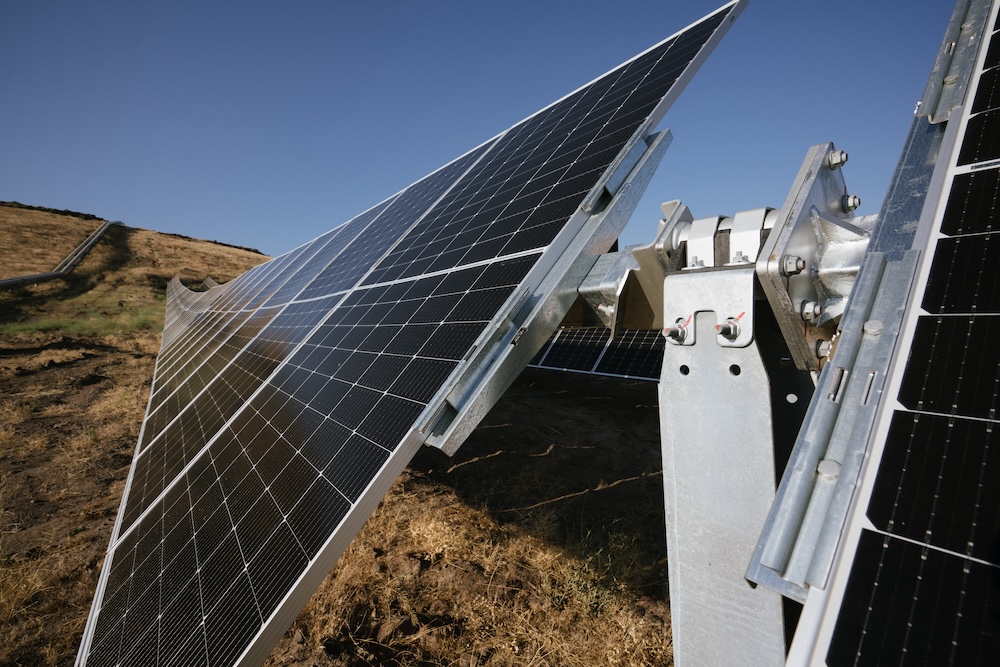

Gonvarri Solar Steel, a Spanish solar racking solutions manufacturer, bagged a deal to supply 396 MWac/472 MWdc of its hardware to a subsidiary of Spain’s Enhol Group for a project in Peru. The solar trackers will be crucial in the development of the largest photovoltaic (PV) complex in Peru and South America. The construction of the PV park is underway and will provide clean energy to over 230,000 households in northern Peru. These tracking systems will support over 740,000 modules at the solar park in La Joya, Southern Peru. The solar farm is expected to generate 1.2 TWh of electricity annually. Gonvarri Solar has been delivering its tracking systems for projects in the Peruvian market since 2014. It has also delivered a total of 500 MW of solar trackers, establishing itself as a key player in the energy sector. Using insulator ties in the projects ensures safety and system reliability.
Solar trackers will enhance energy efficiency by optimizing panel alignment with the sun for increased energy output by 15%. Using solar trackers improves project economics, which makes energy more competitive against fossil fuels. The use of the trackers also helps to reduce Peru’s reliance on fossil fuels and large-scale solar projects. This is crucial in diversifying its energy matrix. Solar panels generate high-voltage direct current electricity for energy production. Using insulator ties helps prevent unwanted electrical conduction between the tracker structure and the ground. This is crucial in reducing the risk of leakage currents that could degrade performance. Insulator ties help avoid ground faults, which can trigger system shutdowns or damage equipment.
Solar trackers and insulator ties in Peru’s solar farms
Insulator ties are mechanical and electrical connectors used to secure conductors to insulators on utility-scale solar tracker systems. They ensure electrical insulation between the conductor and metal hardware. They also ensure mechanical stability to prevent conductor movement due to wind, vibration, or temperature fluctuations. Insulator ties bridge the mechanical with the electrical to link steel structures with the sensitive power systems. They help Peru meet the clean energy targets by ensuring tracker systems deliver consistent power with minimal disruptions. Investing in high-quality insulator ties ensures the long-term success and resilience of its renewable infrastructure. Here are the roles of insulator ties in solar trackers and solar projects in Peru.

- Enhancing system reliability—solar trackers rotate to follow the sun’s movement, which means the attached cabling is under dynamic stress. Insulator ties secure cables and conductors along tracker arms, prevent wear and tear from friction, and reduce the risk of arcing.
- Supporting safety compliance—high-quality UV- and weather-resistant insulator ties withstand temperature extremes and solar irradiation.
- Efficient installation and maintenance—insulator ties help speed up conductor attachment processes and enable standardized, low-error installation practices. They also allow quick replacements to reduce downtime in case of faults.
- Reducing electrical losses and downtime—properly installed insulator ties ensure optimal conductor positioning. It reduces line losses due to poor alignment and also reduces the risk of hot spots.
Installation of the insulator tie for solar project development in Peru
Peru’s solar farms depend on using insulator ties to maximize energy generation while ensuring system safety and longevity. It therefore demands proper installation to prevent power losses, minimize degradation, and optimize performance in Peru’s high-irradiance and high-altitude environment. Insulator ties are crucial in electricity output as they prevent potential induced degradation, reduce leakage currents, and enhance bifacial panel performance. Use of insulator tie in solar farms boosts output by 2-5%, reduces corrosion risks, and lowers O&M costs. For instance, the Gonvarri solar steel’s 396 MW project used advanced polymer insulator ties integrated into their tracker design. They ensure compliance with Peru’s grid codes while maximizing return on investment for developers. The following are the key installation practices for optimal performance in Peru’s solar industry.
- Material selection—materials like fiberglass-reinforced polymers resist UV, humidity, and salt corrosion. Ceramic insulators serve in high-voltage applications or regions with extreme temperature swings.
- Proper mounting techniques—insulator tie installs between the solar module clamps and the torque tube to prevent electrical contact. They ensure no conductive path exists between panels and the tracker structure. Other techniques include rail-based systems and grounding continuity checks.
- Seismic and wind load considerations—Peru is prone to earthquakes and high winds. The insulator ties used must withstand mechanical stress without cracking and maintain isolation under movement.
