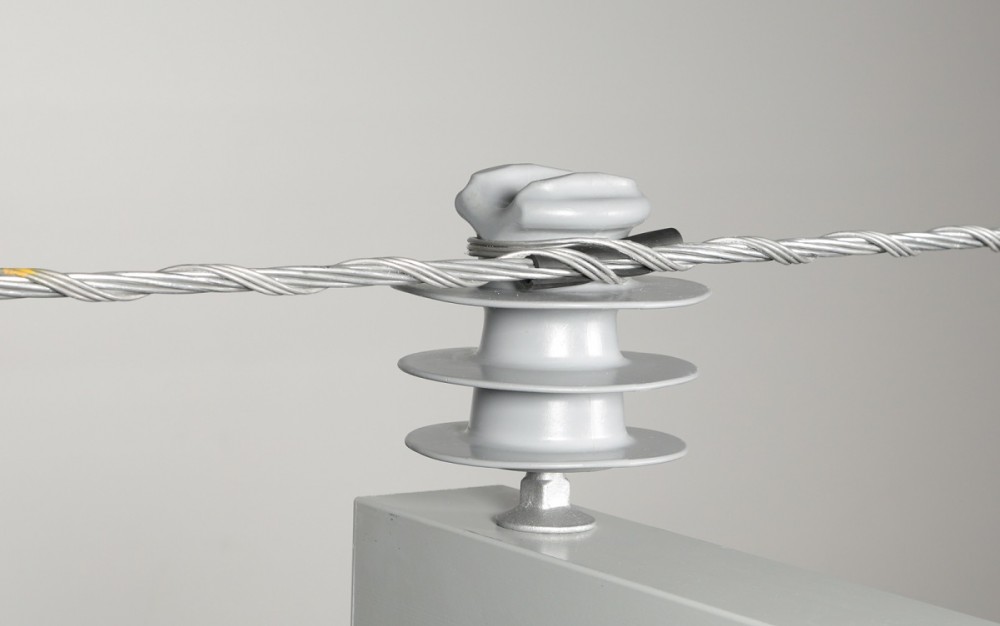

A side tie is a specialized method for attaching a conductor to the insulator that supports it on a pole. The side tie maintains the stability and safety of the transmission line by preventing the conductor from moving. It wraps around the conductor and insulator, providing lateral support that keeps the conductor in place. Side ties are useful when the conductor needs to maintain proper alignment and spacing. The side tie comprises of several components, including a conductor, an insulator, and a side tie. They have design to hold the conductor even in the presence of wind, ice, and other pressures. Preformed and hand-held side ties are two common forms of side ties. They work in distribution lines and high-voltage transmission.
How to choose the perfect side tie
Choosing the correct side ties for overhead transmission lines requires careful consideration of several criteria. This ensures the transmission lines’ performance and durability. When you choose the right side tie, the conductor remains in the same place. The following are the criteria to consider when choosing the best side ties.
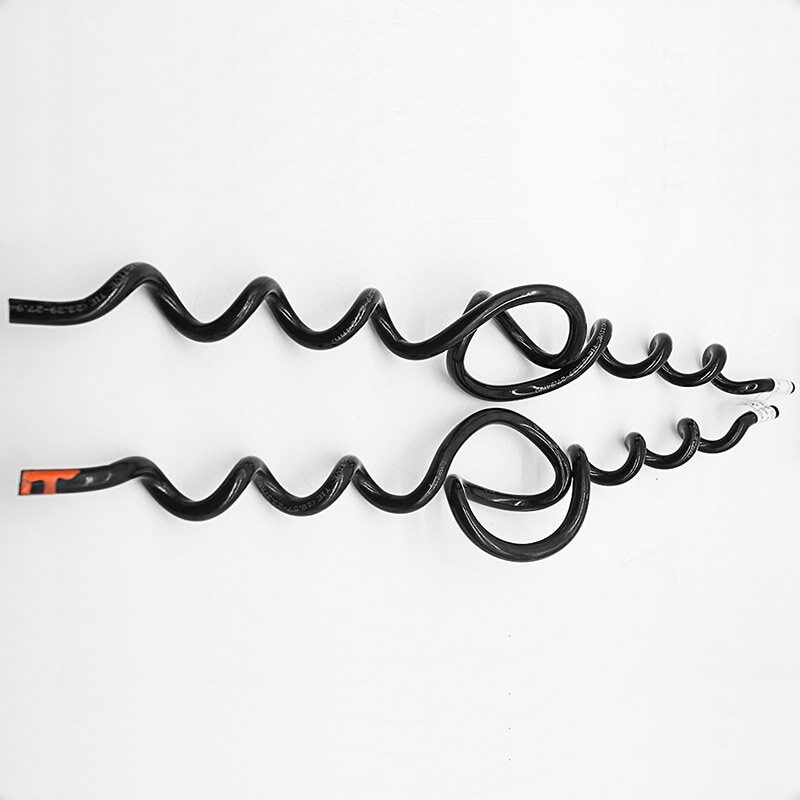

- Conductor type and size – different conductors need side ties made of compatible materials. This is to prevent galvanic corrosion. The side tie must fit the conductor’s size to provide a secure attachment without damage.
