
Colombia recently eased rules governing energy consumption, aiming to foster competition and increase the use of renewables. These rules say that individuals can generate their own electricity for personal use without the need for permits. They also allow generators to produce electricity for self-consumption in one location and supply it to another part of the national grid. Colombia’s energy policies provide tax incentives and other benefits that encourage investment in nonconventional renewable sources. The country is also addressing energy access disparities by promoting off-grid solar solutions and community microgrids. This aims to support 338,000 households that lack grid connectivity. It also aims to provide electricity through decentralized energy systems. Pole line hardware supports the infrastructure for self-consumption renewable energy systems in Colombia.
Components such as clamps and brackets help to mount solar panels to roofs of other structures. Hardware like connectors and cables help in connecting individual solar panels and combine their output. Pole line hardware also includes components such as insulators and grounding hardware. These prevent electrical current from flowing to the support structure. They also provide a path for lightning strikes and other electrical disturbances. Use of pole line hardware in self-consumption renewables enables the efficient and safe operation of the systems. The new rules in Colombia have no capacity limit for off-grid systems, and generators may use the assets of the national transmission grid for self-supply needs. This article looks at the importance of pole line hardware in renewable systems and the latest trends in self-consumption renewables in Colombia.
Functions of pole line hardware in self-consumption renewables
Pole line hardware ensures the safe and efficient transmission of electricity from renewable sources to local consumption points. They contribute to the reliability and resilience of Colombia’s expanding renewable energy infrastructure. They support decentralized energy models for self-consumption. Pole line hardware includes poles, crossarms, brackets, insulators, clamps, connectors, and conductors. Discussed below are the common functions of pole line hardware in self-consumption renewables.

- Structural support and stability—pole line hardware provides the physical framework that supports conductors. It ensures the durability and stability of the energy distribution systems in areas with challenging terrain.
- Insulation and protection—insulators and bushings in pole line systems protect conductors from short circuits and grounding issues. They prevent energy loss and reduce the risk of power outages.
- Renewable integration—self-consumption areas depend on microgrids, especially in remote areas. Pole line hardware serves in lower voltage systems to track and control power flow. These components include smart sensors and switchgear.
- Conductor management—components such as clamps, connectors, and splicing tools—helps to manage and secure the conductors. This helps to ensure continuous power flow from renewable energy sources. The components also maintain proper tension and prevent sagging or damage due to environmental factors.
- Lightning and surge protection—surge arresters and grounding rods protect renewable energy systems from voltage surges.
- Rural electrification projects—pole line hardware enables the extension of microgrids powered by solar and wind systems. It supports the deployment of hybrid energy solutions where grid connections are impractical.
Trends in self-consumption renewables in Colombia
Advancing trends in self-consumption renewables in Colombia reflect a shift toward decentralized, flexible, and user-centered energy systems. These are crucial for achieving global renewable energy targets and enhancing energy resilience. TTF has established itself and continues as a world-class global supplier of high quality pole line hardware, overhead line steel structures, insulators, anchoring products, cutout switches, cables & conductors and grounding products. These components support the development of self-consumption renewables in Colombia. Here are the trends shaping the future of self-consumption renewables.
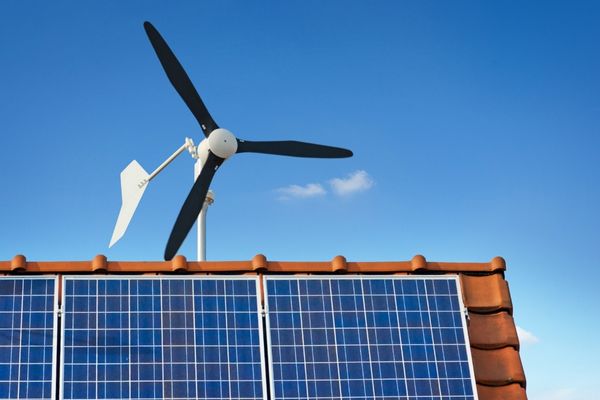
- Solar energy expansion—declining costs of solar panels and government incentives supports the domination of self-consumption renewables. Rooftop solar installations are growing due to their potential to reduce electricity costs. This highlights the shift towards decentralized energy generation.
- Hybrid systems and storage—the growing interest in hybrid renewable energy systems combine solar, wind, and battery storage. The systems enhance energy reliability for self-consumption in remote areas.
- Regulatory push and challenges – the government aims to increase the share of non-conventional renewables to 10% total capacity. There are several efforts underway to streamline administrative processes to speed up project timelines.
- Wind energy potential—the high wind speeds in the region make it ideal for large-scale wind projects. Wind energy is expanding in areas like La Guajira, which support self-consumption projects.
- Corporate and industrial interest—businesses adopting self-consumption renewables to meet sustainable goals and reduce energy costs. This is prominent in sectors such as agriculture and manufacturing.
