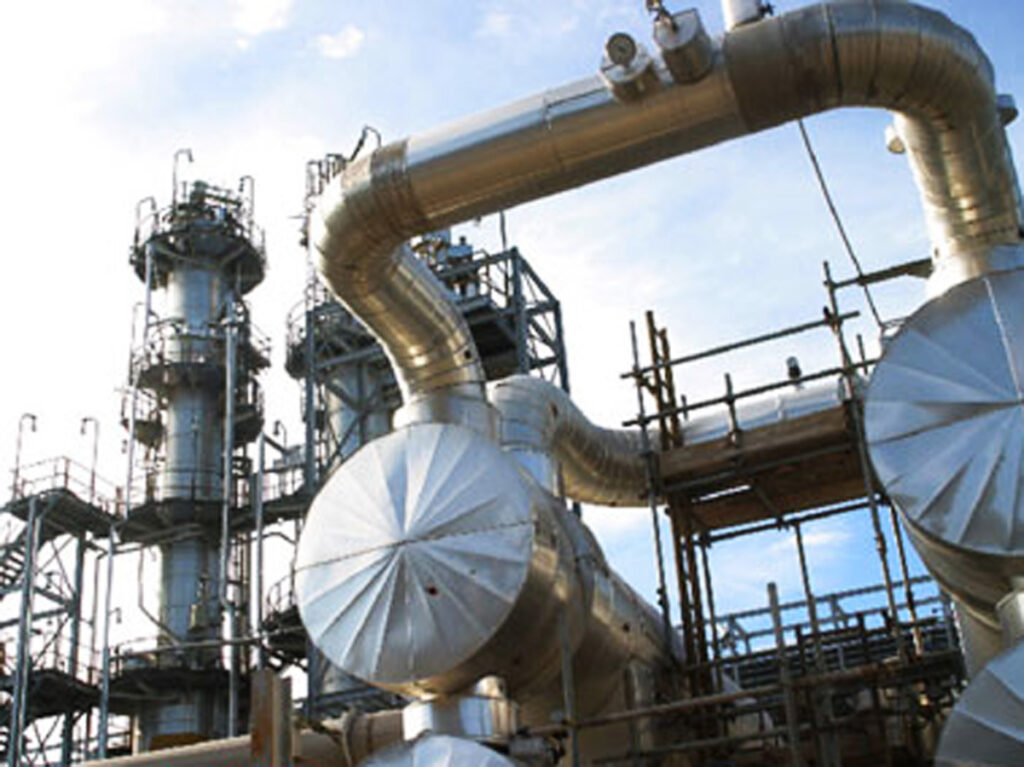

South America has the second largest hydrocarbon reserves in the world. With oil and gas production in Brazil, Colombia, and Venezuela. Despite the efforts to reduce global fossil fuel consumption, hydrocarbon demand has been on the rise. Hydrocarbons are compounds made up of hydrogen and carbon atoms, which are the main components of coal, oil, and natural gas. Natural gas forms over millions of years from the remains of plants and animals buried under layers of sediments and rocks. The specific type and mixture of hydrocarbons in a natural gas deposit depend on various factors. These include depth, temperature, and the composition of the original material. Use of hydrocarbons in South America’s energy sector provides economic and energy benefits. A surge arrester helps in supporting the infrastructure needed for the extraction, processing, and transportation of these resources.
A surge arrester protects electrical equipment from damage caused by voltage surges. The surge arrester protects electrical equipment such as transformers, motors, and control systems. It protects them from damage caused by voltage surges from lightning strikes and switching operation. The arresters ensure the reliable operation of hydrocarbon production facilities. This helps to reduce downtime and production losses. This contributes to the safety of workers and the environment by preventing electrical accidents. This article highlights the benefits of growth in hydrocarbon production in South America. It also looks at the importance of using surge arresters in the infrastructure needed for the production.
Relevance of a surge arrester in hydrocarbon production in South America
Surge arresters protect critical equipment and infrastructure from damages caused by electrical surges. They play a crucial role in ensuring operational reliability and safety considering the challenging environments. A surge arrester helps in protecting hydrocarbon production facilities in South America. It ensures safety and operational efficiency of the infrastructure. This is by safeguarding equipment, controlling costs, and preventing downtime. The following are the various functions of a surge arrester in hydrocarbon production in South America.