- Insulator type – side ties must be compatible with the insulator’s design and material. The insulators should support the tension and stress applied by the side tie without damage.
- Environmental conditions – the side ties should be strong enough to handle high winds and ice accumulation. They should also withstand extreme temperature changes without losing integrity.
- Mechanical strength – the side tie must support the conductor’s weight and extra forces from environmental conditions. They should also allow some movement to absorb shock without causing damage.
- Ease of installation – preformed side ties are easier to install and provide consistent performance. Consider the tools needed for easier installation methods to reduce labor costs and time.
- Cost effectiveness – check the upfront cost of side ties relative to their benefits and durability. Choose side ties that cut long-term maintenance costs and ensure reliable performance.
- Electrical conductivity – ensure the side tie material has suitable conductivity. This aids in avoiding electrical losses. Select materials that reduce the risk of galvanic corrosion.
- Mechanical load and tension – assess the tensile strength needed for the side tie to support the weight and tension of the conductor. Consider the extra load from wind and ice which can increase the tension on the conductor.
Installation techniques for side tie
The installation method guarantees appropriate alignment and prevents displacement. Proper installation increases the life of the transmission line, improving safety and reliability. Also, it is advisable that side ties install according to the manufacturer’s instructions. The following is a step-by-step guide for installing side ties.
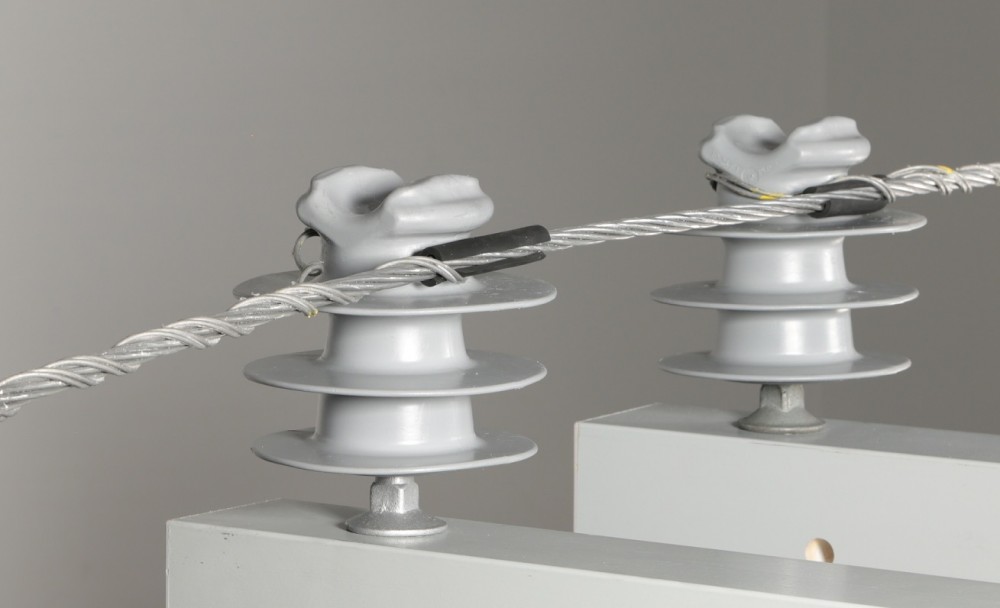

- Preparation – use personal protective equipment such as hard hats, gloves and safety glasses. Ensure the line is de-energized and grounded to avoid electrical hazards. Check the conductor, insulator and side tie for any damage before installation.
