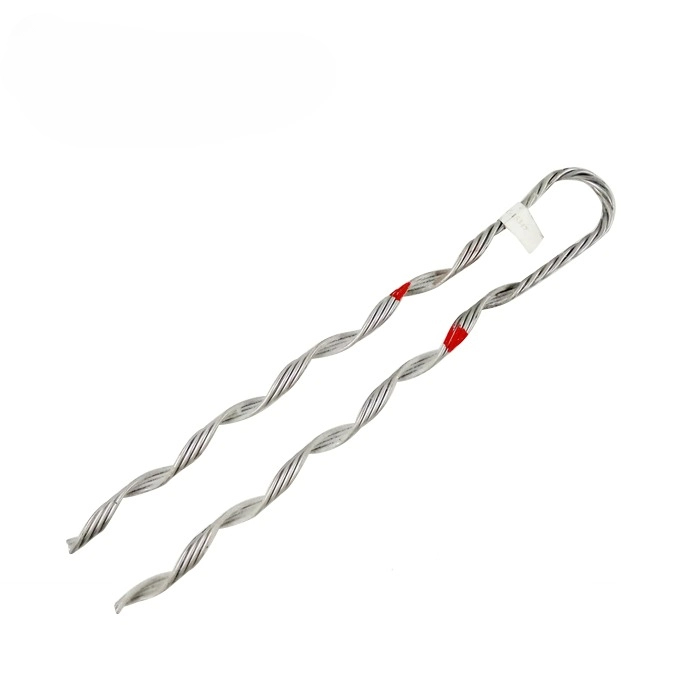

A big grip dead end is a termination or end point of a cable where a grip holds the cable in place. The term “dead end” refers to the point at which the cable terminates without further continuation. A big grip is a cable grip made to accommodate larger cables. The termination offers stability and support for the wires in regions where they are under tension. The big grip dead end has designs to accommodate the increasing diameter and weight of transmission and telecommunication cables. The dead end also keeps the cable from shifting or sagging. Big grip dead ends are from steel, aluminum, or galvanized steel. These materials provide a firm grasp on the cables while also being durable. The large rip dead end also serves to secure the ADSS cable to a support structure.
Attributes of a Big Grip Dead End
Big grip dead end has features that promote stability, dependability, and lifespan. They also assist the big grip dead end in fulfilling its roles in a variety of applications. These tasks include anchoring above cables, distributing tension, and ensuring their integrity. The following are the characteristics of a big grip dead end.

- High strength – the big grip dead end is from materials with high tensile strength, which can endure tension and stress. Steel and other tough alloys are among the materials used.
- Secure grip – in a variety of applications, the big grip dead end’s primary role is to provide a secure hold. It includes a design that wraps around the cables, providing a secure grip to avoid slippage.
- Environmental resistance – the big grip dead end can tolerate exposure to a variety of environmental variables. This includes UV radiation, high temperatures, and wetness.
- Corrosion resistance – they should be corrosion resistant to survive changing weather conditions. Coatings and treatments keep them from rusting and degrading.
- Compatibility – the big grip dead end must have designs to work with the precise type and diameter of cable used. It should be able to handle the size and weight of the cables without causing damage.
- Conductor protection – it should also include designs to safeguard the cables’ conductors from harm.
- Installation ease – the large grip dead end should help make installation easier. They may have simple tightening mechanisms.
Uses and operations of a big grip dead end
Big grip dead ends function in overhead transmission and telecommunications networks. They contribute to the stability, reliability, and safety of infrastructure. This works by offering anchoring, distribution, and stability. The following are the uses of big grip dead ends.

