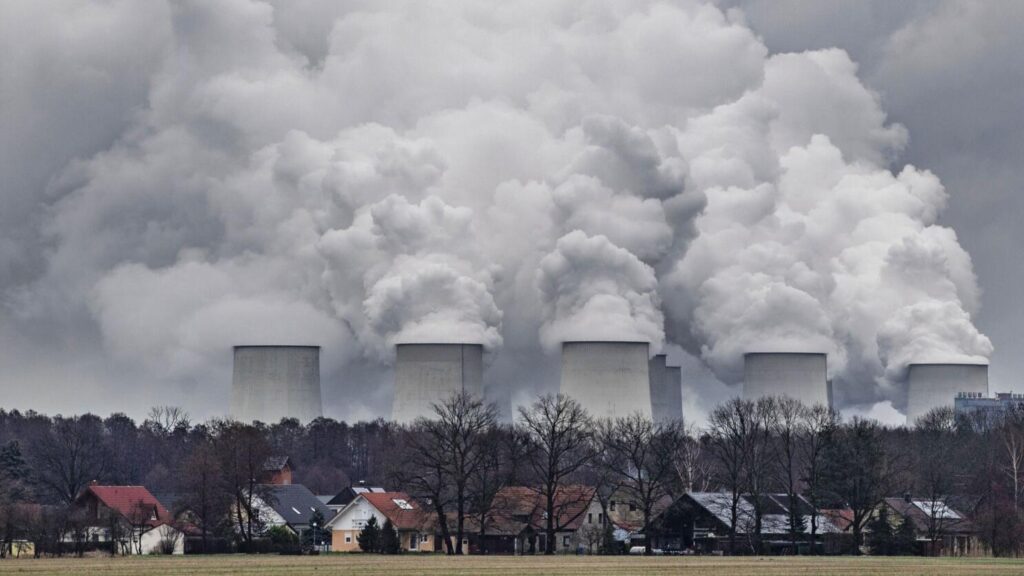

As the world transitions to a clean energy future, some South American countries still rely on coal generation. For instance, Colombia is one of the world’s top coal exporters, given its vast coal reserves. Most South American countries, however, are actively working towards phasing out coal-fired power plants. Countries like Chile and Panama have set targets for coal phase-out. This is by turning towards renewable energy resources like solar, wind, and hydropower. The region has abundant renewable resources that are cost-competitive and have no carbon footprint. By phasing out coal, South America can reduce greenhouse gas emissions, improve air quality, and create new economic opportunities in the renewable energy sector. A cutout fuse protects the coal generation power plants from electrical damage caused by overcurrent or short circuits.
A cutout fuse is designed to provide visual sign of its operation in coal plants. When the fuse blows, the fuse holder drops open to make it easy for maintenance personnel to identify the fault and replace it. In the case of a short circuit, the fuse element melts to break the electrical circuit. This prevents damage to the equipment connected to the circuit, such as transformers, motors, and generators. A cutout fuse is a reliable and cost-effective way of protecting the electrical equipment in coal generation plants. This article looks at the phasing-out of the coal process in South America and cleaner energy options. It also highlights the role of a cutout fuse in coal generation power plants.
Measures put in place to phase out coal generation in South America
Many South American countries have put in place several measures to phase out coal-fired power generation. This is to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and adapt to the use of cleaner energy resources. The measures put in place to phase out coal generation in South America include carbon pricing mechanisms, renewable energy expansion, and transition programs. They also include grid modernization, energy storage, public-private collaborations, international financing, and partnerships. The success of these measures will depend on sustained political will, stakeholder engagement, and financial support. Following these measures faces challenges such as employment impact, political resistance, infrastructure barriers, financial challenges, social acceptance, and environmental trade-offs. Each country in South America must adapt its strategies to local circumstances to ensure an effective energy transition.

A cutout fuse plays an important role in coal-generating power plants.
A cutout fuse plays a crucial role in protecting electrical distribution systems in South America. Coal plants in South America operate within a mix of older and newer infrastructure. Cutout fuses serve in regions where grid stability can be challenging due to aging equipment. The following are the common roles of a cutout fuse in coal generation power plants.
- Overcurrent protection – a cutout fuse protects transformers and other critical infrastructure from damage caused by overcurrent.
- System reliability and safety – the cutout fuse ensures the rest of the system remains operational and safe.
- Maintenance ease – the devices allow for mutual isolation of electrical equipment during maintenance. This allows operators to replace the fuse link for planned work to improve plant reliability.
- Coordination with other protection systems—cutout fuses help in localized protection while breakers and relays handle broader system coordination.
Challenges facing coal-fired power plants phase out in South America
Phasing out coal-fired power plants in South America faces several challenges. Countries like Chile and Panama are leading the way by setting clear goals, policies, and financial mechanisms. Coal phase-out can be a pathway to cleaner and more sustainable energy systems. To address the challenges, the region can ensure an fair and successful transition to clean energy. Discussed below are the common challenges in phasing out coal-fired power plants in South America.
- Energy security – the transition towards renewable energy needs significant investments in grid infrastructure to handle its intermittent nature.
- Infrastructure development – expanding renewable energy needs upgrading transmission and distribution networks. Delays can hinder the pace of coal phaseouts and renewable energy integration.
- Economic dependence – many countries in the region depend on coal for local economies, which creates resistance to closures.
- Regulatory frameworks and financial hurdles – implementing policies to promote renewable energy and discouraging coal can be politically and economically challenging.
- Social and political resistance – resistance from coal-dependent communities and lobbying by coal industries—can slow the adoption of phase-out strategies.
