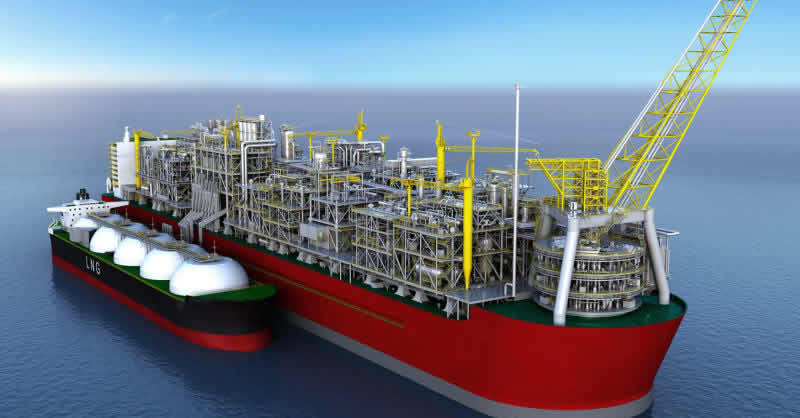

Floating liquid natural gas (FLNG) is a technology revolutionizing the LNG industry by enabling gas production in remote fields. With the Vaca Muerta shale formation, Argentina could leverage similar technology to tap into gas reserves. Top companies are competing to secure the front-end engineering and design (FEED) contract for the pioneering FLNG. Floating LNG provides Argentina a flexible, fast-tracking route to global gas markets. The FEED contract has the potential to shape the economic viability, timeline, and risk profile of Argentina’s first FLNG. Natural gas can play a crucial role as a bridge fuel. Key players include Samsung Heavy Industries, Wison New Energies, Shell, and YPF. FLNG projects need innovative engineering solutions to handle the complexities of offshore gas liquefaction. Using electrical crossover clamps ensures the safe and efficient operations in Argentina.
An electrical crossover clamp is a mechanical connector used in piping systems to join pipelines, provide structural support, and allow maintenance. They are essential for subsea umbilicals, risers, and flowlines (SURF). Cable crossover clamps help connect flexible jumpers to rigid pipelines. The clamps are able to accommodate thermal expansion from cryogenic LNG temperatures. Electrical crossover clamps secure piping between gas pretreatment systems, liquefaction modules, and storage systems. This helps manage high-pressure and low-temperature stresses in offshore environments. As Argentina moves forward with its FLNG projects, crossover clamps are essential for safe, flexible, and efficient operations.
Challenges facing floating LNG development in Argentina
Floating LNG presents opportunities for Argentina’s energy sector, which helps monetize vast natural gas reserves and expand into LNG markets. The development faces challenges such as high upfront capital, policy uncertainty, infrastructure gaps, local supply chain limitations, and competition from other LNG exporters. The success of this development will depend on its ability to create a stable investment climate, build infrastructure, and address environmental and social risks.
Floating LNG development using crossover clamps
Crossover clamps are mechanical components used to connect two intersecting pipes or tubulars. They help in joining flowlines, risers, or pipeline systems where they cross paths. Electrical crossover clamps enable safe, scalable, and flexible offshore LNG development. The clamps are crucial for Argentina’s floating LNG development because they connect critical piping systems offshore and reduce installation time. Here are the roles of crossover clamps in Argentina’s FLNG project.