- Cable termination – a big grip dead end ends overhead cables at the conclusion of their run. This prevents cables from extending further and offers a secure anchor point.
- Tension distribution – they also serve to distribute tension along the length of the cables. This helps to prevent excessive tension on the cables, lowering the danger of damage.
- Prevention of cable damage – the strong grip helps prevent cable damage. This could result from movement, vibration, or abrasion. It also maintains the cable in place, lowering the chance of wear and strain.
- Maintenance and inspection – the big grip dead end makes cable maintenance and inspection easier. This happens by establishing defined termination points.
- Anchoring to structures – the primary function of the big grip dead end is to secure overhead cables. It keeps the cables in place, preventing them from sagging or shifting.
- Support and stablity – big grip dead ends add support and stability to the system. This helps to maintain the integrity of the infrastructure and ensures continuous transmission.
- Safety – proper installation improves the safety of transmission and telecommunication systems.
- Adaptability – they offer designs that can support a variety of cable kinds and sizes.
Application areas of dead ends
Big grip dead ends function in a variety of industries and applications where overhead cables need anchoring to structures. The application also differs based on the performance, dependability, and safety of infrastructure systems. Also, it is advisable to seek professional assistance in understanding the applications of the chosen big grip dead end. The following are the applications for big grip dead ends.
- Transmission lines – big grip dead ends work in power transmission lines to secure overhead cables to utility poles. They maintain stability and prevent sagging.
- Telecommunication lines – they also attach fiber optic cables, coaxial cables, and other lines to poles. They maintain optimum cable tension and enable reliable data transfer.
- Line angle changes – this occurs when transmission lines shift direction or angle to meet the variation.
- Wind and solar farms – big grip dead ends function in renewable energy projects. They aid to secure the cables that connect turbines to substations or grid interconnection points.
- Railway electrification – these use big grip dead ends to secure overhead catenary cables. They support and assure the uninterrupted power supply of electric trains.
- Temporary connections – large grip dead end work in temporary connections during building or maintenance operations.
- Tensioning – they play an important role in maintaining adequate tension in transmission lines. This happens by grasping the conductor and dispersing the applied load. This prevents excess sagging or stretching.
- Aerial fiber optic installations – dead ends help terminate and anchor fiber optic cables to poles. They contribute to the integrity of the fiber optic network and prevent signal loss.
- Guyed structure – big grip dead ends work in guyed structures, which offer extra support to the transmission line via guy wires or cable.
Big grip dead ends foundation.
The construction of a big grip dead end requires various components and methods. It also includes installation to guarantee that cables are reliably and securely anchored. It is also recommended that you get advice from experts during the installation process. The following is a detailed explanation of how big grip dead ends originate and work.
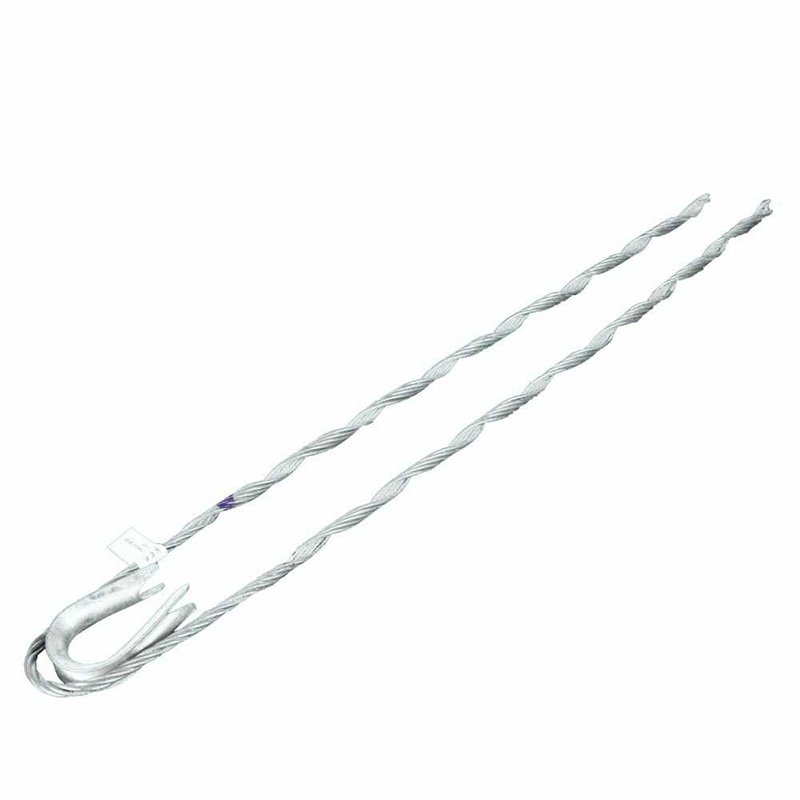

- Big grip assembly – this comprises of a grip mechanism meant to grasp the cable. It has a mesh-like structure constructed of strong materials such as steel. It also works with clamps or bolts to tighten the cable.
- The support structure – this is the utility pole, transmission tower, or other structure on which the cables anchor. It should be able to withstand the tension from the cable.
- Attachment to cable – the big grip assembly slips into the cable’s end to guarantee proper termination positioning. This provides a tight grip on the cable, preventing slippage.
- Positioning and anchoring – place the big grip dead end in the preferred spot for termination. Secure it to the framework using appropriate hardware, such as bolts and brackets.
- Tensioning – this entails applying tension to a cable using tensioning equipment to produce the desired level of tension. This helps to maintain stability and prevent sagging.
- Trimming – trim any excess cable protruding from the big grip assembly with cable cutters.
- Inspection – inspect the big grip dead end to ensure that all components are securely fastened and tensioned.
- Functionality – the big grip dead end anchors the overhead cables to the support structure. It maintains stability and avoids movement or sagging. It also distributes tension along the cable’s length, ensuring dependable transmission.
Public discussions and interactions for big grip dead ends
Community forums for big grip dead ends can give debates and exchanges that bring more information. This includes platforms geared for electrical engineering, power transmission, telecommunications, and other industries. Active involvement in such venues can facilitate learning from others. The following forums contain discussions regarding big grip dead ends.

- Electrical engineering forums – locate websites dedicated to electrical engineering where professionals can converse.
- Telecommunication forums – these are venues for telecoms experts cover installation and maintenance concerns.
- Linkedin groups – join relevant LinkedIn groups focused on electrical engineering, power transmission, and telecommunications. They provide opportunity to meet with industry leaders who can share thoughts on major scale dead ends.
- Industry-specific professional associations – they may offer online forums, discussion boards, or networking events.
- Power engineering communities – online groups dedicated to power engineering and utilities may have conversations concerning installation, maintenance, and performance.
- Industry-specific websites – websites dedicated to the electrical, power, or telecommunications industries may include forums for discussion. Professionals and fans can engage and share knowledge about the equipment and components used in each area.
Frequently asked Questions
A big grip dead end is a specialised termination point found in overhead transmission and telecommunications lines. It firmly fastens cables or wires to support structures.
Big grip dead ends serve in a variety of industries, including power transmission, telecommunications, railway electrification, and distribution networks.
Benefits include providing stability and support for overhead wires, as well as spreading tension along their length. It also prevents drooping or movement, ensuring the infrastructure’s reliability.
There could be industry-specific rules governing the design, fabrication, and installation of big grip dead ends.
