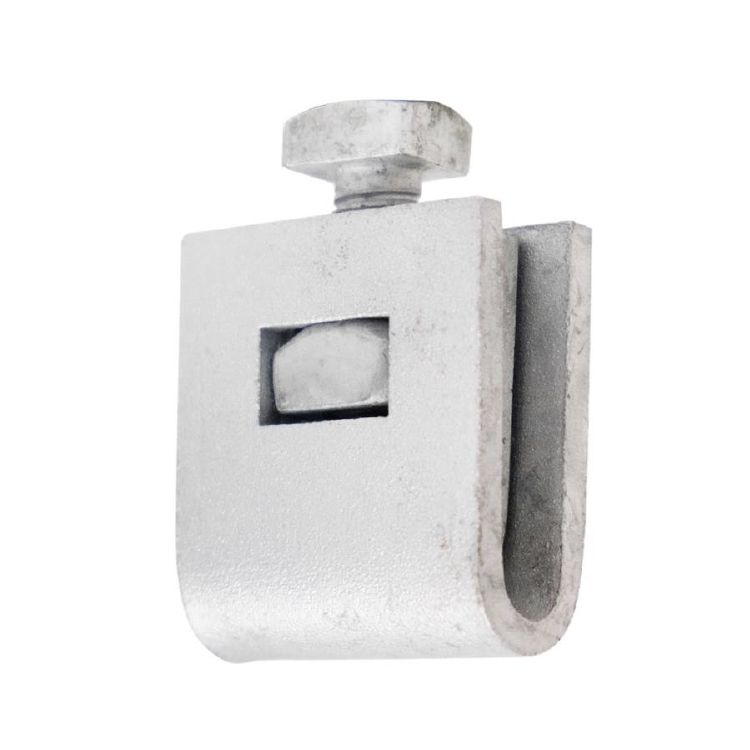

A b strand ground clamp is an equipment that secures an electrical connection to a grounded system. It establishes a reliable connection between the grounding wire and the ground. This aids in the dissipation of fault currents and provides static safety techniques. The b strand ground clamp comprises a set up of various components, including the body, clamp mechanism, and contact points. Each of these components performs a specific purpose within the application. They serve to maintain best conductivity, secure the clamp, and protect against corrosion. The clamp provides a low-resistance electrical connection. This is critical for the proper dissipation of electrical faults and lightning strikes. South American b strand ground clamps can survive a variety of weather conditions. They also prevent unsafe voltage levels from building up during transmission.
Design and building of the B-strand ground clamp
The building and layout of the b strand ground clamp contribute to a dependable and secure connection. This is an effective connection between the ground wire and the grounded structure. The use of high-quality materials contributes to the safety and functionality of overhead transmission lines. The following are the major components and design structures of the b-strand ground clamp.
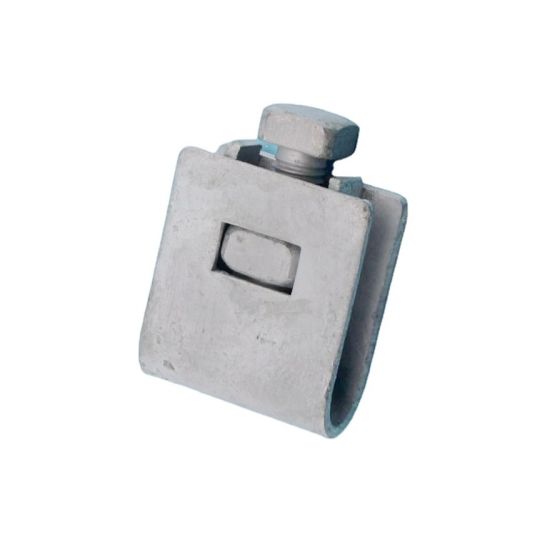

- Body – this is the main structure of the b strand ground clamp. It is from materials like bronze, brass, or copper for excellent conductivity. It is a solid piece with a strong structure to withstand mechanical stresses and environmental conditions. The body may be c-shaped or U-shaped to wrap around the grounding conductor.
