
A suspension insulator is a component used to support and insulate conductors. It supports and electrically insulates conductors. Suspension insulators contribute to the reliability and safety of the power system. It consists of stacked porcelain or glass discs joined by metal connections. The conductor then goes across the middle of the discs. These discs aid to create electrical insulation, preventing current from entering into the tower. Suspension insulators assist prevent power outages and lower the likelihood of electrical failures. They offer electrical insulation, mechanical support, and durability. Suspension insulators are from porcelain, glass, or composite. These materials are resistant to corrosion and weathering, ensuring their endurance.
Design of a suspension insulator
Suspension insulators originate from a variety of components and materials. These are specifically engineered to withstand mechanical and electrical loads. It also requires careful material selection to maintain the grid’s stability and endurance. The following is an overview of suspension insulator construction.
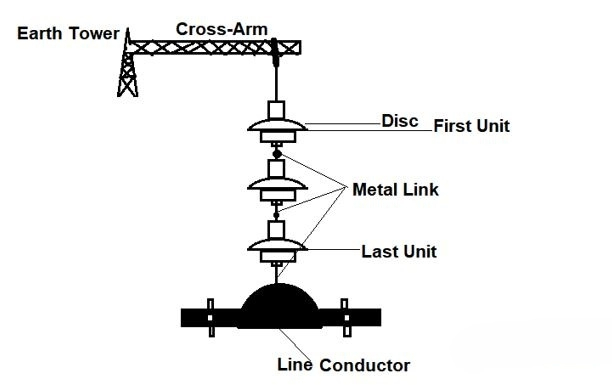
- Core material – the core of a suspension insulator consists of high-strength materials such as steel or iron. The core provides structural support and rigidity to the insulator.
- Insulating discs – these are the heart of the suspension insulator, consisting of porcelain or toughened glass. These materials provide both electrical insulation and mechanical strength. Porcelain discs manufacture by pressing and burning high-grade clay. They go through thermal tempering to increase their strength and resistance to fracture.
- Cementing compound – this serves to glue the discs together and hold them to the core. The cementing compound must be mechanically strong and resistant to environmental influences.
- Metal fittings – these connect the insulator discs to the core. They also include attachment points for the conductors. These fittings have designs to withstand mechanical loads. They also provide a secure connection between the insulator and the transmission line.
- End fittings – these function at both ends of the insulator to ease its attachment to the support structure. They contribute to a strong and sturdy connection while facilitating installation and maintenance.
- Surface treatment – Suspension insulators can have glaze or coatings. Glazing is the process of putting a layer of ceramic glaze to the surface to provide further protection against moisture and tracking. Coating improves the insulator’s resistance to pollutants and its electrical performance.
Working concept of a suspension insulator
A suspension insulator works to keep transmission lines intact and safe. The primary purpose of the suspension insulator is to provide insulation and support. They also feature designs to avoid current leakage and provide safe and dependable transmission of electricity. Also, it is important to guarantee that the insulators can endure all situations. The following is the fundamental functioning principle of a suspension insulator.

- Electrical insulation – the insulator keeps current from going through a tower or pole. This ensures the safe transfer of electricity.
- Dielectric characteristics – the insulators are from materials that have exceptional dielectric properties. This includes porcelain, toughened glass, and composite materials. The materials are very resistant to electrical conductivity, allowing them to obstruct the flow of current.
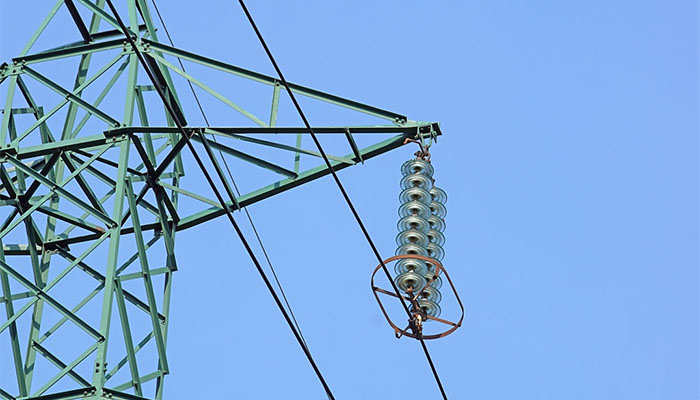
- Multiple disc design – the insulators have a multiple disc construction, with insulating discs stacked together and joined by metal fittings. The conductor travels through the middle of these discs, providing further insulation.
- Surface leakage path – the insulating discs form a continuous surface, preventing current from flowing to the support structure. Pollutant accumulation may form a conductive route for leakage current.
- Surface treatments – these help to reduce the impacts of pollutants and tracking. The treatments increase the insulator’s hydrophobic characteristics, which repel water and impurities. This reduces surface leakage on the application.
Choosing the optimal suspension insulator
Suspension insulators are available from a variety of manufacturers and sources. It may be difficult to decide who to buy from. There are several aspects to consider while choosing suspension insulators. Your suspension clamps should meet the specific needs of your power system. There are several criteria that contribute to selecting the finest, as stated below.

