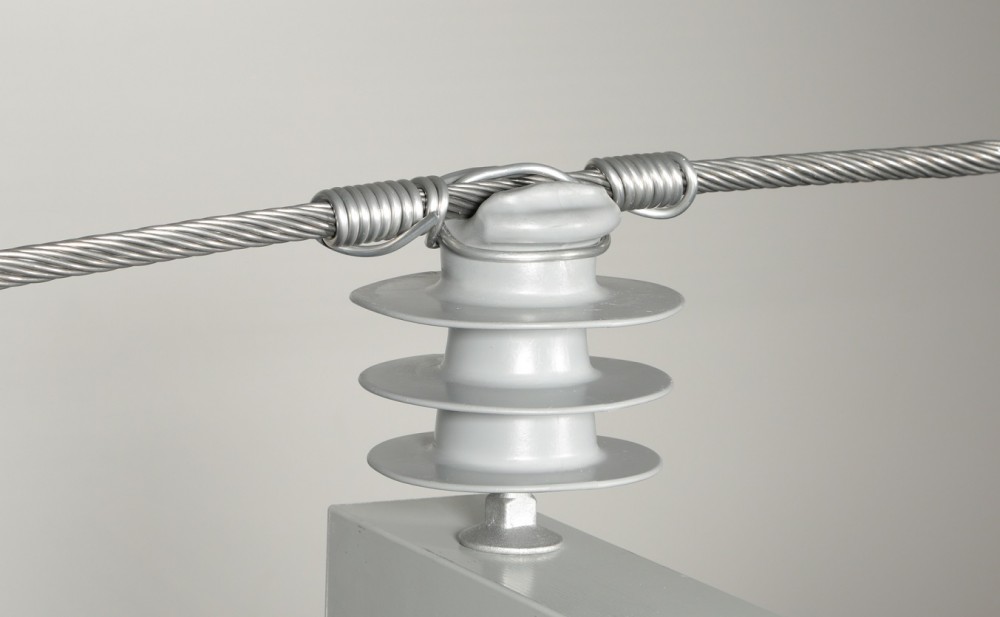

A line guard is also known as a line or conductor guard and is a device used to provide mechanical protection. It also helps maintain proper spacing between power transmission conductors. A line guard installs on overhead power lines and helps to prevent electrical faults and short circuits. The faults are from conductor contact, animal interference or adverse weather conditions. The line guard creates a physical barrier between adjacent conductors preventing them from direct contact with each other. They are from materials like fiberglass, plastic or composite materials. These materials offer high electrical insulation properties since they can withstand environmental factors. Line guards also help minimize the risk of power outages, electrical faults and damage to the power transmission infrastructure. They also play a crucial role in ensuring the reliability and safety of the power grid. This is by reducing the likelihood of short circuits and electrical arcing.
Components of line guard
Line guards are of different designs that have various components working together for proper functionality. The components work together to provide mechanical protection and spacing between the power transmission conductors. Discussed below are the main components of the line guards.
- Spacer/ insulator – this is the main component of the line guard which is responsible for maintaining the desired spacing between conductors. It is from insulating materials to provide electrical insulation and prevent conductor contact.
- Fasteners – fasteners or clamps help to secure the connection of the line guards to the power transmission conductor. They are from metal or other durable materials. They help to withstand the mechanical forces and environmental conditions.
- Mounting hardware – mounting hardware include bolts, nuts and other fastening elements. They help to attach the line guard to the power transmission tower or other structures.
- Reinforcement elements – line guards incorporate the reinforcement elements like ribs or rods depending on the design and application. They enhance the structural integrity of the line guard providing extra strength and stability.
- End caps – these caps prevent the ingress if moisture, dust or other contaminants that could affect its performance or longevity.
- UV protection – line guards may include additives or coatings that provide UV protection since they are prone to sunlight.
Types of line guards used on the overhead transmission lines
Types of line guards depend on the design, voltage level, conductor type, environmental conditions and other requirements of the transmission lines. Different types of line guards may work together to provide optimal protection and spacing between the power transmission conductors. Below are some common types of the line guards.