- Tool preparation – prepare unnecessary tools like pliers, wire cutters, and wrenches.
- Conductor positioning – position the conductor on the insulator for proper aligning. Use a temporary tie or support to hold the conductor in place during installation process.
- Side tie attachment – place the preformed side tie around the conductor and insulator according to the specifications. Wrap the ends of the side tie around the conductor in a spiral motion to ensure it sits tight to the conductor. For hand-tied side ties, wrap it around the conductor and insulator by hand. Twist the ends of the wire to lock the side tie in place
- Final adjustment and inspection – check the tightness of the side tie and that it is snug on the conductor and insulator. Inspect the installation for any signs of damage to the conductor or insulator.
- Installation of armor rods – place the armor rods around the conductor near the insulator to provide extra protection. Wrap the rods around the conductor according to the manufacturer’s instruction.
- Conduct a load test – apply tension to the conductor to simulate operational conditions and check the stability of the side tie. Ensure that the side tie holds the conductor securely without slippage.
- Documentation – document the installation process including the type of side tie used, installation date and any observations.
Maintenance and inspection of the side ties
Regular maintenance and inspection of side ties maintains their performance and dependability. Additionally, adhering to the protocols and utilizing appropriate equipment and techniques might aid in determining the condition of the bonds. The following is a basic guide for maintaining and inspecting side ties.

- Visual inspection – examine the condition of the side ties for any visible signs of damage, wear, or displacement. Check for corrosion, rust and signs of mechanical wear.
- Routine inspection and cleaning – inspect the side ties more frequently especially in harsh environments. Remove dirt, debris and corrosion from the side ties using a soft brush or cloth. Look for signs of wear, corrosion, cracks or any other damage.
- Lubrication – apply a corrosion-resistant lubricant to metal side ties to prevent rust and wear. Apply a thin layer of lubricant to avoid attracting dust and debris.
- Tightening and adjustments – ensure the side ties remains tight around the conductor and insulator. Adjust the side tie to reposition it correctly.
- Replacing worn or damaged ties – replace side ties that show signs of corrosion, cracks or damage. Use side ties that match the specifications of the original installation.
- Environmental protection – apply a protective coating to the side ties exposed to harsh environmental conditions.
- Checking for fatigue and fractures – check the stress points where the side tie wraps around the conductor and insulator.
- Thermal and weathering effects – check for signs of damage or melting near conductors that may experience high temperatures.
Testing the side ties
Side ties for overhead transmission lines undergo inspection to guarantee their integrity, reliability, and compliance with safety standards. Testing provides a method for checking and ensuring the performance of side ties. Additionally, regular testing contributes to the safety and efficiency of the electricity infrastructure. The following are some frequent tests for side ties.

- Mechanical testing – this helps to assess the greatest load the side ties can withstand without breaking. This is to record the breaking strength and ensure it meets or exceeds the required specifications. Impact testing determines the side tie’s resistance to sudden forces or shocks.
- Environmental testing – this test checks the resistance of the side tie to corrosion under various environmental conditions. It also includes UV resistance test to check their resistance to UV radiation. Temperature cycling tests checks the side tie’s performance under varying temperature conditions.
- Electrical testing – this is to measure the electrical conductivity of the side tie to ensure it does not impede the conductor’s performance. Dielectric strength tests the side tie’s insulating properties for ties used in areas with high-voltage applications.
- Non-destructive testing – this is to detect internal flaws within the side tie. Eddy current testing also helps identify surface and near-surface defects in conductive side.
- Inspection and monitoring tests – this test is to identify visible defects, wear or corrosion on the side tie. It also helps to detect thermal anomalies that state mechanical stress.
