes with to help meet application requirements. The following are the common features of the shackle insulator.

- Electrical insulation – the main function of the shackle insulator is to provide electrical insulation. This prevents the flow of electrical current from the conductor to the support structure.
- Corrosion resistance – the insulators are from materials that resist corrosion. This helps to maintain the integrity of the insulator in different environmental conditions.
- Versatility – the insulators come in various types and designs to suit different applications. This allows them to work in a wide range of electrical installations.
- Mechanical strength – the insulators have designs to withstand mechanical loads. Thisis including tension, compression or environmental conditions. They withstand stresses from factors such as wind, ice and temperature variations.
- High voltage performance – shackle insulators work in various voltage applications. The applications range from low voltage to extra high voltage systems.
- Weather resistance – they should be resistant to weather elements such as rain, snow and UV radiation. Materials like porcelain, glass and polymers have the ability to withstand these conditions.
- Ease of installation – the insulators have simple designs that help during installation. They have standardized dimensions and attachment points for efficient assembly.
Uses and functions of shackle insulators
The main use of the shackle insulator is to provide electrical insulation and mechanical support. They also have other roles in electrical installations providing support and reliability. Additionally, it is advisable to understand the functions before selecting for use. This is to ensure they meet the specific needs of your application. the following are the common uses and functions of the shackle insulator.

- Support – the shackle insulators work as support points for overhead conductors to suspend them at a safe distance. They hold the weight of the conductors and maintain their position to prevent sagging.
- Isolation – the insulators isolate the conductors from ground or other nearby conductive objects. This prevents unintended electrical paths that could cause short circuits.
- Voltage regulation – the insulators help regulate the voltage distribution along the length of the conductor. This helps to maintain the desired the separation between the conductor and support structure.
- Prevention of contamination flashovers – shackle insulators are able to resist the buildup of contaminants. Contaminants create conductive paths on the surface of insulators which leads to flashovers.
- Mechanical strength – they are also designed to withstand mechanical loads. They provide structural support to the conductor and ensure stability under challenging conditions.
- Electrical insulation – the insulators provide electrical insulation between the conductor and the support structure. The insulation prevents the flow of electrical current along the support structures.
Material used in the construction of shackle insulators
A shackle insulator is from materials that offer specific properties, durability and suitability. Selecting a specific material depends on several factors like voltage rating, mechanical strength and environmental conditions. Also, it is advisable to select the right material to ensure the reliability and performance of the insulator. Each of the material has its advantages and disadvantages depending on the intended application. The following are the common materials used in the construction of shackle insulators.

- Porcelain – this is the traditional and most used material for shackle insulators. It provides electrical insulation properties, high mechanical strength and resistance to weathering. They find use in medium to high voltage applications due to their reliability.
- Composite polymers – these include materials like silicone rubber or polyethylene. They offer lightweight construction, excellent weather resistance and resistance to erosion.
- Ceramics – this offers excellent performance in extreme conditions. This is especially where high temperatures are high.
- Glass – glass insulators provide electrical insulation and mechanical strength. They are also resistant to surface contamination. They work in areas with high pollution levels and high voltage transmission lines.
- Steel – steel shackles provide mechanical strength and durability in areas where high mechanical loads are frequent. They are mostly combined with insulating materials such as rubber or polymer to ensure electrical insulation.
Applications of shackle insulators
Shackle insulators find use in various applications like power lines and distribution networks. They work in a wide range of electrical installations providing support and insulation for power lines. The applications have different voltage rating o it is advisable to select the right shackle insulator. Additionally, it is wise to consult industry professionals whenever in doubt. The following are the common application areas for shackle insulators.

- Distribution lines – shackle insulators work in distribution lines to deliver electrical power from transmission lines to consumers. They work at service drops, pole lines and other distribution infrastructure
- Overhead transmission lines – they provide electrical insulation and support to the conductors on the electrical transmission lines. they suspend the conductors at a safe distance from support structures.
- Railway electrification – shackle insulators work in railway electrification systems. This is where overhead catenary wires serve to supply power to trains.
- Substations – they help insulate and support the conductors within the substation. This ensures the safe and efficient flow of electricity.
- Telecommunication lines – the insulators help maintain the integrity and reliability of telecommunication infrastructure.
- Industrial installations – shackle insulators work in various applications like manufacturing facilities or mining operations. They provide support and insulation for power distribution within industrial complexes. This helps to power machinery and equipment.
- Urban infrastructure – they work in overhead power distribution in densely populated areas. They help ensure the reliable supply of electricity to residential, commercial and distribution buildings.
- Renewable energy projects – the insulators work in wind farms and solar power installations. They support and insulate transmission lines carrying renewable energy from remote locations.
- Rural electrification – shackle insulators provide support and insulation for power lines that extend over long distance. This is especially in areas with scattered populations or challenging terrain.
Frequently asked questions
A shackle insulator is a component used to provide electrical insulation and mechanical support. It works by suspending the conductor at a safe distance from supporting structures.
Common features include electrical insulation, mechanical strength, weather resistance, corrosion resistance and ease of installation.
Shackle insulators find application in power lines, distribution networks, rural electrification, telecommunication lines and industrial installations. Others include railway electrification systems, renewable energy projects and urban infrastructure.