- Spiral line guards – these line guards consist of spiral-shaped or helical shaped elements that wraps around the conductor. They provide a physical barrier and maintain the desired spacing between the adjacent conductors. This prevents the animal interferences by creating a deterrent.
- Static line guards – static line guards provide fixed spacing between the conductors. They also maintain a constant separation between the conductors. This helps to prevent them from touching and causing electrical faults.
- Vibration dampers – vibration dampers are commonly used in conjunction with line guards to reduce the vibration caused by winds. This reduces the risk of conductor fatigue and improve longevity of the power transmission system.
- Dynamic line guards – these allow for limited movement between the conductors and work in areas prone to significant conductor motion. They also help to accommodate conductor sag and minimize the risk of conductor contact.
- Hoop line guards – hoop line guards are circular or semi-circular guards that encircle the conductors. This helps provide mechanical protection and maintain proper spacing between the conductors.
Application areas of line guards
The specific applications of line guards vary depending on design, requirements on the line, voltage levels and environmental conditions. Line guards can hence help in the following applications.

- Ice and debris mitigation – line guards help to mitigate the effects of debris or ice storms. They help prevent the formation of ice bridges between conductors. They also reduces the risk of conductor contact for potential damage.
- Conductor protection – the main purpose of the line guards is to protect power transmission conductors from physical damage and contact with each other. This reduces the risk of electrical faults, short circuits and power outages.
- Safety enhancement – line guards enhance safety by preventing conductor contact. They also minimize the risk of electrical hazards and electrical arcing.
- Line maintenance and repair – line guards facilitate the easier maintenance and repair of transmission lines. This is by providing a clear separation between conductors.
- Line clearance – line guards help maintain proper clearance between power transmission conductors and nearby vegetation or structures. They also contribute to the effective right-of-way management and ensure reliable power transmission.
Installation process of line guard
The installation process varies depending on the specific power transmission system, type of line guards used and any requirements present in the installation site. Some manufacturers in the market provide installation guidelines for the line guards. It is also advisable to consult with experienced professionals when in doubt. The following is a basic installation process for the line guards.
- Assess the power transmission system by checking factors like conductor type, voltage level, spacing requirements, environmental conditions and other guidelines to follow.
- Prepare the material and equipment to help during the installation. This includes fasteners, line guards, mounting hardware and other necessary materials.
- Conduct a safety briefing to ensure all personnel involved understand the potential hazards and necessary safety precautions.
- Access the transmission line using appropriate equipment like aerial platforms, cranes or specialized climbing gear depending on the height and location of the power transmission towers.
- Prepare the line guards by attaching the necessary clamps or fasteners and ensure they ae in proper working conditions.
- Install the line guards by carefully placing the power transmission conductors. They also maintain the required spacing and clearance.
- Secure and test the connections for stability and proper positioning. Test the guards and ensure they provide the desired protection and spacing between the conductors.
- Ensure the installation process if documented with details like location, date type of line guards used. Schedule regular maintenance and inspection schedules. This is to ensure the ongoing effectiveness and safety of the line guards.
Selecting the best line guards for your application
There are various manufacturers and suppliers of line guards in the market today. The selection process should have guidance of power transmission experts for the best choice. This is because they can provide valuable insights and guidance to help select the most suitable line guard for the application. The following are several factors before selecting line guards for your application.

- Consider the voltage level of the power transmission systems since different voltage levels have varying clearance requirements.
- The type and size of the conductor should also should be compatible with the conductor material and size. This is to ensure a proper fit and adequate protection.
- Consider the environmental conditions at the installation site including wind speed, ice or snow accumulation, temperature variations, UV exposure and presence of corrosive substances.
- Check the mechanical strength of the line guards to withstand the tension, compression and bending forces exerted on them.
- Consider the electrical insulation to prevent conductor-to-conductor contact and minimize the risk of electrical faults.
- Consider the installation and maintenance requirements of the line guards. They should have easy installation methods, compatibility with existing infrastructure. They also have accessibility for inspection and maintenance for cost effective operations.
- Ensure that the selected line guard follow relevant industry standards, regulations and safety guidelines.
- Consider the reputation of the manufacturer and their track record of production. Assess the manufacturer’s support services like technical assistance, warranty coverage and availability of spare parts.
Frequently asked questions
What are line guards as used on the power transmission lines?
Line guards are devices used on the transmission lines to provide mechanical protection. They also maintain proper spacing between conductors.
What are the main feature of the line guards?
Line guards have various components that ensure the smooth operability of the transmission lines. These include spacer or insulators, fasteners, mounting hardware, reinforcement elements, end caps and UV protection.
What are the advantages of using line guards?
Line guards offer several benefits that make them a popular chooice on the transmission industry. They include prevention of electrical faults, enhanced safety, protection against animal interferences, reduction of outage frequency and duration, mitigation of environmental factors and ease of maintenance.
What are the limitations of line guards?
They also have several limitations that hinder their adoption in the industry. They include high initial cost, limited protection against extreme weather events, maintenance, compatibility and installation challenges, risk of conductor fatigue and space limitations.