Application areas for side ties
Side ties have designs to keep conductors properly aligned and spaced. This is to provide efficient and dependable power transfer. The use of side ties varies depending on the kind of power system, environmental circumstances, and special application requirements. The following are the application areas for side ties.
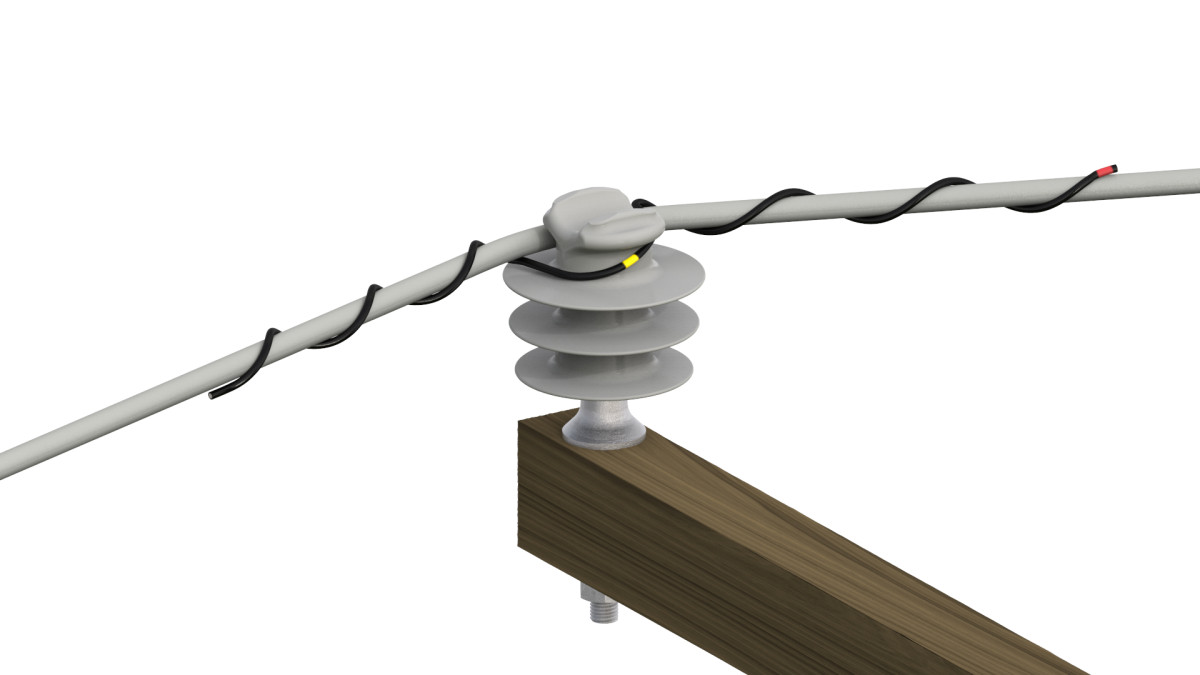
- Power transmission lines –side ties serve in systems transmitting electricity over long distances at high voltages and medium voltages. Side ties maintain proper alignment and spacing. This iscrucial in preventing electrical faults and reduce power loss.
- Distribution lines – this includes applications in urban and suburban distribution and rural distribution applications. Side ties aid in maintaining conductor spacing and protect against movement caused by wind, wildlife and other environmental factors.
- Renewable energy systems – this includes wind farm power lines and solar power lines. Side ties ensure reliable connections to insulators in challenging weather conditions and prevent conductor displacement.
- Industrial and commercial facilities – provide electricity to large industrial and commercial complexes. Side ties manage heavy conductor loads to power supply lines and substation connections.
- Transmission applications – side ties maintain conductor alignment to avoid disruptions in power supply and train operation. They serve in railway electrification and telecommunication systems.
Frequently asked questions
A side tie is a component used to secure conductors to insulators on transmission and distribution lines. It helps to maintain the alignment and spacing of the conductor.
Side ties suitable for harsh environments are from corrosion-resistant materials. They may have protective coatings to withstand extreme weather, high humidity, and salt exposure.
Side ties secure contact wires to insulators and ensure stable power supply for trains. This is by maintaining proper conductor alignment.
