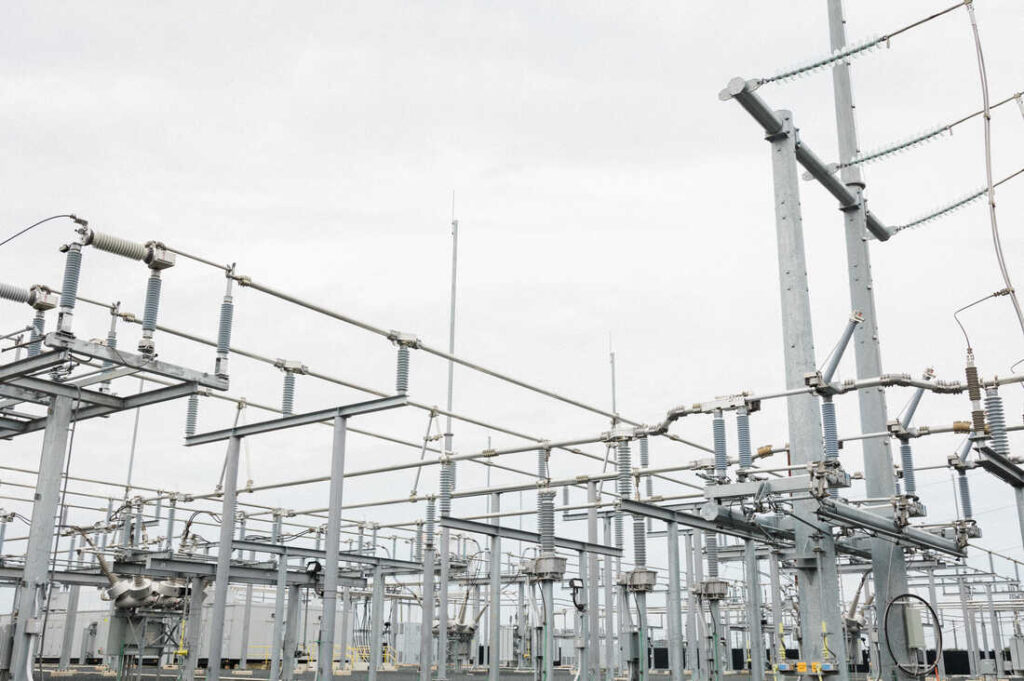

Given the abundant renewable energy options and extensive oil and gas reserves, Argentina has the potential to stabilize its grid infrastructure. The infrastructure is constructed around a varied energy framework that includes natural gas, hydroelectric power, nuclear energy, renewables, and oil extraction. Argentina’s electrical grid infrastructure encounters issues such as deteriorating facilities, uneven electricity access across regions, and financial strain from subsidies on the national budget. The country seeks to diversify its energy sources, enhance and extend the grid, draw in foreign investment, and progress toward energy independence while managing imports. A balanced grid may assist in lowering energy expenses, enhancing energy security, and decreasing dependency on imported fossil fuels. Updating the grid infrastructure establishes the nation as a possible major contender in energy exports. It might also assist in achieving climate objectives and boost the adoption of smart technologies. C-span clamps provide reliable, sturdy, and effective support for conductors on overhead power lines.
C-SPAN clamps are crucial for maintaining the physical integrity of the grid. They are crucial as Argentina expands transmission and distribution networks to accommodate renewables, rural electrification, and growing demand. C-SPAN clamps secure spacer dampers that maintain the proper separation between bundled conductors. They prevent the conductors from clashing due to wind or electromagnetic forces. By doing so, they ensure mechanical stability, reduce wear, and optimize power flow in the transmission network.
Argentina’s grid infrastructure modernization using C-Span clamps
C-span clamps are hardware fittings used to suspend or secure conductors. They also distribute mechanical loads evenly and prevent conductor slippage or abrasion. It is designed to grip cables without damaging them. They provide flexibility and support to Argentina’s grid infrastructure. The clamps play a crucial role in upgrading and expanding Argentina’s electric grid. They also support the integration of renewable energy to ensure stability and reliability. Here are the roles of C-Span clamps in Argentina’s grid modernization.

- Grid expansion in remote areas—the expansion into rural regions demands strong, reliable support structures for overhead lines. C-SPAN clamps allow flexibility in difficult terrains and help reduce line sag and vibration.
- Integrating renewable energy projects—new transmission lines carry clean energy to urban centers. C-SPAN clamps anchor high-voltage conductors from remote projects. They also help absorb tension in lines affected by strong winds and temperature shifts. The clamps support dynamic load balancing to keep conductors aligned and stable.
- Improving safety and grid stability—poor-quality clamps cause line sag, breakages, and electrical arcing. High-performance C-SPAN clamps enhance safety, reduce blackouts, and ensure compliance with international grid standards.
- Supporting modernization of aging infrastructure—C-SPAN clamps stabilize connections in areas with increased load demand.
- Withstanding harsh weather conditions—the diverse climate in Argentina demands hardware that performs under pressure. C-SPAN clamps are able to resist corrosion, UV degradation, and thermal fatigue. They are able to support long-term reliability with minimal maintenance.
Advantages of upgrading Argentina’s grid infrastructure
Updating and enhancing Argentina’s grid infrastructure is essential for economic development, energy security, and sustainability. The adoption of renewable energy is essential for establishing Argentina as a regional energy center. It is also an essential step toward a sustainable, inclusive, and resilient energy future. Here are the advantages of updating Argentina’s grid infrastructure.
- Enhanced dependability and reduced service interruptions—an enhanced grid minimizes blackouts and voltage fluctuations during times of high demand. Utilities can identify faults more quickly, isolate problematic zones, and restore power more effectively. They involve utilizing advanced sensors, automation, and monitoring in real time.
- Effortless incorporation of renewable energy—Argentina’s plentiful natural resources need an adaptable, intelligent grid to manage fluctuating generation. Contemporary infrastructure enables immediate modification to fluctuating supply and distributed energy sources such as rooftop solar.
- Improved energy efficiency and decreased losses—a modernized grid can cut technical losses via smart metering, optimize the flow of power, and identify theft. This signifies that increased energy reaches end-users through reduced costs.
- Economic expansion and employment generation—upgrading the grid generates job prospects in electrical engineering, construction, infrastructure, and software development for grid automation. It draws foreign direct investment in areas such as renewable energy, electric vehicles, and energy storage solutions.
- Energy security—modern grid infrastructure improves national security by decreasing reliance on energy imports, enabling better regulation of energy distribution, and aiding in emergency power management.
- Facilitating a smart energy future—digital technologies such as AI, blockchain, and IoT influence how electricity is produced, stored, and utilized. It facilitates real-time pricing models and the integration of battery storage and electric vehicles.
