A big grip dead end is a type of hardware used to terminate or anchor overhead conductors on transmission lines. it has a design that provides a secure attachment point and prevents the conductors from coming loose or sagging excessively. “Big grip” refers to the type of gripping mechanisms used in the dead-end hardware. It consists of a set of serrated jaws that grip the conductor tightly and provides a strong and reliable connection. The “dead end” is the point at which the conductor terminates or ends. It is the last point along the transmission line before the conductor anchors or terminates. The purpose is to ensure the stability and integrity of the conductor in overhead transmission lines. They also help maintain proper tension while minimizing the risk of sagging or detachment.
Components of the big grip dead end
The components of the devices vary depending on conductor type, voltage rating and manufacturer’s specifications. Below are the common components of the big grip dead end.

- Grips – these are the main components responsible for gripping the conductor. They consists of serrated jaws or clamps made of high strength materials such as steel.
- Preformed rods – preformed rods are typically made of high strength materials like aluminum steel. These materials help provide structural support to the grip. This helps maintain the desired shape and alignment of the dead-end assembly.
- Dead end sleeves – these are protective sleeves made of insulating materials like rubber or composite polymers. They mainly cover and insulate the gripping area where the conductor is in contact with the grip.
- Thimble – thimbles are protective metal fittings placed inside the grip to protect the conductor from abrasion or damage.
- Structural components – structural components include bolts, nuts, washers and other fastening hardware. They secure the components together and provide structural integrity.
- Anchoring hardware – additional anchoring hardware helps to secure the dead-end assembly to the supporting structure.
Types of big grip dead end
The types of the big grip dead ends vary depending on the specific requirements on the transmission lines. Other also depend on the manufacturer and suppliers in the market. The following are the main types of the big grip dead ends.

- Swage dead end – swage dead ends use mechanical swaging techniques to create a permanent connection between the grip and conductor. Swaging involves compressing the metal around the conductor creating a secure and low resistance joint.
- Bolted dead end – this type of big grip dead ends uses bolts and nuts to secure the grip to the conductor. This offers a strong reliable connection and is commonly used for medium to high voltage overhead transmission lines.
- Armor rod dead end – armor rod dead ends incorporate extra components known as armor rods. They help to provides extra protection and support. This reduces the risk of abrasion and damage. They are mostly used in areas prone to high wind or vibration.
- Compression dead end – compression dead ends utilize compression fittings to secure the grip onto the conductor. They help to create a tight and durable connection without the need for bolts or other tools.
- Hydraulic dead end – hydraulic dead ends use hydraulic pressing methods to achieve a reliable and robust connection. They work in high tension application and handle significant loads.
Application of big grip dead end
The application of big grip dead ends depends on the design of the transmission lines, conductor type, voltage rating and other factors. They work on various applications to ensure termination and proper tensioning of conductors. The following are the applications of big grip dead end.
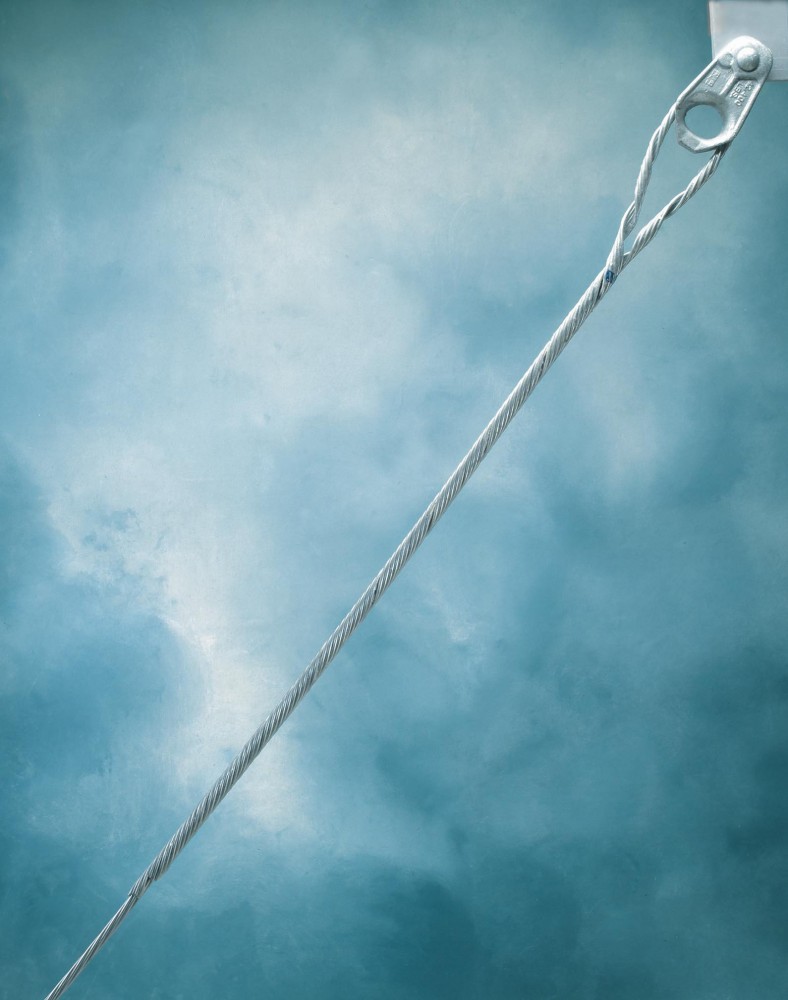

