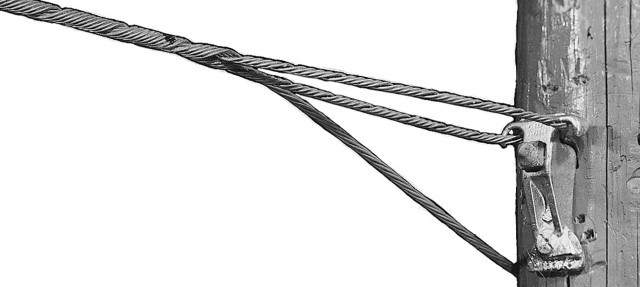
A false dead end is a specific configuration where the conductors terminate or anchor at a structure. It occurs at an intermediate structure where conductors anchor for mechanical reasons. A false dead end helps to handle mechanical stresses such as tension and sag. It creates an illusion that the line does not continue beyond that point when it actually does. It maintains the electrical continuity of the transmission line to extend beyond the point. The primary purpose of the false dead end is to provide extra mechanical support. Its design offers flexibility in the design and construction of transmission lines. They also allow operators to divide the line into manageable sections without disrupting the flow. They work at intermediate points along the line, terrain challenges and load distribution. A false dead end helps reduce the risk of conductor failure due to excessive sag.
Challenges and issues facing use of a false dead end
False dead ends offer several benefits to overhead transmission lines. They also come with a set of challenges and issues. These challenges relate to mechanical complexity, maintenance and environmental factors. There are various ways to address these challenges such as regular inspections, use of durable materials and training. The following are the various challenges and issues facing use of false dead ends.

- Mechanical complexity – creating false dead ends requires precise calculations. This is ensuring that mechanical stresses are well managed. The support structures must be robust enough to handle the added mechanical load.
- Maintenance and inspection – false dead ends install in challenging terrain or at high elevations. This makes them difficult to access for regular inspections and maintenance. Maintenance and inspection of false dead ends need specialized equipment and trained personnel.
- Environmental factors – harsh weather conditions can impact the mechanical stability of false dead ends. These conditions include high winds, ice accumulation and temperature fluctuations. Exposure to the elements can lead to corrosion and wear of the components.
- Cost implications – the initial cost of installing false dead ends is higher due to the need for more robust structures. The long term maintenance costs can also be significant in remote or difficult-to-access areas.
- Electrical considerations – false dead ends ensure electrical continuity. This is while providing mechanical support can be complex. The dead ends can introduce points of vulnerability where the faults might occur.
- Load distribution – improperly designed false dead ends can lead to uneven load distribution along the transmission line. They must be able to accommodate these varying loads without compromising the integrity of the line.
Cost comparisons and considerations for false dead end
There are different costs and prices for false dead ends in the market. These depend on various factors like material and designs. The dead ends have the ability to provide enhanced mechanical support and improve the reliability of the transmission system. Also, it is advisable to ask for quotations from different manufacturers for comparisons. The following are the factors that influence the prices of false dead ends.

