
Argentina’s YPF has ruled out the construction of an onshore natural gas liquefaction plant. It will depend on floating vessels for the liquefaction process. YPF is leading the development of Argentina’s Vaca Muerta shale formation. It has also signed a deal with Shell under which the oil major will take part in the production, liquefaction, and sale of LNG. This development represents a strategic, lower-cost pathway to quickly start LNG exports from its shale formation. The floating vessels will capture seasonal export opportunities to Europe and Asia. Floating vessels can be relocated if upstream supply shifts or if market conditions change. Additionally, early production levels can be handled without overbuilding expensive facilities. These facilities have the ability to support Argentina’s energy sector with low environmental impacts. The use of a downlead clamp ensures the safe and efficient transfer of cryogenic LNG from vessel tanks to offloading systems.
A high-quality downlead clamp secures the vertical downcomer pipes carrying cold LNG from the topside liquefaction to storage tanks. It prevents excessive movement due to thermal contraction, vessel motion, or mechanical stress. LNG piping undergoes thermal contraction when cooled. The downlead clamp allows controlled movement while maintaining structural integrity. Downlead clamps incorporate sliding mechanisms to accommodate extraction and contraction without pipe damage. The clamp is designed for accessibility, which allows easy inspection and maintenance for piping connections.
Development of floating vessels via downlead clamps
A downlead clamp plays a crucial role in securing and protecting cables or flexible risers running vertically along the side of the structures. It ensures the safe and efficient transfer of cryogenic LNG from the storage to offloading systems. Its main role is to ensure structural stability, thermal flexibility, and safety of LNG transfer systems. Its design should account for cryogenic stresses, dynamic marine loads, and stringent safety needs. Here are the roles of downlead clamps in developing floating vessels for natural gas production.
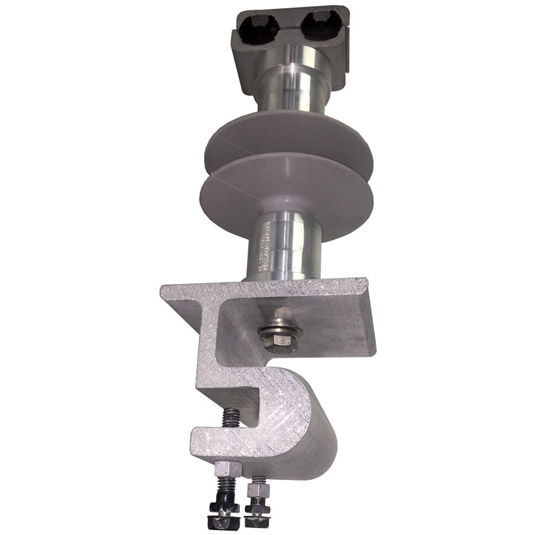

- Support and secure cables—downlead clamps fix power cables, control lines, or flexible gas along the topside. It maintains their alignment and prevents excessive movement.
- Protect against dynamic forces—floating vessels are in motion like waves, currents, and wind. The downlead clamp ensures the connected cables do not experience fatigue, abrasion, and mechanical stress caused by vessel movement.
- Maintain bend radius—the clamps help maintain the proper bend radius for flexible lines, preventing sharp bends. This is crucial for cryogenic LNG lines or control cables.
- Distribute load—the downlead clamps help distribute mechanical load more evenly. This is crucial to prevent overstress at any single point.
- Ensures leak prevention—a secure clamp reduces the risk of pipe misalignment or failure, which could lead to dangerous LNG leaks. This is a crucial concern in cryogenic systems.
- Safety and integrity—proper use of downlead clamps is crucial for operational safety of the FLNG unit. They prevent catastrophic failures like cable rupture or riser damage. This could lead to production shutdowns.
Strategies and innovations supporting the development of floating vessels in Argentina
The development of floating LNG vessels in Argentina arises from strategic international partnerships, modular scalable projects, and innovations in LNG handling. These strategies allow Argentina to tap into its vast shale gas resources quickly and flexibly. The following are the strategies and innovations used to develop floating vessels for natural gas liquefaction in Argentina.
- Modular and small-scale approaches—the country has adopted a modular, small-scale FLNG vessel capable of producing about 0.5 MTPA. This project allows Argentina to export LNG without large infrastructure.
- Leveraging existing infrastructure—existing gas pipelines from Vaca Muerta are repurposed to feed FLNG units and cut the need for costly new pipeline infrastructure.
- Innovations in technology and operations—these include cryogenic transfer systems, digital monitoring, and rapid mobilization. These technologies improve the safety and efficiency of LNG transfer between FLNG and LNG carriers.
- Market export and flexibility—the country can flexibly sell LNG cargoes into spot markets, responding quickly to global price signals. They also support seasonal exports and maximizing the economic value of excess production without long-term rigid commitments.
- Policy and regulatory support—the government streamlined environmental operational permitting for FLNG deployment to reduce delays. There are new policies able to offer incentives to LNG investors.