- Line angle changes – This is in areas where transmission lines change direction or angle to accommodate the variation.
- Dead-end terminations – big grip dead ends apply at the ends of transmission lines to terminate conductors securely. This provides reliable attachments point to prevent the conductor from being loose.
- Temporary connections – big grip dead end works for temporary connections during construction or maintenance activities.
- Tensioning – they play a crucial role in maintaining proper tension in overhead transmission lines. This is by securely gripping the conductor and distributing the applied load evenly. This helps prevent excessive sagging or stretching.
- Guyed structure – big grip dead ends work in guyed structures that need extra support on the transmission lines.
Installation of the big grip dead ends
The installation process depends on the instructions provided by the manufacturer of the devices. It is advisable to consult with a qualified professional for the installation process if in doubt. The following is a basic series of steps used for the installation process.
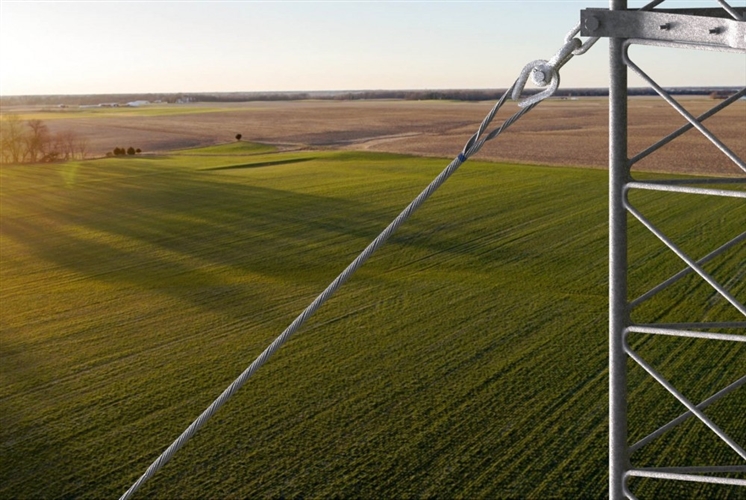