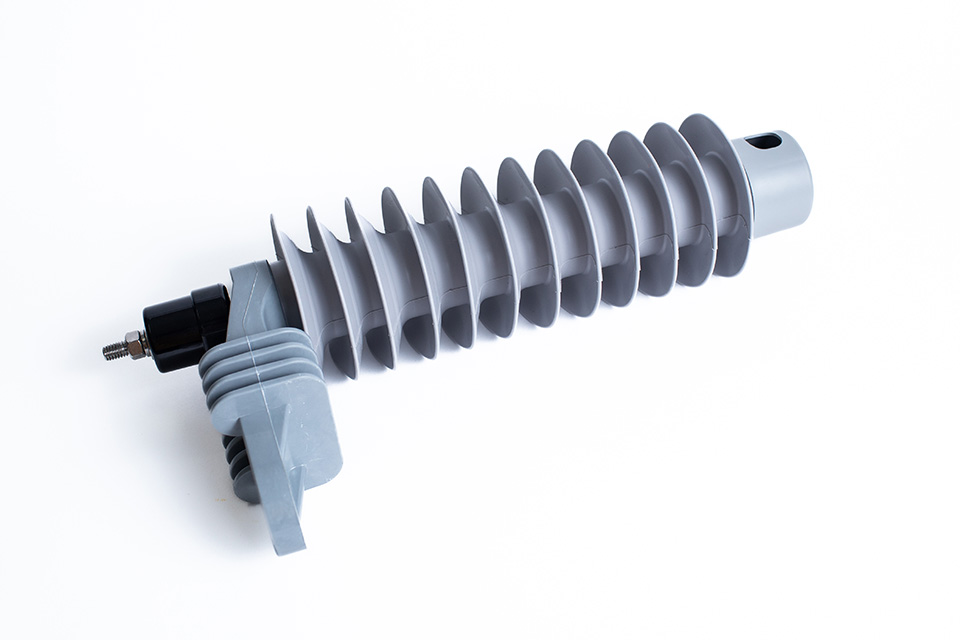
- Protection against lightning strikes—most of the hydrocarbon facilities are susceptible to lightning strikes. A surge arrester diverts the high voltage caused by lightning to the ground. This prevents it from damaging sensitive equipment and control systems.
- Safeguarding electrical equipment—hydrocarbon production facilities depend on high-powered equipment. These include pumps, compressors, and control systems that are vulnerable to voltage surges. A surge arrester prevents the spikes from damaging the electrical systems to extend the lifespan of equipment.
- Ensuring operational continuity—electrical disturbances and surges can cause significant production delays in case of equipment failure. Surge arresters help maintain uninterrupted operations, which is important in offshore production.
- Protecting control and communication systems—surge arresters protect critical control systems and other automated technologies. These systems ensure the safety and efficiency to prevent damages leading to production and safety risks.
Benefits of hydrocarbon production in South America’s energy sector
The increased production of hydrocarbons in Brazil and Argentina will allow South America to surpass the production levels. This could position the region as a major producer among private international oil companies. The production could also increase investment in decarbonization goals. This could in turn help to reduce greenhouse gas emissions. Hydrocarbons provide a range of economic and social benefits that support regional development and energy security. TTF is a world-class global provider of high quality overhead line hardware, transmission hardware, distribution hardware, conductors, insulators, cutout switches, anchoring and grounding products. Listed below are the common benefits of hydrocarbons in South America’s energy sector.
- Economic growth and government revenue—hydrocarbon production provides revenue for countries such as Brazil, Colombia, and Venezuela. Oil and natural gas exports provide foreign exchange earnings and support public budgets.
- Energy security and independence—hydrocarbons provide energy security by allowing countries to rely on domestic resources. This also reduces their vulnerability to global market fluctuations.
- Technological innovations—the hydrocarbon reserves attract international companies that bring in capital, technology, and expertise. It also promotes knowledge transfer, skill development, and improved technical capabilities.
- Infrastructure growth—hydrocarbon production leads to the development of infrastructure. This is including pipelines, refineries, export terminals, and roads. Investment in infrastructure brings other effects, such as promoting industrial development.
- Support for regional energy trade—South American hydrocarbon resources ease regional energy trade. This trade promotes economic integration and cooperation, which makes energy accessible and affordable.
- Transition to renewable energy—natural gas is a cleaner form of energy that can serve in the transition to renewable energy. Natural gas produced fewer emissions than coal or oil, which makes it a practical option.