- Material costs – the initial cost of materials for false dead ends can be higher die to the need for robust structures. These structures are capable of handling increased mechanical loads.
- Labor costs – installation of false dead ends requires more specialized labor and equipment. This leads to higher labor costs compared to standard intermediate supports.
- Design and engineering – the design phase may incur higher costs due to the need for precise engineering calculations. Standardize components and designs where possible to reduce cost related with custom fabrication.
- Maintenance costs – these may arise from routine maintenance, repairs and replacements, and accessibility. Components may need repair due to wear and tear or corrosion. The cost of repairs and replacements can be higher than for simpler configurations.
- Long term costs – designed and maintained false dead ends can improve the durability of the transmission system. The extended lifespan and improved stability can increase these initial expenses.
- Innovative materials – consider the use of innovative materials such as composite materials or advanced coatings. They can provide enhanced durability at a lower cost.
Comparative analysis for the dead ends
Conducting a comparative analysis for false dead ends involves considering costs, mechanical support, reliability and environmental impact. False dead ends offer a balance between mechanical support and electrical continuity. This makes them ideal for challenging environments and long spans. Consider the specific requirements of the transmission line including span length and mechanical loads. Additionally, false dead ends are often preferred in scenarios where enhanced mechanical support and uninterrupted electrical continuity are critical. The following are the factors to consider when conducting a comparative analysis.
- Cost comparison – consider the initial installation cost, maintenance cost, and long-term costs. Check the need for specialized anchoring hardware and maintenance needs. This is to enhance improved reliability and reduce the risk of conductor failure.
- Mechanical support and stability – false dead ends should provide strong anchoring points to handle high mechanical loads, sag and, tension. Also consider the stability of the dead ends in challenging environments.
- Reliability and electrical continuity – false dead ends should have high reliability as they maintain electrical continuity while providing mechanical support. They should also ensure uninterrupted electrical continuity for maintaining consistent power supply.
- Environmental impact – the dead ends work in moderate to high initial impact due to robust construction needs. Lower maintenance and repairs may reduce their environmental impact. They should also have high resilience to handle weather conditions and environmental stresses.
Supplier or vendor information for false dead ends
There are various suppliers, vendors and manufacturers for false dead ends in the market. There are various factors that come into play when selecting the false dead ends. Considering these factors help to ensure you get high-quality products and reliable service. Additionally, considering these factors helps ensure selection of durable and reliable products. The following are the factors to consider when selecting the right false dead end supplier.

- Product quality and compliance – ensure the false dead ends meet industry standards such as IEEE, ANSI and IEC among others. Check for materials that are resistant to corrosion, UV exposure and other environmental factors. High quality materials ensure the longevity and performance of the dead ends.
- Supplier reputation and experience – select suppliers with a proven track record in the industry. They should provide reliable products and services. Check customer reviews and ask for references.
- Cost and value – compare prices from different suppliers to ensure competitive pricing while balancing with quality. Consider the total cost of ownership including initial purchase price, installation costs and long-term maintenance.
- Logistics and delivery – assess the supplier’s logistics capabilities including shipping methods, delivery times and ability to handle large orders. Ensure the supplier can deliver to your location and handle specific logistical challenges.
- Sustainability – check if the supplier follows sustainable manufacturing practices and environmental regulations. Consider the environmental impact of the product throughout its lifecycle.
- Product range and availability – ensure the supplier provides a wide range of transmission line hardware and accessories. Check the availability of products and lead times of the suppliers.
- Engineering and technical support – look for suppliers who offer custom design services. This helps to meet specific project requirements. Check their availability of engineering support for installation, troubleshooting and maintenance.
- Support and service – check the quality of customer service including responsiveness, problem resolution and after-sales support. Training programs also ensure proper installation and maintenance of the false dead ends.
Troubleshooting
Troubleshooting false dead ends involves identifying and resolving issues related to their mechanical and electrical performance. It involves a combination of regular inspections, precise mechanical and electrical testing. The following is a guide to troubleshooting false dead ends.

- Initial inspection – check for physical damage like cracks, corrosion, wear or deformation of the dead ends. Ensure all connections are tight and secure without signs of arcing. Verify the conductors are at correct sag and tension as per design specifications.
- Mechanical issues – use tension measuring tools to check if the conductors are well tensioned. Check the integrity of the supporting structures. Look for any leaning, foundation issues, or structural damage. Inspect all hardware including clamps, insulators and anchoring points.
- Electrical issues – use proper equipment to check for continuity across the false dead ends. Measure the resistance across the connections. Inspect insulators for cracks, ships or contamination and clean or replace them as needed. Look for signs of arcing or corona discharge.
- Environmental and operational factors – check for issues related to thermal expansion and contraction. Ensure the dead end can hold the movement. Inspect for signs of vibration-induced fatigue such as wear patterns or breakage.
- Advanced diagnostics – use thermal imaging to detect hotspots and potential points of failure in the electrical connections. Employ ultrasound testing to detect corona discharge or arcing.
Frequently asked questions
A false dead end is a configuration where conductors are mechanically anchored to a structure to handle tension and sag. It maintains the electrical continuity allowing the line to continue beyond that point.
False dead ends provide enhanced mechanical support, improve stability in challenging terrains and maintain electrical continuity.
Consider initial material and labor costs, ongoing maintenance expenses and the total cost of ownership. Consider the potential for reduced long-term operational costs due to increased reliability.