- Clamp mechanism – this consists of bolts, screws and compression plates. Bolts and screws serve to tighten the clamp onto the grounding conductor. The compression plates distribute the clamping force and ensure a solid connection.
- Contact points – the internal surfaces of the clamp may have teeth, grooves or serrations. This is to grip the conductor and prevent slippage.
- Coatings and finishes – South American b strand ground clamps should have anti-corrosive coatings. This ensures they are suitable for the wide range of weather conditions.
- Compression feature – some clamps may have a spring mechanism to maintain constant pressure on the grounding conductor.
- Versatility – b strand ground clamps have designs to work with a range of conductor sizes and types. Some are adjustable to fit different grounding applications.
Materials used in the manufacture of a B-strand ground clamp.
There are many different materials for b strand ground clamps that are acceptable for the South American environment. Factors to consider include humidity, salinity, temperature changes, and UV exposure. The performance, durability, and dependability of the b strand ground clamp are all improved with the proper material selection. The following are the most commonly utilized materials and their benefits.

- Bronze – this provides excellent electrical conductivity, good mechanical strength and superior corrosion resistance. It is ideal for humid and coastal environments due to its resistance to salt water.
- Brass – this material has good electrical conductivity, corrosion resistance and mechanical strength. It is suitable for various environments and provides a balance of durability and performance.
- Copper – this provides electrical conductivity and good corrosion resistance. It requires coatings or treatments to enhance corrosion resistance in harsh environments.
- Tin plating – this provides corrosion resistance while maintaining good electrical conductivity. It protects copper and bronze components from oxidation and environmental damage.
- Nickel plating – this offers excellent corrosion resistance and enhances mechanical durability. It is ideal for areas with high humidity and industrial pollutants.
- Galvanization – this coats steel or iron with a protective layer of zinc to prevent rusting. It works for components that need extra mechanical strength and corrosion resistance.
- Stainless steel – this offers high tensile strength, corrosion resistance and durability. It is best used for bolts, screws and other fastening components.
- Silicone bronze – this combines the strength of bronze with the durability of silicon. It provides high corrosion resistance and mechanical strength. It is suitable for fasteners exposed to harsh weather and saline conditions.
- Composite materials – these materials are lightweight, corrosion-resistant and have high mechanical strength.
- Aluminum – this is also lightweight, good electrical conductor, and corrosion resistant. It is less common for grounding clamps.
Technical details for b-strand ground clamps.
The technical specifications for a b strand ground clamp include physical dimensions, materials, and mechanical strength. The specs ensure that the clamp satisfies the necessary standards in South America. These standards improve safety and performance in electrical transmission systems. Also, the standards are critical to the reliable and safe operation of grounding systems in overhead transmission lines. The following are common technical specifications for a b-strand ground clamp.