- Ensure that you have the appropriate tools and equipment for the job. These includes wrenches, torque wrenches, hoists, insulation removal tools and safety equipment before the installation.
- Inspect the conductor and the area where the big grip dead end will install. Check for signs of damage, corrosion or wear that may affect the installation and performance.
- Clean the conductor surface where the big grip dead end will attach. Remove any dirt, grease or corrosion using an appropriate cleaning agent.
- Follow the manufacturers instruction to assemble the components of the big grip dead end. This involves using attaching the grip, thimbles and other fittings as required.
- Attach the big grip dead ends over the stripped conductor end. Make sure the conductor is fully inserted into the grip and properly aligned. Use the appropriate fasteners like bolts, nuts and washers to secure the connections.
- Install any insulation if required and ensure they cover the gripping area for proper protection.
- Perform any required tests or tensioning procedures as specified by the manufacturer or engineering standards.
- Keep a record of the installation which can be useful for future maintenance and inspections.
Choosing the best big grips for your applications
You can select the best big grip dead ends that meets your specific needs. This ensures a reliable and secure termination of your transmission line conductors. The following are the factors to consider before selecting the device for purchase.
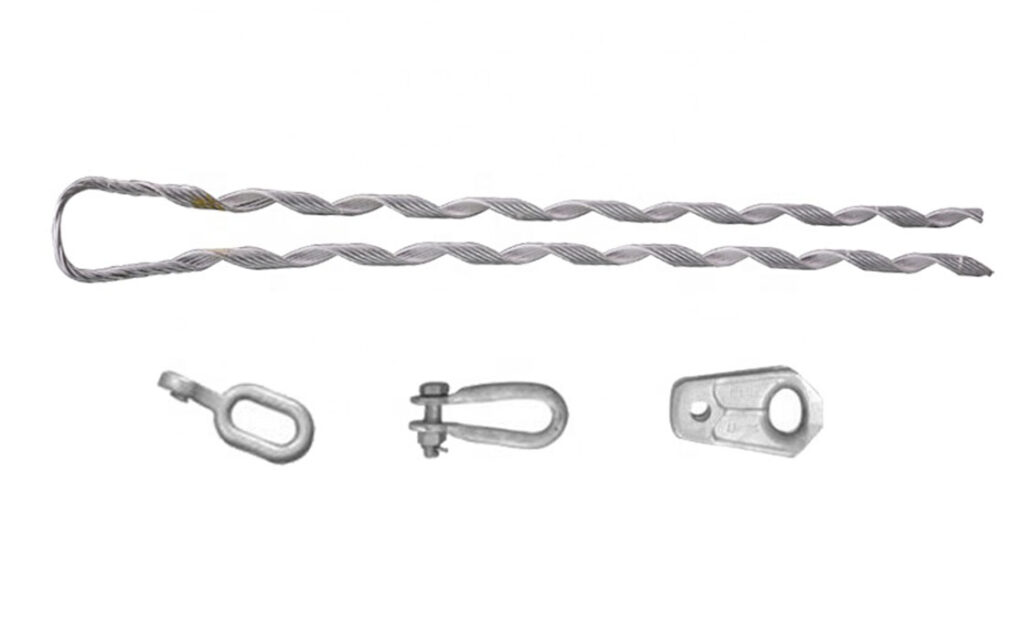

- Consider the type and size of the conductor you will be working with. Big grip dead ends help for specific conductor materials and different size ranges.
- Determine the voltage rating of your transmission line and make sure the dead end meets the voltage requirements of your application.
- Evaluate the load capacity or tensile strength of big grip dead end. Consider the maximum tension the dead end can handle without compromising performance or safety.
- Consider the environmental conditions where the big grip dead ends will install.
- Select a dead end from a reputable manufacturer known for producing high-quality products.
- Consider any specific requirements or challenges of your application. Considering factors like line configuration, anticipated loads or other specifications depending on your application.
- Seek guidance from transmission line engineers, consultants or industry professionals who have experience with big grip dead ends.
Frequently asked questions
What is a big grip dead end used on the transmission lines?
A big grip dead end is a type of hardware used to terminate and anchor overhead conductors on transmission lines. They provide a secure attachment point and helps maintain proper tension in the conductors.
How often should big grip dead end maintainenance?
Regular inspection and maintenance are important to ensure the ongoing performance and safety of big grip dead ends.
What are the benefits of using big grip dead ends?
Distrbution grip dead ends offer several benefits to the installations of overhead transmission lines. These include ease of installation, durability, tension maintenance, secure termination, temporary connection capability and industry compliance.
What are the limitations of the big grip dead end?
They also have various limitations that reduce their adaptability in the market. They include compatibility, limited application range, installation complexity, maintenance and complexity, reusability challenges and safety considerations.