- Voltage rating – Determine the voltage rating required by the application to accommodate various voltage levels. The voltage rating may range from low to extremely high.
- Mechanical strength – the insulator should be able to tolerate stresses from a variety of environments.
- Pollution performance – check the pollution performance standards for the installation location. This guarantees that the insulators’ designs and coatings limit the accumulation of contaminants.
- Environmental conditions – check the environmental conditions in the installation area. This includes humidity, UV exposure, and corrosive atmospheres. Consider surface treatments to prevent pollution and tracking for consistent performance.
- Standard compliance – this entails ensuring that the insulators chosen adhere to all applicable industry standards and regulations. Standards help to ensure product quality, dependability, and safety.
- Supplier reputation – consider the supplier’s reputation and track record. They should have a track record of providing high-quality items and after-sales support.
- Cost considerations – compare the costs of various suspension insulators. Maintain a balance of performance, quality, and durability.
- Material type – examine the strength and corrosion resistance of the chosen material. Porcelain insulators provide both electrical insulation and durability. Glass insulators have superior mechanical strength and resistance to fracture.
Installation of suspension insulators
To ensure best operation, the installation process consists of several steps. To ensure the transmission line’s success and reliability, thorough planning is necessary. Additionally, it is advisable to get professional advice on the finest installation procedures. It is also recommended that you follow the manufacturer’s installation instructions. This is a step-by-step installation tutorial.

- Preparation – make sure the transmission channel is clear of impediments and that safety precautions are in place. Also, make sure the supporting structures are in good condition. Remove all barriers and debris from the installation area to ensure safe and efficient work.
- Insulator inspection – before installation, inspect each insulator to ensure that it is defect-free. They should also have the specified voltage rating.
- Insulator string assembly – this is by connecting individual insulator discs with metal fittings.
- Insulator positioning – determine the right spacing and location of the suspension insulator. Make careful you follow the design specifications. Maintain appropriate alignment with the conductors and support structures.
- Attachment to conductors – this entails connecting the suspension insulators to the conductors using appropriate hardware and fittings.
- Hoisting and installation – this entails lifting the suspension insulator using appropriate equipment and techniques. Place the insulators on the indicated crossarms, aligning them with the conductor path.
- Conductor attachment – this entails connecting the conductors to the insulator strings using conductor gear. Make that the conductors are appropriately tensioned and aligned with the insulators.
- Securement – secure the suspension insulators to the supporting structures. This happens through the employment of appropriate clamps, bolts, or other devices.
- Tensioning – this entails applying the appropriate tension to the conductors to ensure that the insulators are appropriately loaded and aligned.
- Inspection – conduct an inspection of the installed suspension insulators, conductors, and attachment hardware. This will ensure proper installation and alignment. Inspect for indicators of damage, flaws, or incorrect installation.
- Testing – this entails conducting electrical tests to ensure that the insulators match the electrical insulation specifications.
- Documentation – maintain complete documentation of the installation process. This includes the locations, tensioning values, and any adjustments done.
Maintenance procedures for suspension insulator
Regular maintenance of suspension insulators improves their longevity and reliability. It also aids in identifying and addressing any problems that could lead to failures and accidents. Furthermore, the frequency of maintenance depends on the various environmental circumstances. The following is a basic guide for maintaining and inspecting suspension insulators.

- Conduct regular visual inspections to detect any obvious damage, cracks, or contamination on the insulator surface. Check for indicators of wear that could jeopardize the insulator’s integrity.
- To prevent pollution and contamination, use appropriate cleaning chemicals and processes.
- Ensure that the creepage distance along the insulator’s surface is free of any tracks or deposits.
- Conduct periodic tests, such as high voltage tests, to determine insulation resistance and electrical performance.
- Ensure that the suspension insulator strings are in appropriate alignment with the conductors and supporting structures.
- Determine the mechanical stress on the suspension insulator while taking into account various aspects. This includes wind, ice, and conductor strain.
- Examine the insulators for evidence of corrosion on metal components. Consider adding a protective coating.
- Use thermal imaging tools to detect any anomalous temperature swings on the insulator’s surface.
- Keep detailed records of all inspections, tests, and maintenance operations conducted.
Frequently asked Questions
Suspension insulators provide electrical insulation between the live conductor and the support structure. This happens through the employment of several insulating discs comprised of materials with strong dielectric characteristics.
Suspension insulators have designs to endure varied environmental conditions. This includes pollutants, temperature changes, humidity, wind, and ice. Surface treatments help to resist impurities and preserve insulator performance in severe situations.
Consider the voltage rating, mechanical strength, ambient conditions, and material kind. Consider the severity of pollution, the installation requirements, regulatory compliance, and the reputation of the supplier.