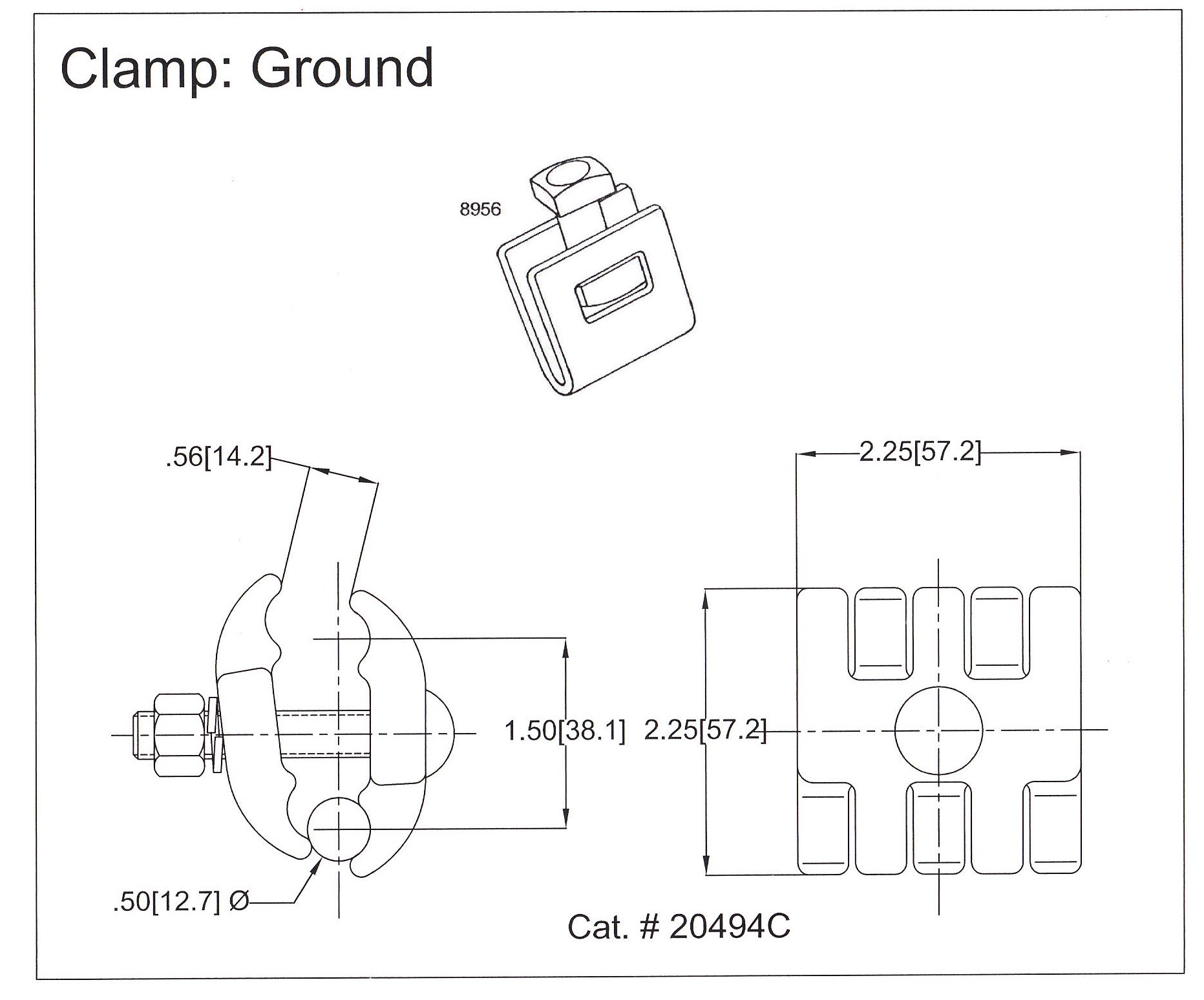
- Material specifications – the common materials include bronze, brass or copper for the body, and stainless steel or silicon bronze for bolts and screws. The specifications should detail clamp size, bolt or screw size and torque requirements.
- Electrical specifications – this includes conductivity, current carrying capacity and contact resistance. High electrical conductivity materials ensure a low resistance measured in micro-ohms.
- Environmental specifications – the b strand ground clamps must withstand environmental exposure. This is including moisture, salt, pollutants and UV radiation.
- Mechanical strength – the specifications should include ratings to withstand mechanical stresses from tension and compression without deformation. The ground clamps should also be able to withstand impacts during installation and operation.
- Standards and certifications – this includes compliance with relevant standards in the region. These include ANSI, IEE, UL listing and NEMA standards.
- Dimensions – this includes the length, width and height of the b strand ground clamps. The measurement should ensure a stable and secure connection.
- Installation specifications – this includes specific tools needed for installation and installation instructions.
Industry advancements and developments for B-clamps
The industry for b strand ground clamps is constantly evolving, with advances targeted at enhancing performance and durability. The advancements prove a dedication to enhancing safety and performance. This occurs while adapting to new technologies and environmental concerns. The following are some important advancements in the b-clamp industry.
