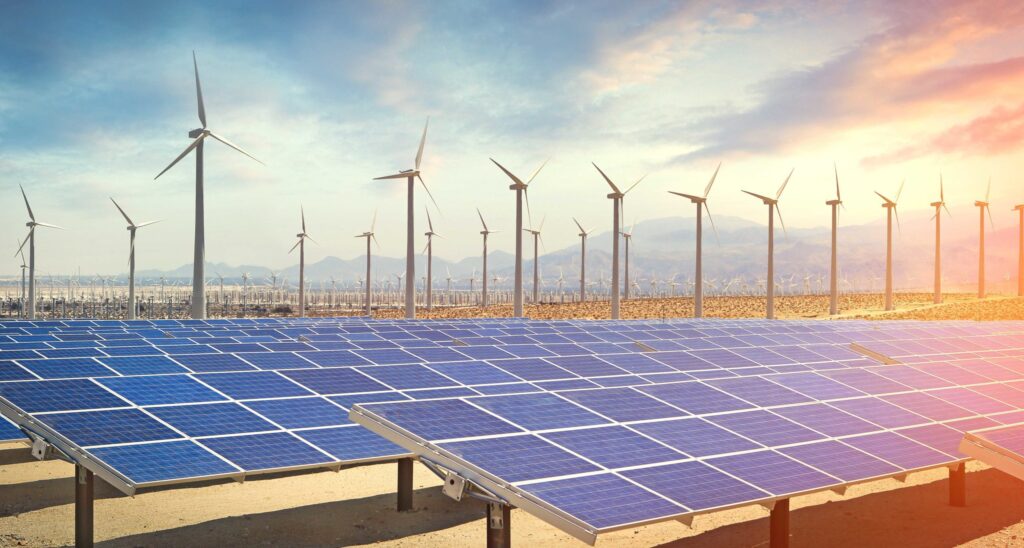

Renewable energy sources provide electricity to the South American national grid, reducing reliance on fossil fuels and greenhouse emissions. Distributed energy generation (DEG) offers decentralized, localized solutions to meet the growing energy demands in South America. Distributed energy generation reduces transmission losses and enhances energy security. DEG is a small-scale, decentralized energy production system. These includes rooftop solar panels, wind turbines, biomass generators, and micro-hydro plants. The systems operate independently or in conjunction with the main grid. For instance, Chile’s Atacama Desert receives the highest solar radiation, making it an ideal location for DEG. A hybrid solar-diesel microgrid project in the Toconce village is an example of DEG, powering homes and businesses. Guy wires anchor power lines to the ground, providing stability against environmental forces.
Distributed energy generation systems, such as rooftop solar or small wind turbines, connect to the local distribution grid. The distribution grids depend on power lines supported by towers that use guy wires for stability. Guy wires connect different renewable energy sources such as wind and solar. This helps maintain the stability of the infrastructure to allow for efficient energy production and distribution. Guy wires enhance the safety and reliability of the energy system to reduce the risk of power outages and accidents. They also provide extra support and tension to power lines and other infrastructure to ensure the safety of the energy system. Guy wires are also designed to withstand harsh environmental conditions.
Functions of guy wires in distributed energy generation in South America
Guy wires are tensioned cables that provide structural support to towers, poles, and other installations used in DEG systems. They ensure the stability, safety, and longevity of the distributed energy generation systems. The following are the functions of DEG projects in South America.

- Structural stability—guy wires stabilize wind turbines, communication towers, and poles for solar panels. They enable the installation of structures on slopes by distributing loads evenly.
- Wind resistance—the stay wires prevent towers and turbines from toppling by counteracting lateral forces.
- Earthquake resilience—guy wires provide extra support to DEG infrastructure. This reduces the risk of structural failure during earthquakes.
- Cost-effective design—guyed structures reduce upfront costs for DEG installations in remote communities.
- Maintenance and safety—stay wires prevent structures from swaying excessively, which can cause wear and tear.
Applications of guy wires in South American DEG projects
Guy wires provide stability, enhance safety, and enable cost-effective installations in diverse and challenging environments. Incorporating robust and sustainable guy wire designs ensures the reliability and resilience of energy systems powering communities. The following are the application areas of guy wires in DEG systems.
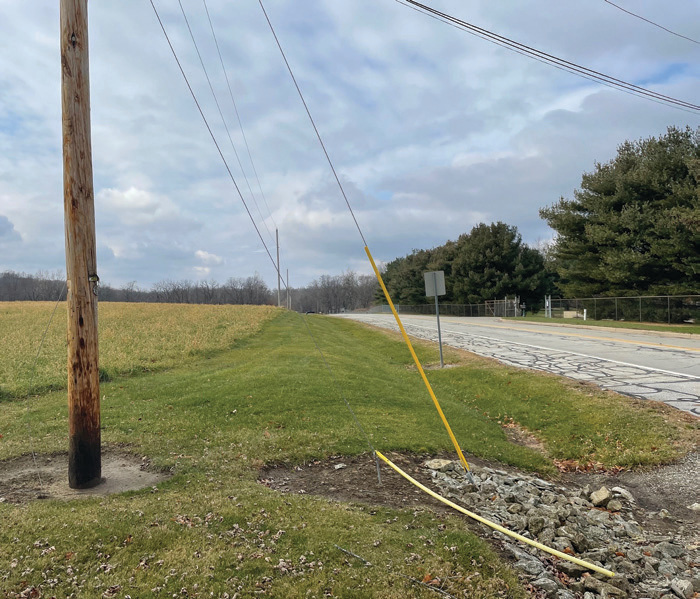

- Wind energy in Patagonia—Patagonia has wind resources that have made it a hub for wind energy development. Guy wires stabilize the wind turbines in areas prone to high-speed winds to ensure consistent energy generation.
- Off-grid systems in the Amazon—the Amazon Basin has solar energy systems that involve poles for mounting panels. Guy wires help secure these structures in various geographical locations.
- Hybrid microgrids in rural areas—DEG systems in the Andean communities combine solar, wind, and micro-hydro power. Guy wires help to anchor tall structures like turbine masts exposed to weather conditions.
Impacts of distributed energy generation in South America’s energy sector
Distributed energy generation is a technology transforming South America’s energy sector. This brings economic, social, and environmental benefits while presenting new challenges. TTF is a world-class global provider of high quality overhead line hardware, transmission hardware, distribution hardware, conductors, insulators, cutout switches, anchoring and grounding products. Our products also include construction and switching products, tools, insulators, arresters, pole line hardware, and cable accessories. Discussed below are the impacts of distributed energy generation in South America.
- Economic impacts – DEG reduces the need for long-distance transmission infrastructure to reduce energy losses. They also lead to the creation of jobs and lead to energy independence, improving energy security and boosting local economies.
- Social impacts – DEG provides reliable electricity to rural and off-grid communities and improves living standards. Solar microgrids in Colombia have transformed indigenous Wayuu communities.
- Environmental impacts—the systems reduce carbon emissions by replacing fossil fuels with renewable energy sources. They also reduce the land disruption and preserve natural landscapes. Guy wires provide stability and reliabilty for the DEGs to ensure safety in the environment.
- Technological impacts – DEG brings innovation in renewable energy technologies, battery storage, and grid management. For instance, Uruguay is piloting blockchain-based energy trading systems for DEG projects.
- Policy and regulatory impacts – South American governments are adopting more decentralized and renewable-friendly energy policies. DEGs have opened opportunities for private investments and public-private partnerships in the energy sector.
