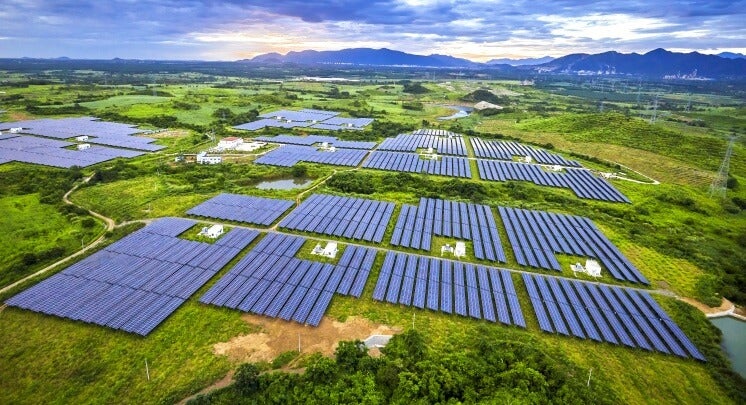

Recently, Brazil achieved a significant milestone in solar energy generation, reaching 50 GW of installed solar capacity. This positions Brazil as the 6th country in the world to surpass this mark, joining China, the United States, India, Germany, and Japan. This highlights Brazil’s commitment to expanding its renewable energy infrastructure. Of the 50 GW, 33.5 GW comes from distributed generation, which includes small and medium-sized systems installed on rooftops and land plots. The remaining 16.5 GW is from large-scale solar plants. Solar energy now accounts for 20.7% of Brazil’s total power capacity. This makes a total of 95% of capacity released this year from renewable sources. As of November 2024, Brazil has 279 plants in operation: 273 are renewable, 134 are solar, 114 are wind, and 8 are small hydroelectric plants. ADSS/OPGW cables create reliable communication links between different parts of the solar farm and the grid.
All-Dielectric Self-Supporting and Optical Ground wire cables enable remote monitoring and control of the solar panels and other infrastructure. This allows operators to optimize performance and address any issues that arise. The cables also provide high-speed data transmission capabilities, which are crucial for transmitting large amounts of data generated by the solar farm. Additionally, the cables support the integration of solar farms into smart grids. This enhances the efficiency and reliability of the energy system. This article highlights the factors leading to increased solar output in Brazil and the role of ADSS/OPGW cables.
Functions of ADSS/OPGW cables in Brazil’s solar output
ADSS/OPGW cables play a crucial role in enhancing grid reliability, communication, and data management. They allow the construction of resilient, smart, and efficient energy grids. The cables enable real-time monitoring, enhance grid stability, and support the integration of renewable energy. The following are the functions of ADSS/OPGW cables in increasing Brazil’s solar output.

- Data transmission and grid monitoring—these cables install along power lines without the need for grounding. ADSS cables transmit operational data, ensuring real-time communication between solar plants. OPGW cables provide both lightning protection and data transmission. This is to ensure fast, secure communication across the grid.
- Grid stability and smart grid integration – the cables enable remote monitoring and automation. They support grid stability by ensuring rapid data exchange for load balancing, fault detection, and system optimization.
- Renewable energy coordination – ADSS/OPGW cables ensure seamless integration into Brazil’s national grid. They allow centralized control to coordinate the variable output from different solar farms.
- Cost-effective infrastructure expansion – ADSS cables provide a cost-effective solution for expanding communication networks without extra support structures. This speeds up the deployment of solar projects in new areas.
- Cybersecurity and network resilience – OPGW cables have dual functionality as ground wire and data conduit. They enhance the grid’s physical and cybersecurity. They have a strong construction that protects the network from cyber threats and physical damage.
Factors contributing to increased solar output in Brazil
There are advanced technologies on the market that support Brazil’s increase in solar output. The declining costs, abundant sunlight, and government subsidies also support solar generation. Factors like economic opportunities, environmental concerns, and investment in infrastructure contribute to Brazil’s impressive growth in renewable energy. At TTF power, we support the development and construction of solar farms in Brazil. We are a one-stop-shop for utility pole hardware fittings, transmission line accessories and power line construction equipment, providing our customers with the most extensive range of products in the industry, excellent value and knowledgeable service. Discussed below are the factors contributing to the increase in solar output in Brazil.
- Supportive government policies – net metering policies encourage distributed generation by allowing consumers to feed excess solar energy back to the grid. Energy auctions and tax incentives drive competitive pricing, which facilitates large-scale solar projects.
- Technological advancements – lower costs of photovoltaic modules and balance-of-system components—have made solar energy more economically viable. Integration of battery storage technology improves grid reliability.
- Demand for renewable energy – solar energy provides a solution during droughts that impact hydroelectric output. There is an increased need for reliable electricity in remote and off-grid areas. This spurs the growth of decentralized solar systems.
- Abundant solar resources – Brazil enjoys high solar radiation, especially the Northeast and Southeast regions. The vast underutilized lands provide ample space for large-scale solar farms.
- Foreign and domestic investment – foreign and domestic companies are investing in solar projects given the favorable investment climate for renewables. The collaboration with global solar technology leaders boosts the adoption of innovative solar solutions.
- Public awareness and corporate goals – many companies are adopting solar energy to meet environmental, social, and governance goals.