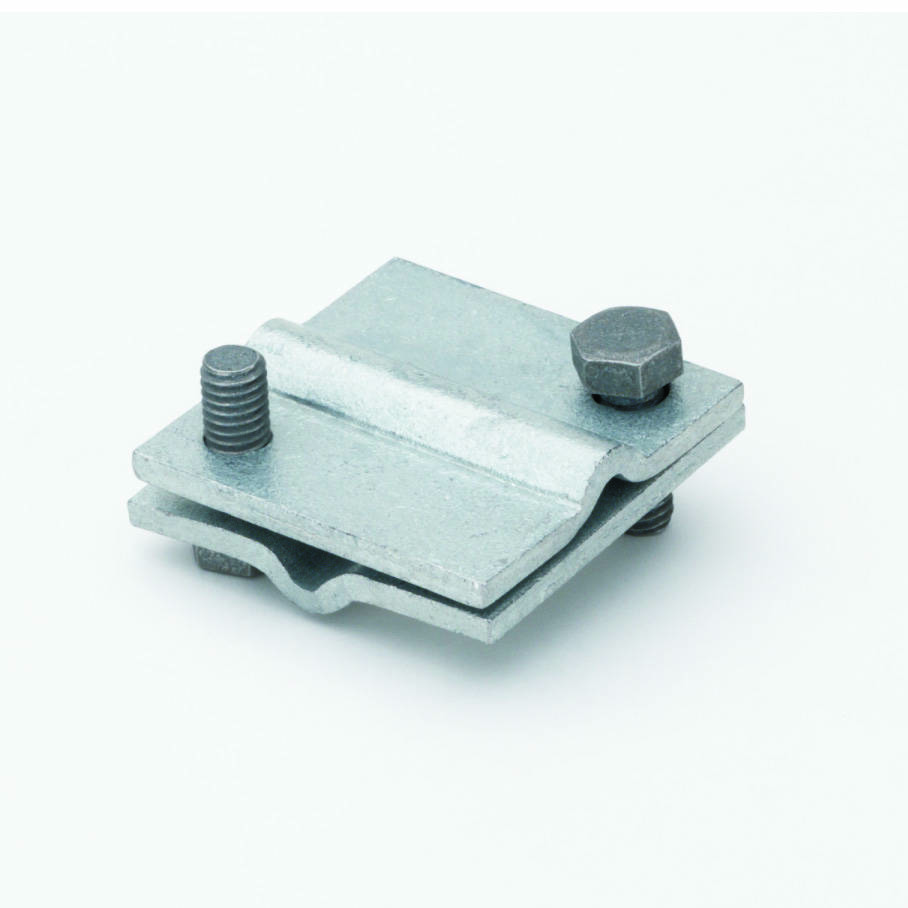

- Flowline integration—the projects will depend on complex subsea flowline networks to transport natural gas from onshore fields. Electrical crossover clamps connect pipelines at junctions, handle high-pressure differentials, and enable safe and leak-free transitions.
- Flexibility in offshore construction—crossover clamps allow fast, on-site modifications to pipe layouts. They also simplify subsea tie-ins and reduce the need for custom-fabricated piping. Crossover clamps support deepwater installation without diver intervention.
- Integrity assurance—FLNG environments may face extreme pressure, temperature changes, and corrosive environments. Heavy-duty crossover clamps help maintain structural and operational integrity. They provide secure sealing, enable rapid repairs, and reduce the risk of leaks and environmental hazards.
- Cost efficiency—this project will need modular design and installation speed. Crossover clamps contribute to faster installation timelines, reduce the need for welding and custom fitting offshore, and lower labor and equipment costs.
Opportunities for floating LNG in Argentina’s energy sector
Floating LNG development has the potential to meet the growing demand for energy exports. It also has the opportunity to reshape Argentina’s place in the global energy landscape. Floating LNG Argentina represents a nimble, scalable solution that can unlock the potential of the Vaca Muerta gas. Crossover clamps enable secure transitions between rigid pipelines and flexible risers. The following are the opportunities for FLNG in Argentina’s energy sector.
- Gas monetization—Argentina’s FLNG enables offshore gas liquefaction and reduces dependence on onshore terminals. It also allows the country to monetize its gas assets from Vaca Muerta.
- Tapping offshore gas potential—construction of traditional onshore LNG infrastructure in remote areas is capital-intensive and slow. FLNG can develop stranded offshore gas fields, avoid long-distance pipeline construction, and reduce land-based environmental impacts.
- Boost export revenues—Argentina faces economic pressure with an urgent need to increase foreign currency earnings. FLNG units can export LNG year-round and diversify its energy export base.
- Technology transfer—the FLNG project has attracted international contractors competing for the FEED contract. It opens the door to new partnerships with global energy firms, technology transfer and skill development, and supply chain growth.
- Energy security—FLNG can smooth out seasonal energy imbalances by enabling year-round export.
