
There are some factors contributing to the growth of the electric vehicle (EV) market in South America. The sector varies by the region’s energy infrastructure, economic conditions, and environmental regulations. The region’s vast renewable energy resources lay a solid platform for the growth of the EV market. South America has the potential to become a key role in the electric vehicle revolution as it progresses. This helps to a more sustainable and resilient energy future. The combination of EVs and renewable energy sources offers a way to a cleaner economy. Additionally, it may aid with the electrification of the transportation industry. This is to address the growing need for efficient and sustainable public transportation.
Electric vehicle network in South America
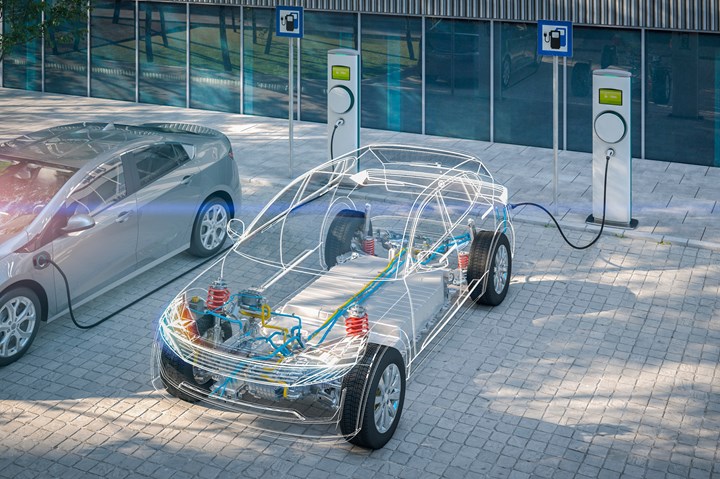
Chinese cars lead the electric vehicle market in South America, accounting for 51% of total EV sales. For example, most South American electric buses are made in China. This affects South America’s transportation infrastructure, particularly in densely populated areas. Furthermore, as the business grows, there will be a greater demand for extra EV infrastructure. This includes charging infrastructure and grid upgrading. The electric car infrastructure contributes to a cleaner, more resilient energy future. Power line hardware comprises components that make maintenance easier in hostile situations. They help to improve the efficiency and safety of overhead transmission lines.
Electric vehicle infrastructure in the energy sector
Electric vehicles help to address the growing need for cleaner and more environmental friendly ways of transportation. Some of these vehicles have innovative features and good build quality, making them affordable. South America’s EV infrastructure requires charging networks, grid capacity, renewable energy integration, and regional collaboration. Countries like as Brazil, Chile, and Colombia have begun to establish charging stations. Also, grid integration is necessary to handle the increased energy demand caused by EV charging. The following is some of South America’s electric car infrastructure.
- Charging stations – this can be public, private, or home charging—aiming to meet the demand for EV adoption. The lack of charging infrastructure is a barrier to EV adoption in the region. For instance, in Brazil, there are several hundred public charging stations in major urban areas.
- Grid capacity – the existing power grids in South America vary by capacity, reliability, and their ability to support an increase in electricity demand. Countries like Brazil, Argentina, and Chile are dependent on specific sources like hydropower. They would therefore need upgrades to handle increased demands and support EV adoption.
- Smart grids and load management – use of smart grid technologies also helps manage the extra load from EV charging. Smart grids can balance supply and demand, integrate renewable energy sources, and optimize charging times to avoid overloading.
- Renewable energy integration – integrating the resources with the EV infrastructure is essential for maximizing the environmental benefits for electric vehicles.
- Policy and regulatory framework – South American countries have to put in place policies that support electric vehicle adoption. This may include incentives for infrastructure development, standardization, and interoperability.
How Electric Vehicles Drive the Economic Transition in South America
Electric vehicles have the potential to cause big financial disruptions in South America by 2024. The adoption of electric vehicles has the potential to alter industries, create jobs, and improve energy sustainability. It also helps to reduce dependence on fossil fuels and imported energy. The adoption of electric vehicles might position the region as a global leader in the transition to sustainable transportation. Here’s how EVs are influencing economic transformation in South America.

- Stimulating new industries – the rise of electric vehicles spurs the development of new industries in the region. There is new development in sectors related to battery production, charging infrastructure, and EV manufacturing. EV adoption also triggers battery production and lithium mining to enhance energy storage.
- Reducing dependence on imported fossil fuels – the shift to electric vehicles is mainly powered by increased renewable energy. This reduces the region’s dependence on fossil fuels, leading to economic and strategic benefits.
- Job creation and workforce transformation – the transition to electric vehicles creates new jobs in various sectors. It brings opportunities in battery manufacturing, electrical engineering, and the construction and maintenance of charging infrastructure.
- Environmental and health benefits leading to economic gains – EV adoption has environmental and health benefits. This includes the reduction in air pollution and climate change mitigation.
