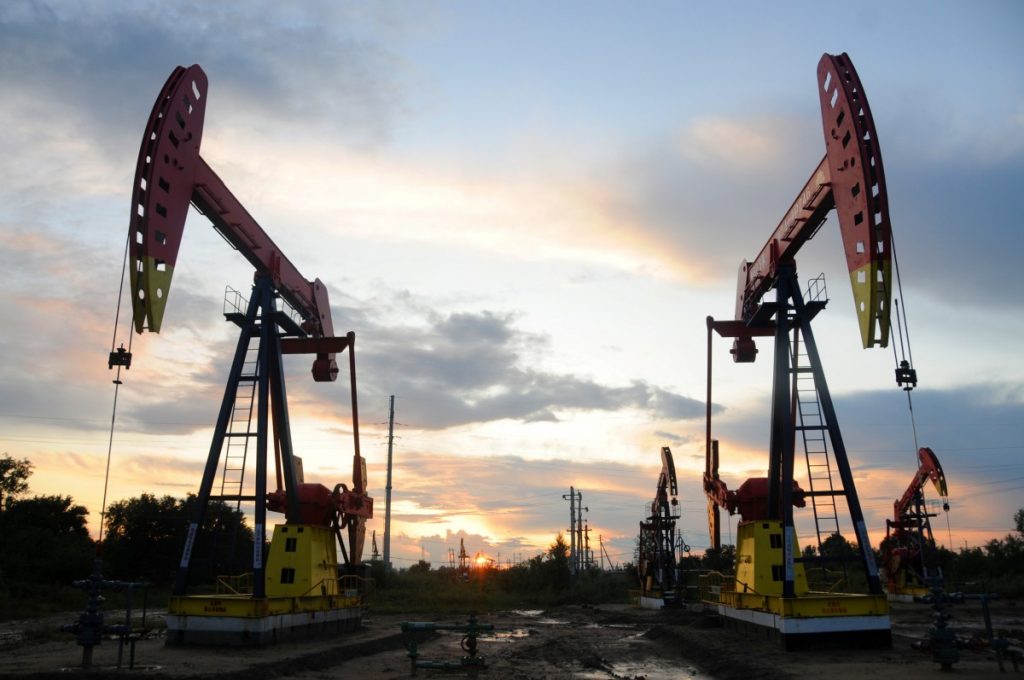

South America ranks as the second largest producer of hydrocarbons with significant reserves, right after the Middle East. The production of hydrocarbons, such as oil and gas, is essential for the energy transition and ensures energy security. Extra income from oil and gas exports could enhance economic development and increase government revenue. The production of hydrocarbons may improve energy security by providing a consistent and local source of energy. Key participants are Brazil, Colombia, Venezuela, and Peru. In energy transition objectives, hydrocarbon production can harmonize with renewable energy options such as solar and wind energy. Nonetheless, its manufacturing may result in environmental effects such as greenhouse gas emissions, pollution, and possible harm to ecosystems. Natural gas is a fossil fuel with lower carbon intensity than coal and can act as a transitional fuel during the energy shift. Helical anchors provide support to the foundations of transportation infrastructure like pipelines.
Helical anchors can serve in challenging environments where traditional foundations are difficult to install. They are easy to install and adjust, which makes them suitable for some challenging ground conditions. This helps reduce the environmental impacts of construction. Helical anchors secure foundations for drilling rigs, storage tanks, and other infrastructure. This helps ensure the structures remain stable in challenging soil conditions. Helical anchors are crucial for maintaining the stability, safety, and efficiency of hydrocarbon production infrastructure.
The role of hydrocarbons in South America’s energy security
Hydrocarbons provide a stable and consistent energy supply, which is crucial for industrial growth and urban development. Hydrocarbons also act as a backup source to address the intermittency nature of renewable energy. Natural gas exports strengthen regional energy ties and reduce dependency on imports. Hydrocarbon infrastructure like pipelines and refineries ensures the efficient energy distribution. Oil and gas companies are diversifying into clean energy technologies, including hydrogen production and carbon capture. Countries like Brazil are leading the efforts to integrate offshore wind, biofuels, and hydrogen production alongside hydrocarbons.
