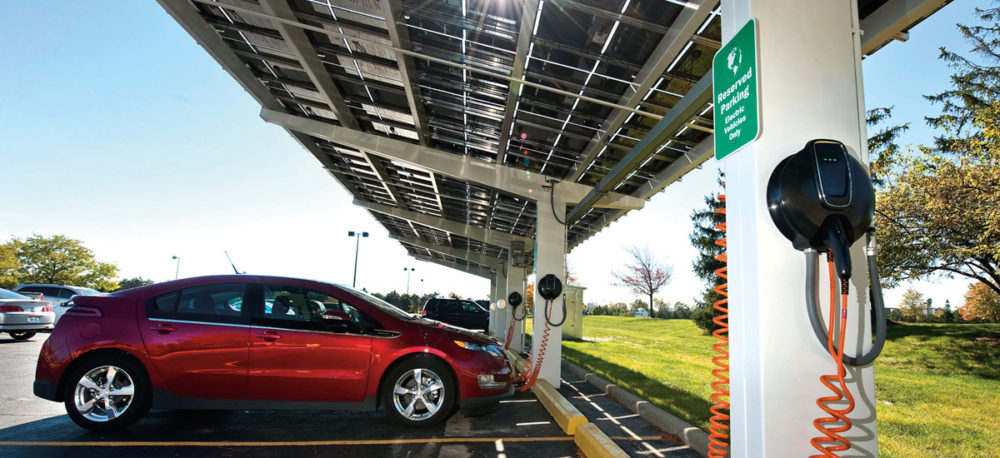

As new technologies are being continuously developed, electric vehicles are playing a key role in transforming South America’s energy sector. Historically, electric vehicles have relied on sustainable energy sources to operate the vehicles. This helps decrease dependence on fossil fuels and lower the release of greenhouse gases. Electric cars help with sustainability efforts, decarbonization, and achieving energy independence. Although the rate of electric vehicle adoption is gradual, there are alternative methods to speed up the adoption process. This involves transforming gas-powered vehicles into electric cars, a more affordable option compared to purchasing new EVs. Additional techniques involve employing internal combustion engines (ICEs) that are powered by ethanol. Furthermore, formed wires function in making batteries for storing energy. This is an important factor in the creation of electric vehicle infrastructure.
Formed wires assist in carrying power, signals, and data across the vehicle’s systems. They make sure that many electrical components work correctly. They also operate in charging systems and solutions for energy management. Foreign investments are attracted to South America due to the market potential, government policies, and the region’s increasing focus on sustainability. The prevalence of hydropower in Brazil, Uruguay, and Paraguay boosts the electric vehicle industry. Other companies focus on utilizing internal combustion engines powered by ethanol for the electric vehicle market. Dive into our analysis on how biofuels aid the electric vehicle industry and the importance of formed wire in the infrastructure.
Contribution of formed wires in the establishment of electric vehicle infrastructure
The function of the formed wire goes beyond the car and reaches into the wider EV network. They operate in charging systems and grid integration to guarantee sustainability. Formed wire plays a role in power distribution, data communication, safety, and thermal management. In the ongoing advancements in technology, the wires will guarantee dependable, effective, and secure energy transmission. Utilizing strong and flexible formed wires will improve the outlook of electric mobility. The following are the functions of formed wires in electric vehicle infrastructure.

- Battery management systems (BMS) guarantee the safe and efficient operation of the battery. Formed wires link the BMS with each battery cell, temperature sensors, and voltage monitors. These links enable the control of charging, discharging, and thermal regulation.
- Charging infrastructure and connectors use formed wires to link EVs with charging stations. This permits the transfer of electricity from the grid to the battery of the vehicle. Specialized formed wires and cables can manage the transfer of large quantities of electrical power.
- Thermal control systems – Electric vehicles rely on thermal management systems to control the battery temperature. Temperature sensors, pumps, fans, and heating or cooling elements are linked together by formed wires.
- Smart grid and vehicle-to-grid applications involve electric vehicles returning energy to the grid at times of high demand. This contributes to grid stabilization and the incorporation of renewable energy sources. Formed wires allow for communication and power transfer in intelligent charging systems that optimize the timing and amount of charging for an electric vehicle.
The ways in which biofuels back electric cars in South America
Biofuels can serve as a complement to electric vehicle infrastructure in many ways. Although EVs rely on electricity, they can use biofuel for hybrid and range-extended vehicles. Combining biofuels with electric vehicles can establish a transportation system that is both sustainable and adaptable. This is how biofuels in South America assist electric vehicles.
- Hybrid and range-extended electric vehicles use a small internal combustion engine to produce electricity when the battery is low. Biofuels such as ethanol, biodiesel, or renewable diesel can fuel the engine. This helps decrease the dependence on fossil fuels.
- Biofuels can fuel generators for generating electricity at charging stations for electric vehicles. Biofuels have the potential to decrease the carbon emissions from electricity production in nations reliant on fossil fuels.
- Decreasing carbon emissions in the manufacturing and recycling of batteries – the production and recycling of electric vehicle (EV) batteries need a lot of energy. Utilizing biofuels in manufacturing plants can decrease carbon emissions.
- Ethanol-powered engines can work alongside electric propulsion for long-distance transportation in heavy-duty and commercial vehicles. Flexible-fuel engines that use a combination of electricity and biofuels can be installed in heavy-duty vehicles.
- Biofuels can serve in fuel cells to convert ethanol into hydrogen using reforming processes. This hydrogen can serve in fuel cells to power electric vehicles.