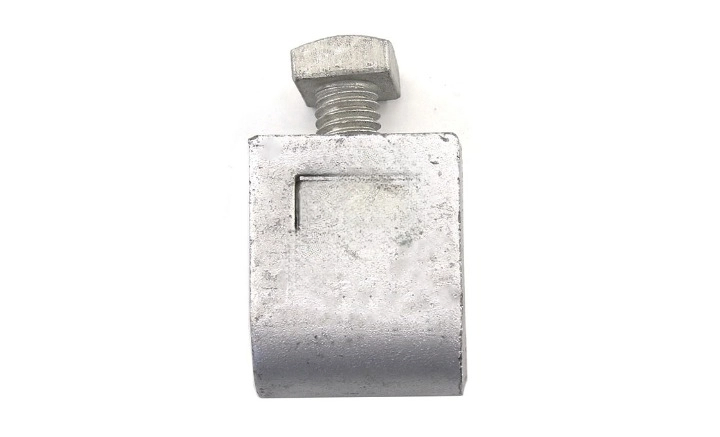

- Material innovations – the development of new copper and bronze alloys offer improved conductivity and corrosion resistance. These materials maintain high performance even in harsh environments. Composite materials combine the strength and durability of metal with the lightweight and corrosion resistant properties of polymers.
- Coating technologies – there are new technologies such as Nano coatings and advanced plating techniques. These provide protection against corrosion and oxidation. There are also coatings that can self-repair minor scratches and damages.
- Design improvements – there are clamps with ergonomic designs that ease handling and installation. This helps to reduce physical strain on technicians.
- Enhanced electrical performance – there is improvement in contact surface engineering. It enhances the electrical connection by reducing contact resistance. Some clamps include integrated testing points that allow easier verification of the grounding.
- Environmental adaptability – the use of UV resistant materials and coatings ensure long term durability. The clamps are also designed to operate over a wide range of temperatures.
- Smart grounding solutions – this is the integration of sensors and IoT technology into ground clamps. They help to track the condition of the grounding system in real time. Use of data analytics to predict maintenance needs also optimizes the performance of grounding systems.
- Manufacturing advancements – advances in manufacturing techniques allow for more precise and consistent production of ground clamps. These include CNC machining and 3D printing.
Servicing b-strand ground clamps on South American overhead transmission lines.
Troubleshooting b strand ground clamps in South American conditions entails recognizing and resolving frequent problems. These are concerns about installation, environmental variables, and upkeep. Additionally, troubleshooting improves the performance of b-strand ground clamps. The following are the methods and considerations for troubleshooting a b strand ground clamp.

- Regularly inspect the clamps for signs of corrosion, rust, discoloration or material degradation. Replace the corroded clamps and consider using clamps with better corrosion resistant materials. Apply anti-corrosive coatings or use protective coverings in highly corrosive environments.
- Check for signs of wear or damage that could cause looseness and replace is necessary. Ensure all bolts and screws are tight to the manufacturer’s recommended torque. Use locking washers to prevent loosening due to vibration.
- Clean the contact surfaces to remove any oxidation, dirt or debris and replace the damaged clamps. and ensure proper installation.
- If the application shows visible cracks, deformation or broken parts, replace them immediately. Use protective barriers in areas prone to mechanical impact.
- Check on damage or performance issues related to specific environmental conditions. This is including temperature extremes, UV exposure and salt spray. Use UV resistant and anti-corrosive coatings to protect against environmental factors.
- Keep detailed installation guides and checklists for the b strand ground clamps. Include details such as dates, actions taken and other observations.
Frequently asked questions
A b strand ground clamp helps to establish a reliable electrical connection between a grounding conductor and a grounded structure. This helps to dissipate fault currents and static charges to protect equipment against electrical hazards.
New developments include the use of advanced alloys and composite materials for increased conductivity and corrosion resistance, ergonomic designs for easier installation, smart grounding solutions with integrated monitoring capabilities, and improved coating technologies for superior environmental protection.