The importance of helical anchors in hydrocarbon production infrastructure
Helical anchors are essential components in the foundation systems of hydrocarbon production infrastructure. The anchors provide stable and durable foundations for oil and gas facilities. Helical anchors are adaptable to diverse terrains, which offers resistance to environmental and seismic challenges. The following is the importance of helical anchors in hydrocarbon production infrastructure.
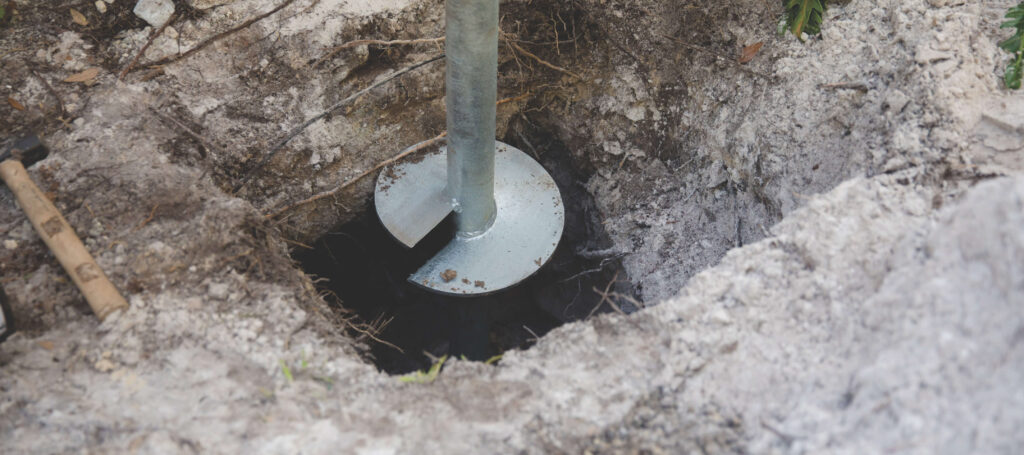

- Foundation stability—helical anchors are best for providing stability in challenging environments. They also provide resistance against soil movements.
- Durability – helical anchors are made from durable materials that ensure long-term performance in harsh environments.
- Versatility – helical anchors secure pipelines and prevent shifting due to soil movements. They also prevent tanks from tilting in regions with loose soil.
- Environmental considerations – the anchors are a low-impact foundation solution compared to traditional foundations. The anchors can install with minimal disturbance to the surrounding environment.
- Ease of installation—helical anchors can install quickly with minimal equipment and labor. This makes them cost-effective for remote or inaccessible locations.
- Seismic resilience—countries like Peru, Chile, and Ecuador experience frequent seismic activity. The anchors are able to withstand lateral and vertical forces. This provides stability to hydrocarbon infrastructure like drilling rigs, refineries, and storage tanks.
Effects of hydrocarbon extraction on climate change in South America.
Although hydrocarbon production has many advantages, it also leads to greenhouse gas emissions. This plays an important role in the climate change dynamics of South America. The environmental impacts of hydrocarbon production increase the region’s susceptibility to climate change. TTF is a world-class global provider of high quality overhead line hardware, transmission hardware, distribution hardware, conductors, insulators, cutout switches, anchoring and grounding products. Here are the effects of hydrocarbon extraction on climate change in South America.
- Greenhouse gas emissions—burning oil and natural gas adds to carbon dioxide emissions. This is emitted during extraction, refining, and export activities. Additionally, methane is generated from oil and gas facilities, contributing to an increased GHG footprint.
- Environmental degradation—oil exploration in nations such as Ecuador, Peru, and Brazil leads to deforestation, which diminishes the ability to sequester carbon. Oil spills occurring during exploration and transportation pollute ecosystems, impairing their capacity to absorb carbon.
- Climate vulnerability—deforestation linked to hydrocarbons and rising temperatures accelerates ecosystem degradation. This is especially true in the Amazon rainforest and the glaciers of the Andes. This diminishes their capacity to function as carbon sinks in the area.
- Economic and social consequences—emissions from hydrocarbon extraction and processing heighten respiratory and cardiovascular illnesses.
- Prolonged energy transition—excessive reliance on hydrocarbons could postpone South America’s shift to renewable energy. This could result in elevated emissions for many years.
